Problem
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has exactly 0 or 2 children.
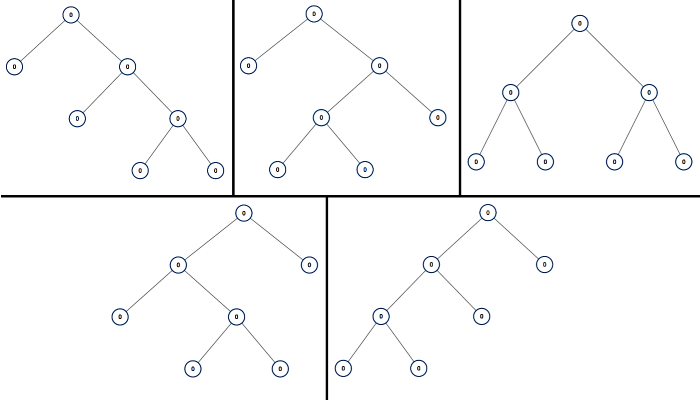
Return a list of all possible full binary trees with N nodes. Each element of the answer is the root node of one possible tree.
Each node of each tree in the answer must have node.val = 0.
You may return the final list of trees in any order.
Example 1:
Input: 7
Output: [[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,0,0]]
Explanation:
Note:
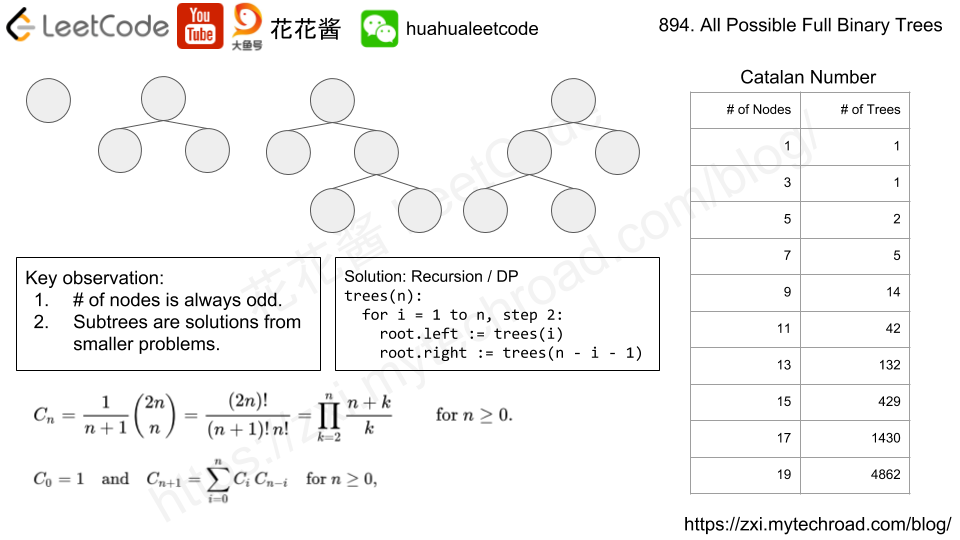
Solution: Recursion Key observations:
n must be odd, If n is even, no possible trees
ans is the cartesian product of trees(i) and trees(n-i-1). Ans = {Tree(0, l, r) for l, r in trees(i) X trees(N – i – 1)}.
w/o cache
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// Author: Huahua
// Running time: 72 ms
class Solution {
public :
vector < TreeNode* > allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return { } ;
if ( N == 1 ) return { new TreeNode ( 0 ) } ;
vector < TreeNode* > ans ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i += 2 ) {
for ( const auto & l : allPossibleFBT(i))
for (const auto& r : allPossibleFBT(N - i - 1)) {
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
root -> left = l ;
root -> right = r ;
ans . push_back ( root ) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
} ;
Java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// Author: Huahua
// Running time: 20 ms
class Solution {
public List < TreeNode > allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
List < TreeNode > ans = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return ans ;
if ( N == 1 ) {
ans . add ( new TreeNode ( 0 ) ) ;
return ans ;
}
for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i += 2 ) {
for ( TreeNode l : allPossibleFBT ( i ) )
for ( TreeNode r : allPossibleFBT ( N - i - 1 ) ) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode ( 0 ) ;
root . left = l ;
root . right = r ;
ans . add ( root ) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
"" "
Author: Huahua
Running time: 396 ms
" ""
class Solution :
def allPossibleFBT ( self , N ) :
if N % 2 == 0 : return [ ]
if N == 1 : return [ TreeNode ( 0 ) ]
ans = [ ]
for i in range ( 1 , N , 2 ) :
for l in self . allPossibleFBT ( i ) :
for r in self . allPossibleFBT ( N - i - 1 ) :
root = TreeNode ( 0 )
root . left = l
root . right = r
ans . append ( root )
return ans
w/cache
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// Author: Huahua
// Running time: 68 ms
static constexpr int kMaxN = 20 + 1 ;
static array < vector < TreeNode* > , kMaxN > m ;
class Solution {
public :
vector < TreeNode* > allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
return trees ( N ) ;
}
private :
vector < TreeNode* > & trees(int N) {
if (m[N].size() > 0) return m[N];
vector < TreeNode* > & ans = m[N];
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return ans = { } ;
if ( N == 1 ) ans = { new TreeNode ( 0 ) } ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i += 2 ) {
for ( const auto & l : trees(i))
for (const auto& r : trees(N - i - 1)) {
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
root -> left = l ;
root -> right = r ;
ans . push_back ( root ) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
} ;
Python
using itertools.product w/ cache
