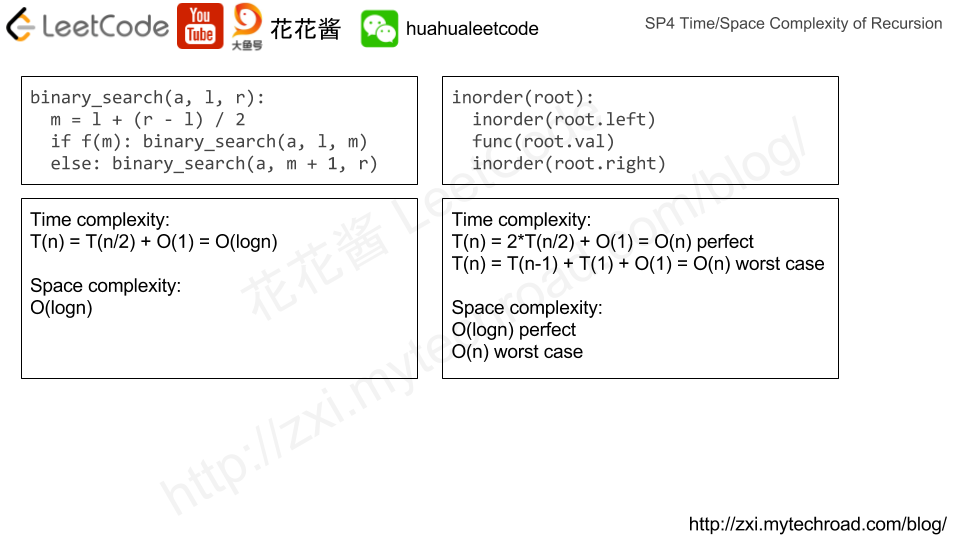
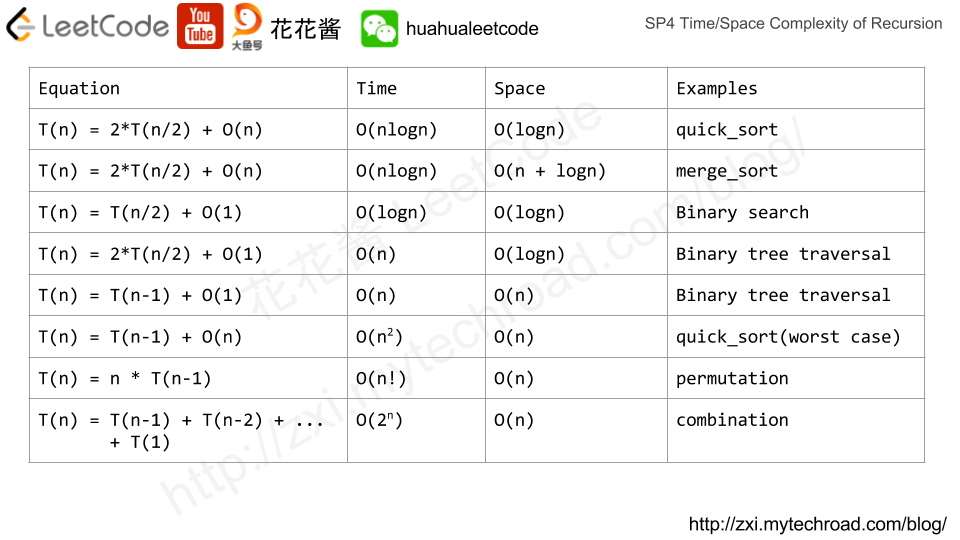
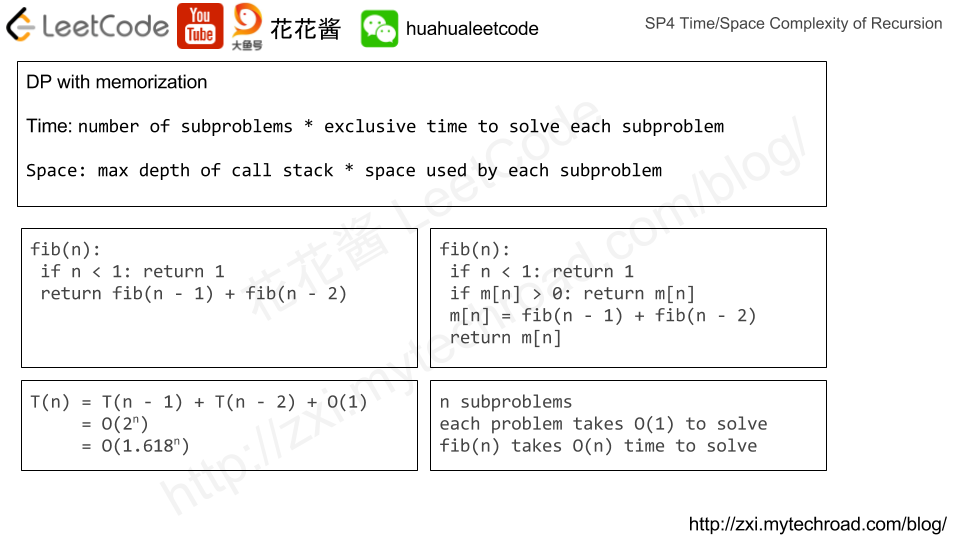
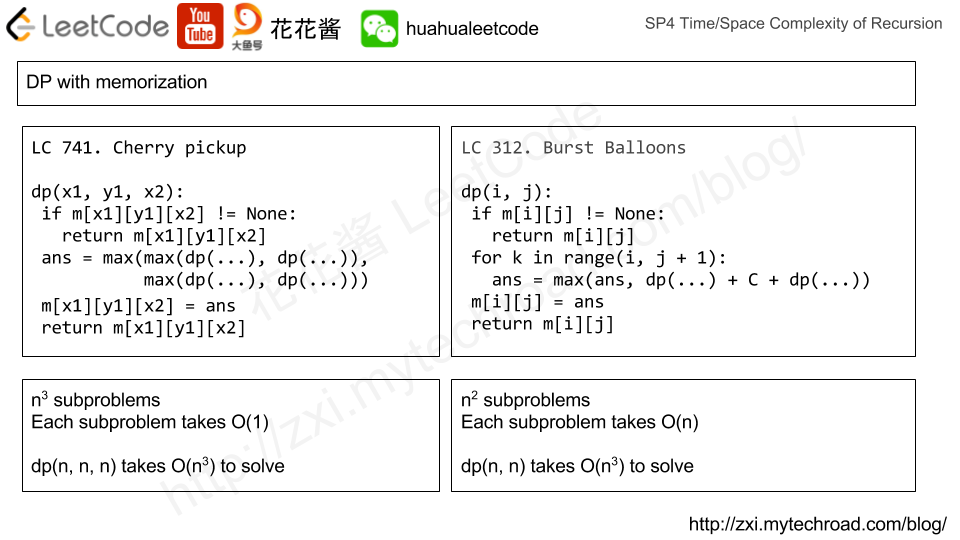
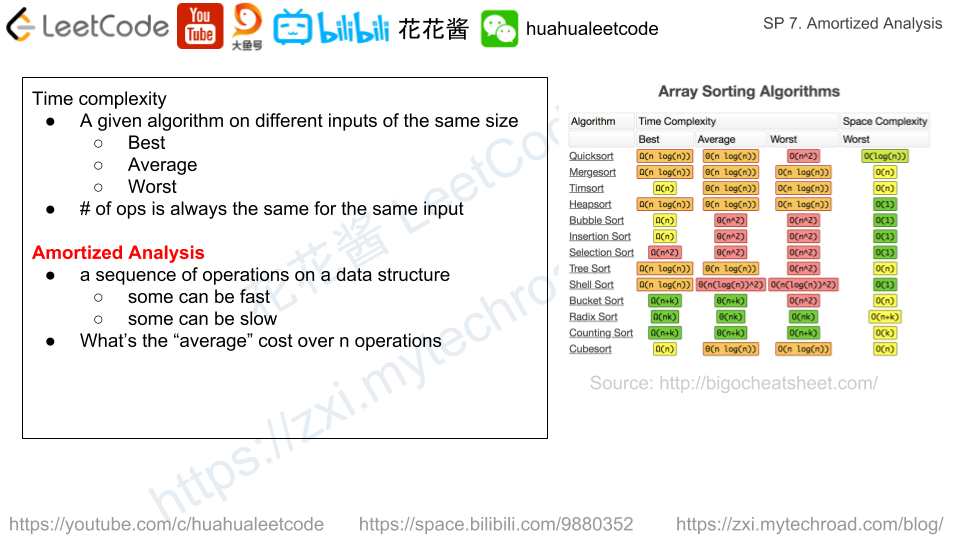
Amortized Analysis
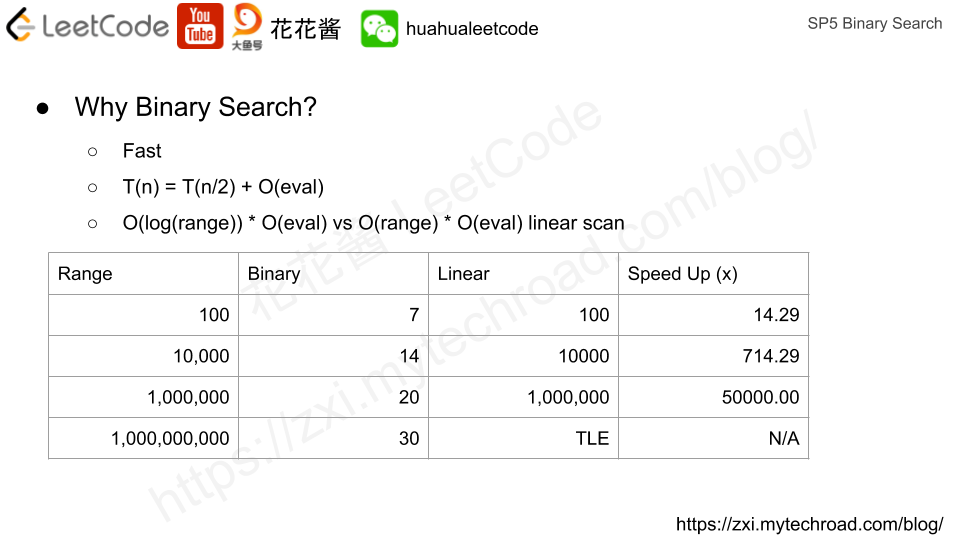
