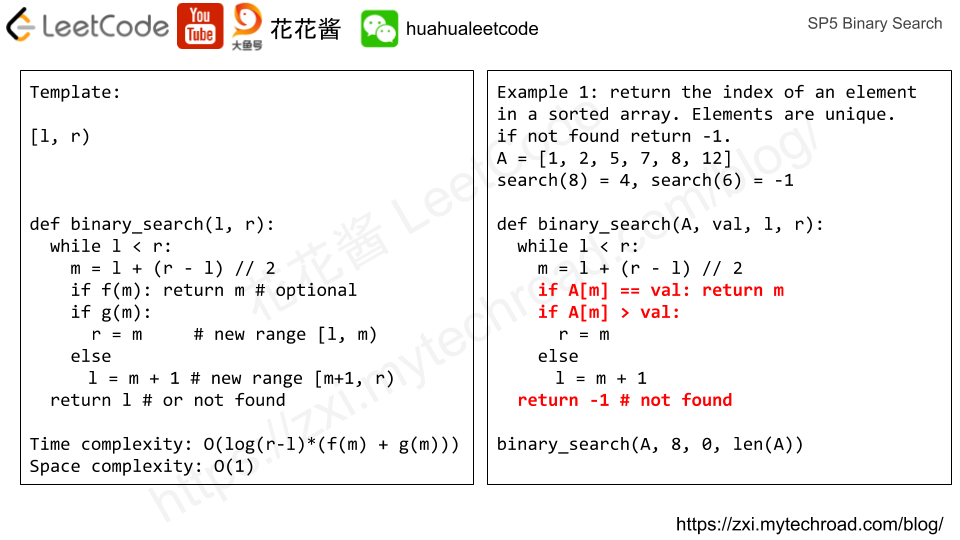
Template:
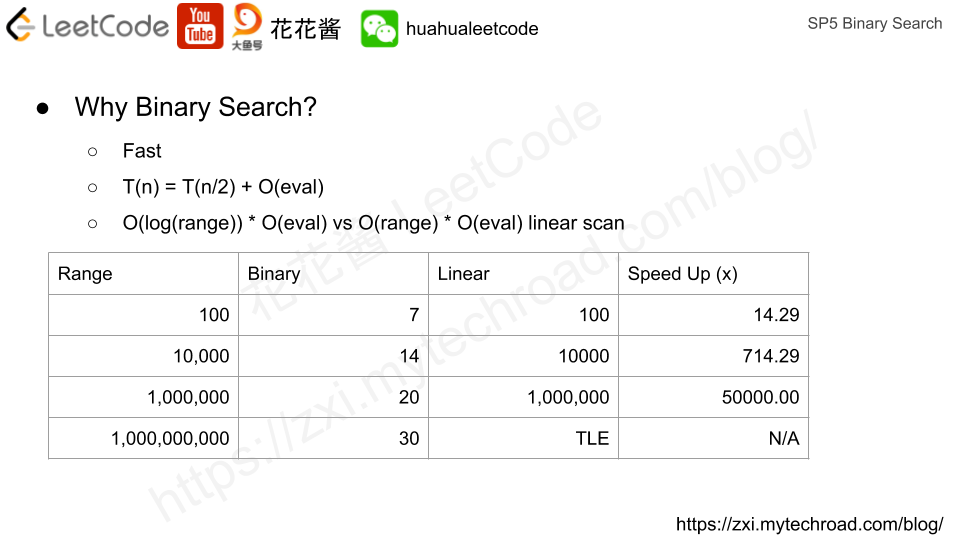
Time complexity: O(log(r-l)) * O(f(m) + g(m))
Space complexity: O(1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
""" Returns the smallest number m such that g(m) is true. """ def binary_search(l, r): while l < r: m = l + (r - l) // 2 if f(m): return m # if m is the answer if g(m): r = m # new range [l, m) else l = m + 1 # new range [m+1, r) return l # or not found |
Slides:

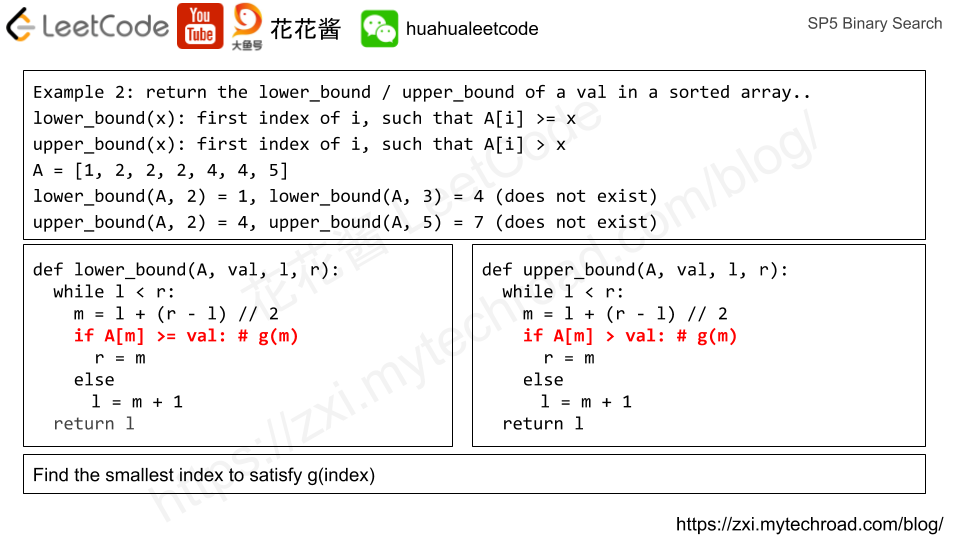
Lower Bound / Upper Bound
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int upper_bound(const vector<int>& A, int val, int l, int r) { while (l < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; if (A[m] > val) r = m; else l = m + 1; } return l; } int lower_bound(const vector<int>& A, int val, int l, int r) { while (l < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; if (A[m] >= val) r = m; else l = m + 1; } return l; } int main() { vector<int> A{1, 2, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5}; cout << lower_bound(A, 0, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 0 cout << lower_bound(A, 2, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 1 cout << lower_bound(A, 3, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 4 cout << upper_bound(A, 2, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 4 cout << upper_bound(A, 4, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 6 cout << upper_bound(A, 5, 0, A.size()) << endl; // 7 } |