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
"""
Author: Huahua
Running time: 188 ms
"""
m = [ [ ] for _ in range ( 21 ) ]
class Solution :
def allPossibleFBT ( self , N ) :
if N % 2 == 0 : return [ ]
if N == 1 : return [ TreeNode ( 0 ) ]
if len ( m [ N ] ) > 0 : return m [ N ]
ans = [ ]
for i in range ( 1 , N , 2 ) :
for l , r in itertools . product ( self . allPossibleFBT ( i ) ,
self . allPossibleFBT ( N - i - 1 ) ) :
root = TreeNode ( 0 )
root . left = l
root . right = r
ans . append ( root )
m [ N ] = ans
return ans
DP
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// Author: Huahua
// Running time: 100 ms
class Solution {
public :
vector < TreeNode* > allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return { } ;
vector < vector < TreeNode* > > dp ( N + 1 ) ;
dp [ 1 ] = { new TreeNode ( 0 ) } ;
for ( int i = 3 ; i < = N ; i += 2 )
for ( int j = 1 ; j < i ; j += 2 ) {
int k = i - j - 1 ;
for ( const auto & l : dp[j])
for (const auto& r : dp[k]) {
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
root -> left = l ;
root -> right = r ;
dp [ i ] . push_back ( root ) ;
}
}
return dp [ N ] ;
}
} ;
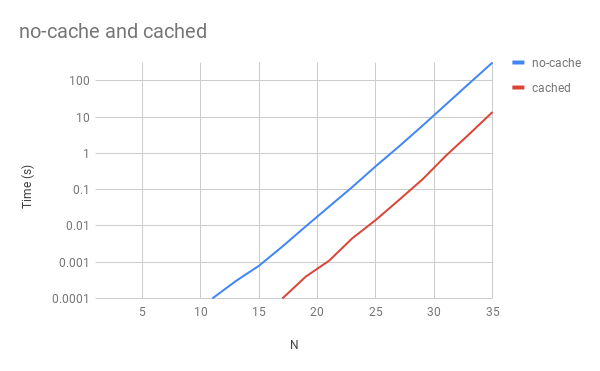
Benchmark No-cache vs cached
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <array>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std ;
struct TreeNode {
int val ;
TreeNode *left ;
TreeNode *right ;
TreeNode ( int x ) : val ( x ) , left ( NULL ) , right ( NULL ) { }
} ;
static constexpr int kMaxN = 101 + 1 ;
static array < vector < TreeNode *> , kMaxN > m ;
class NoCache {
public :
vector < TreeNode *> allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return { } ;
if ( N == 1 ) return { new TreeNode ( 0 ) } ;
vector < TreeNode *> ans ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i += 2 ) {
for ( const auto & l : allPossibleFBT(i))
for (const auto& r : allPossibleFBT(N - i - 1)) {
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
root -> left = l ;
root -> right = r ;
ans . push_back ( root ) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
} ;
class Cached {
public :
vector < TreeNode *> allPossibleFBT ( int N ) {
return trees ( N ) ;
}
private :
vector < TreeNode *> & trees(int N) {
if (m[N].size() > 0) return m[N];
vector < TreeNode *> & ans = m[N];
if ( N % 2 == 0 ) return ans = { } ;
if ( N == 1 ) ans = { new TreeNode ( 0 ) } ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i += 2 ) {
for ( const auto & l : trees(i))
for (const auto& r : trees(N - i - 1)) {
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
root -> left = l ;
root -> right = r ;
ans . push_back ( root ) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
} ;
int main ( int argc , char ** argv ) {
printf ( "N\tno-cache\tcached\n" ) ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < = 35 ; i += 2 ) {
printf ( "%02d\t" , i ) ;
{
auto start = clock ( ) ;
( void ) ( NoCache ( ) . allPossibleFBT ( i ) ) ;
printf ( "%8.4f\t" , static_cast < double > ( clock ( ) - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ) ;
}
{
// Clear the cache.
for ( int j = 0 ; j < kMaxN ; ++j )
m [ i ] . clear ( ) ;
auto start = clock ( ) ;
( void ) ( Cached ( ) . allPossibleFBT ( i ) ) ;
printf ( "%8.4f\n" , static_cast < double > ( clock ( ) - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}