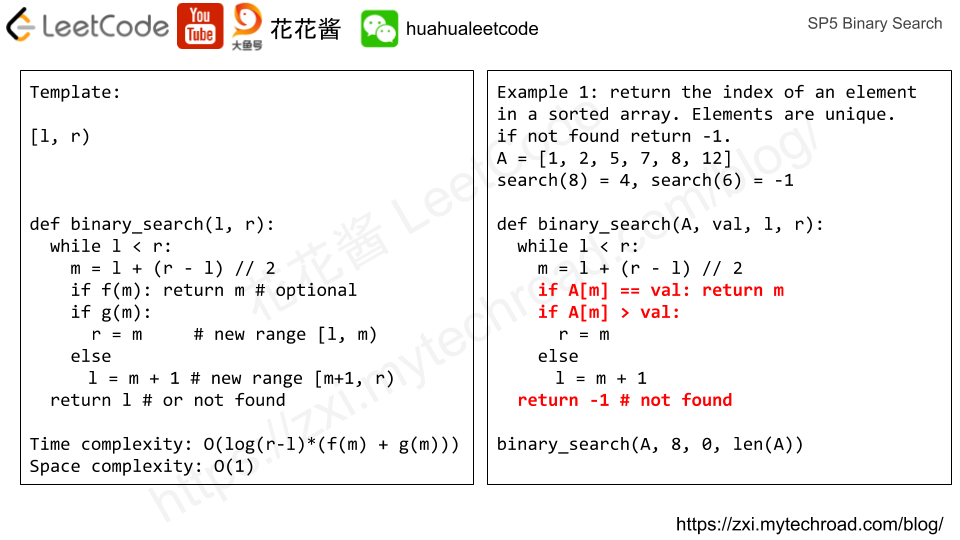
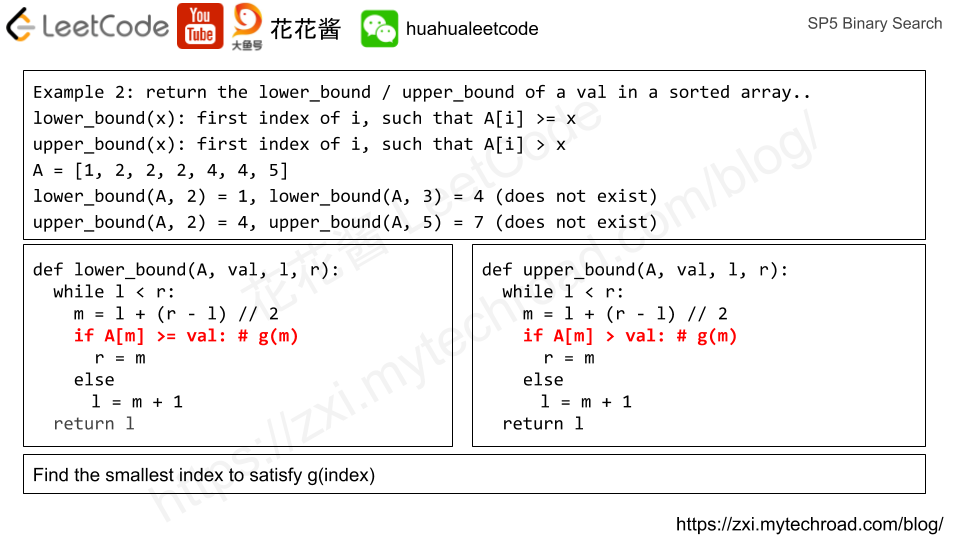
Amortized analysis can help us understand the actual cost of n operations on a data structure. Since some operations can be really fast e.g. O(1), but some operations can be really slow e.g. O(n). We could say the time complexity of that operation is O(n). However, it does not reflect the actual performance. And turns out, we can prove that certain operations have an amortized cost of O(1) while they can take O(n) in the worst case.
