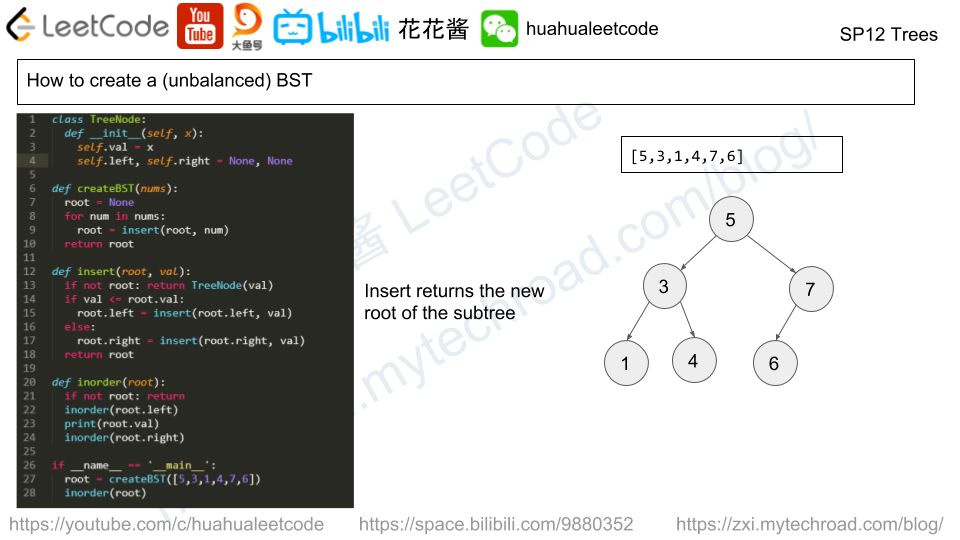
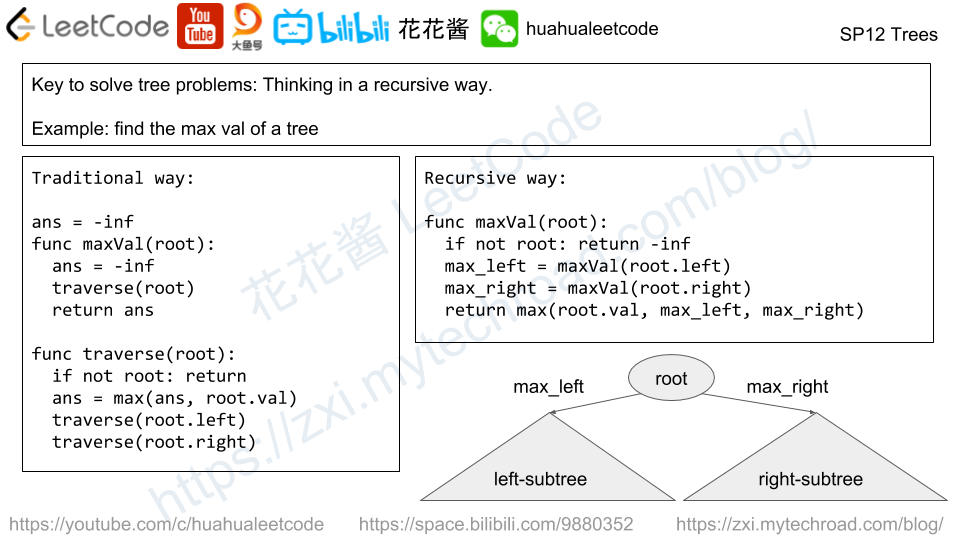
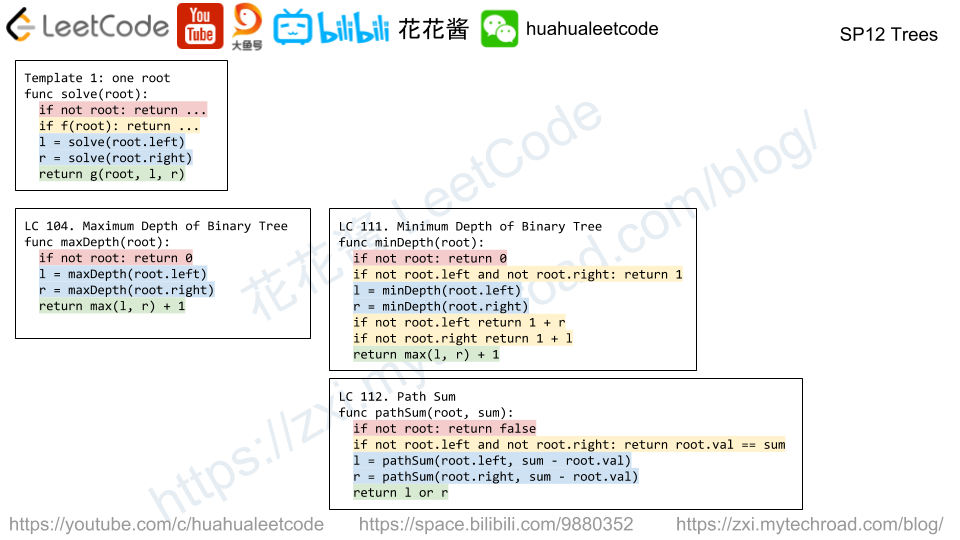
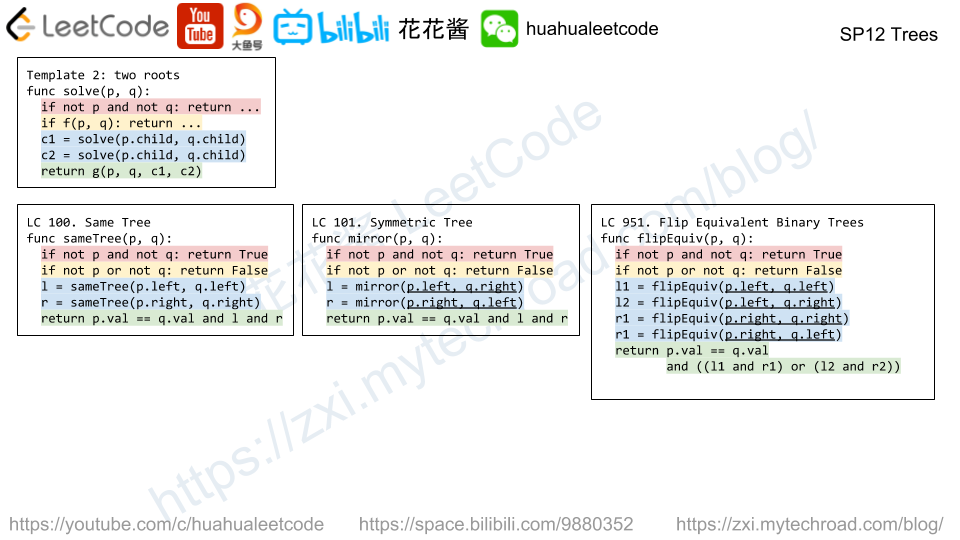
There are 8 prison cells in a row, and each cell is either occupied or vacant.
Each day, whether the cell is occupied or vacant changes according to the following rules:
- If a cell has two adjacent neighbors that are both occupied or both vacant, then the cell becomes occupied.
- Otherwise, it becomes vacant.
(Note that because the prison is a row, the first and the last cells in the row can’t have two adjacent neighbors.)
We describe the current state of the prison in the following way: cells[i] == 1 if the i-th cell is occupied, else cells[i] == 0.
Given the initial state of the prison, return the state of the prison after N days (and N such changes described above.)
Example 1:
Input: cells = [0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1], N = 7
Output: [0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]
Explanation: The following table summarizes the state of the prison on each day:
Day 0: [0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]
Day 1: [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Day 2: [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]
Day 3: [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
Day 4: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
Day 5: [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]
Day 6: [0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]
Day 7: [0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Example 2:
Input: cells = [1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0], N = 1000000000
Output: [0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0]
Note:
cells.length == 8cells[i]is in{0, 1}1 <= N <= 10^9
Solution: Simulation
Simulate the process, since there must be loops, record the last day when a state occurred.
Time complexity: O(2^8)
Space complexity: O(2^8)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
// Author: Huahua, running time: 4 ms class Solution { public: vector<int> prisonAfterNDays(vector<int>& cells, int N) { vector<int> seen(1 << 8, -1); auto getKey = [] (const vector<int>& cells) { int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) key |= cells[i] << i; return key; }; while (N > 0) { const int key = getKey(cells); if (seen[key] > 0) N %= seen[key] - N; seen[key] = N--; if (N < 0) break; vector<int> c(8); for (int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) c[i] = cells[i - 1] == cells[i + 1]; cells.swap(c); } return cells; } }; |