均摊分析可以帮助我们了解对一个数据结构进行n次操作的真实代价。对于相同的操作,有时候可以非常快,例如在O(1)时间内完成,而有时候则需要O(n)。我们当然可以说这个操作最坏情况下的时间复杂度是O(n),但是这并不能真实反映它的实际复杂度。通过均摊分析,我们可以证明,尽管有些操作在最坏情况下是O(n)的时间复杂度,但是均摊下来只需要O(1)。
Dynamic Array
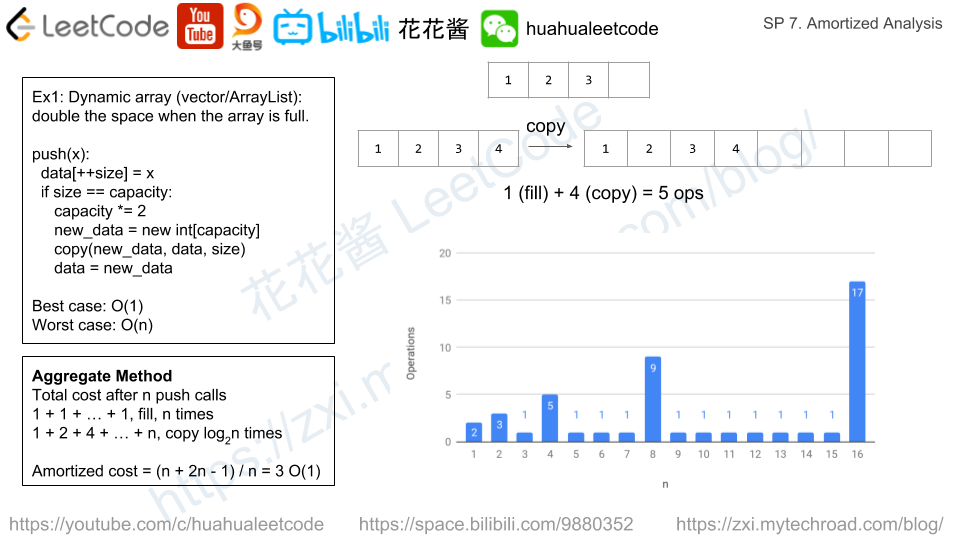
dynamic array doubles its size when it’s full which could take O(i) time where i is the number of elements in the array. Otherwise just store the element which only cost O(1). We can use aggregate method to compute the amortized cost of dynamic array.
动态数组在容量满时将容量翻翻,这一步需要O(i)时间,i是当前数组中的元素个数。如果没有满,只需要将元素存储下来即可,只需要花费O(1)时间。我们可以使用聚合法来计算均摊成本。
((1 + 1) + (1 + 2) + (1) + (1 + 4) + (1) + (1) + (1) + (1+8) + … + (1+n)) / n, assuming n is 2^k.
= (1 * n + (1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … + n)) / n = (n + 2n – 1) / n = 3. O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; class DynamicArray { public: DynamicArray() { data_ = new int[1]; capcity_ = 1; } void add(int x) { data_[size_++] = x; ++total_cost_; if (size_ == capcity_) { capcity_ *= 2; total_cost_ += size_; int* new_data = new int[capcity_]; copy(data_, data_ + size_, new_data); swap(new_data, data_); delete [] new_data; } } int totalCost() const { return total_cost_; } private: int total_cost_ = 0; int size_ = 0; int capcity_; int* data_; }; int main() { DynamicArray arr; for (int i = 1; i <= 16; ++i) { arr.add(i); cout << i << " average cost: " << arr.totalCost() / static_cast<float>(i) << endl; } } |
Output
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
1 average cost: 2 2 average cost: 2.5 3 average cost: 2 4 average cost: 2.75 5 average cost: 2.4 6 average cost: 2.16667 7 average cost: 2 8 average cost: 2.875 9 average cost: 2.66667 10 average cost: 2.5 11 average cost: 2.36364 12 average cost: 2.25 13 average cost: 2.15385 14 average cost: 2.07143 15 average cost: 2 16 average cost: 2.9375 [Finished in 0.4s] |
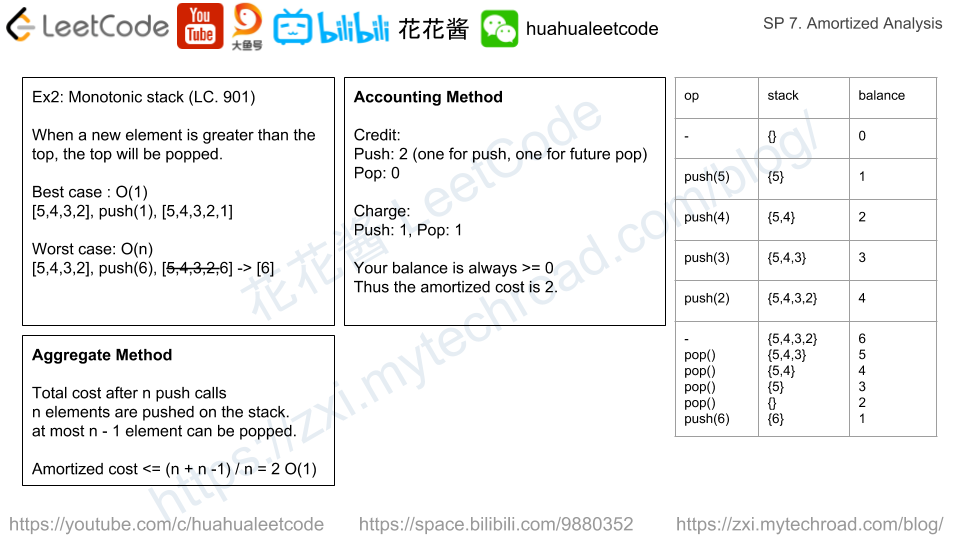
Monotonic Stack
例子2: 单调栈
往单调栈push一个元素的时候,会删除上所有小于等于它的元素。这步操作在最优情况下是O(1)时间,如果它比栈顶元素要小。在最坏情况下是O(i)时间,栈上有i个元素,它比这i个元素都要大,所以一共要pop i次。
聚合法:
由于每个元素都会被push到栈上去1次,最多会被pop1次,所以总的操作数 <= 2n。 2n / n = 2 O(1)。
会计法:
每次push之前先存k块钱,k=2, 一块钱用于push自己,一块钱留着用于pop自己。
push的时候扣除1块钱,pop的时候再扣除1块钱。但不管怎样,我的账户上的钱永远>=0。这样我们可以说push的均摊成本是k=2。同样是O(1),尽管它的worst case是O(n)。
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> using namespace std; class MonotonicStack { public: void push(int x) { while (!data_.empty() && x > data_.top()) { this->pop(); } ++total_cost_; data_.push(x); } int pop() { ++total_cost_; int t = data_.top(); data_.pop(); return t; } int totalCost() const { return total_cost_; } private: int total_cost_ = 0; stack<int> data_; }; int main() { srand(1); MonotonicStack s; for (int i = 1; i <= 32; ++i) { s.push(rand()); cout << i << " average cost: " << s.totalCost() / static_cast<float>(i) << endl; } } |
Output
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
1 average cost: 1 2 average cost: 1.5 3 average cost: 1.66667 4 average cost: 1.5 5 average cost: 1.6 6 average cost: 1.5 7 average cost: 1.42857 8 average cost: 1.75 9 average cost: 1.77778 10 average cost: 1.9 11 average cost: 1.81818 12 average cost: 1.83333 13 average cost: 1.84615 14 average cost: 1.78571 15 average cost: 1.8 16 average cost: 1.8125 17 average cost: 1.82353 18 average cost: 1.77778 19 average cost: 1.78947 20 average cost: 1.75 21 average cost: 1.80952 22 average cost: 1.86364 23 average cost: 1.82609 24 average cost: 1.91667 25 average cost: 1.88 26 average cost: 1.84615 27 average cost: 1.81481 28 average cost: 1.85714 29 average cost: 1.82759 30 average cost: 1.86667 31 average cost: 1.90323 32 average cost: 1.875 [Finished in 0.5s] |