Problem
题目大意:初始位置0速度+1,每次你可以加速(速度*2)或者倒车(速度变成-1*dir)。问最少需要执行多少步操作能够到达T。
https://leetcode.com/problems/race-car/description/
Your car starts at position 0 and speed +1 on an infinite number line. (Your car can go into negative positions.)
Your car drives automatically according to a sequence of instructions A (accelerate) and R (reverse).
When you get an instruction “A”, your car does the following: position += speed, speed *= 2.
When you get an instruction “R”, your car does the following: if your speed is positive then speed = -1 , otherwise speed = 1. (Your position stays the same.)
For example, after commands “AAR”, your car goes to positions 0->1->3->3, and your speed goes to 1->2->4->-1.
Now for some target position, say the length of the shortest sequence of instructions to get there.
Example 1: Input: target = 3 Output: 2 Explanation: The shortest instruction sequence is "AA". Your position goes from 0->1->3.
Example 2: Input: target = 6 Output: 5 Explanation: The shortest instruction sequence is "AAARA". Your position goes from 0->1->3->7->7->6.
Note:
1 <= target <= 10000.
Visualization of the Solution
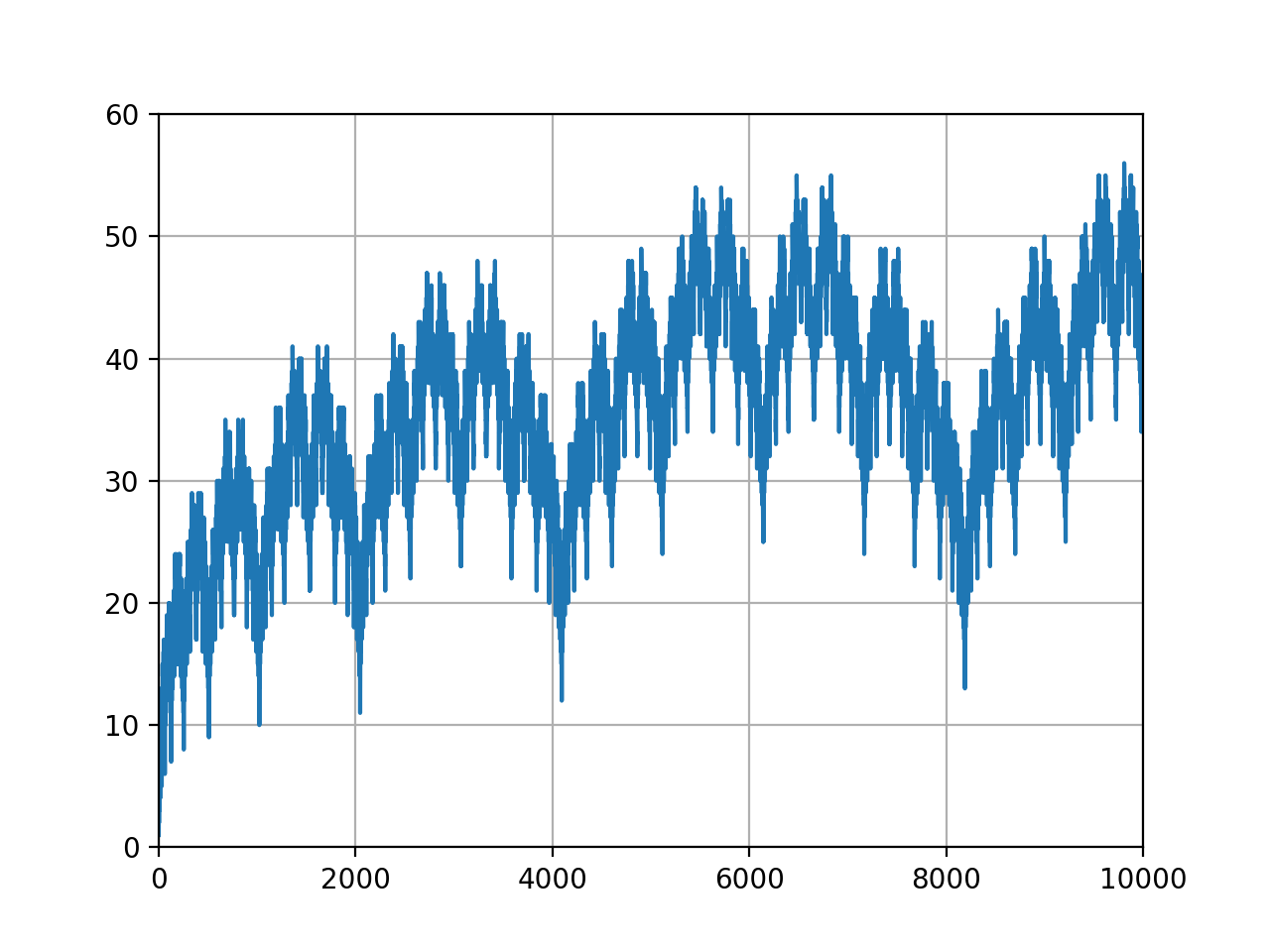
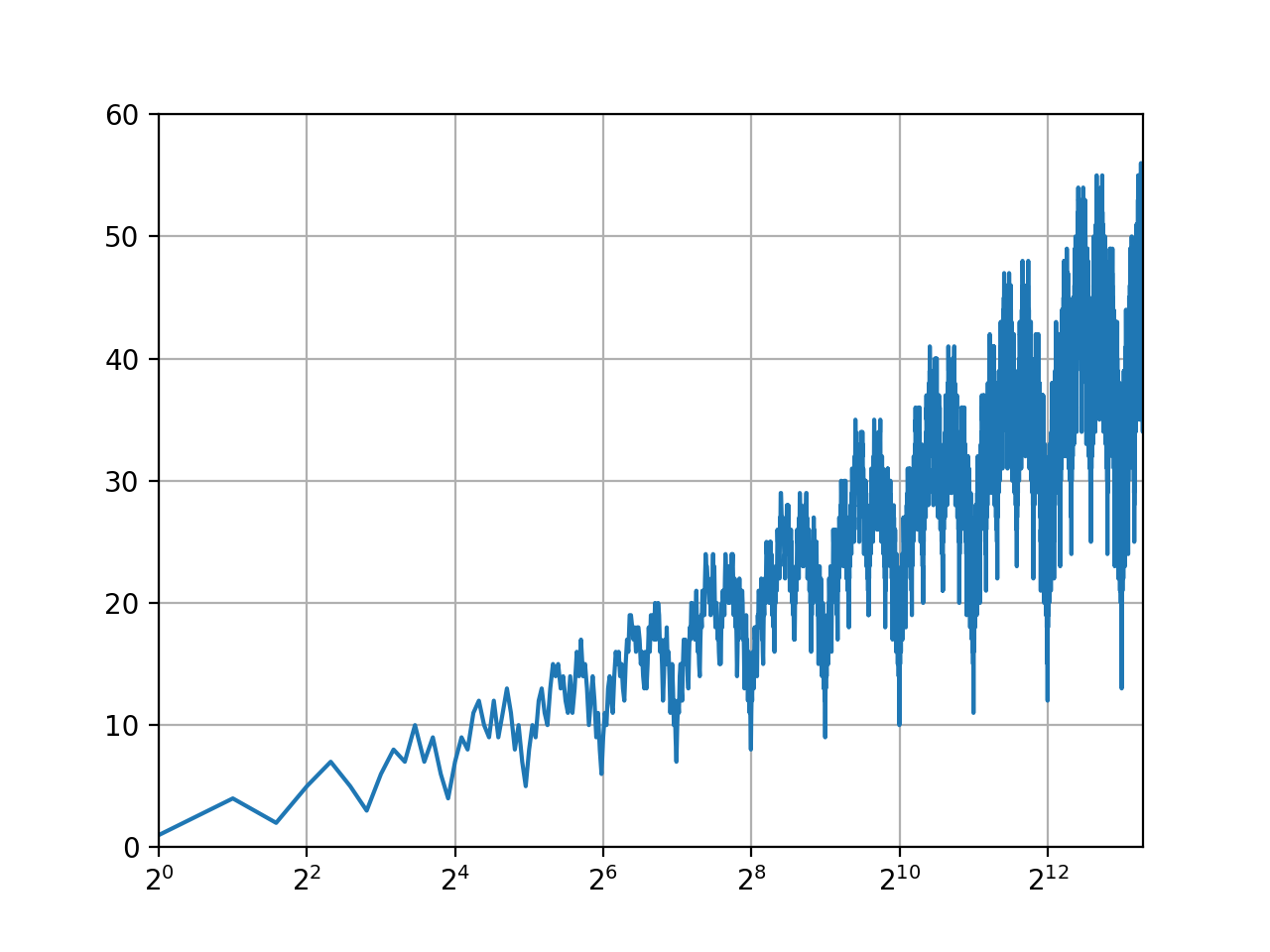
Solution 1: BFS
C++/Str
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 221 ms class Solution { public: int racecar(int target) { queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.push({0, 1}); unordered_set<string> v; v.insert("0_1"); v.insert("0_-1"); int steps = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); while (size--) { auto p = q.front(); q.pop(); int pos = p.first; int speed = p.second; { int pos1 = pos + speed; int speed1 = speed * 2; pair<int, int> p1{pos1, speed1}; if (pos1 == target) return steps + 1; if (p1.first > 0 && p1.first < 2 * target) q.push(p1); } { int speed2 = speed > 0 ? -1 : 1; pair<int, int> p2{pos, speed2}; string key2 = to_string(pos) + "_" + to_string(speed2); if (!v.count(key2)) { q.push(p2); v.insert(key2); } } } ++steps; } return -1; } }; |
C++/Int
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 16 ms class Solution { public: int racecar(int target) { queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.push({0, 1}); unordered_set<int> v; v.insert({0, 2}); int steps = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); while (size--) { auto p = q.front(); q.pop(); int pos = p.first; int speed = p.second; pair<int, int> p1 = {pos + speed, speed * 2}; if (p1.first == target) return steps + 1; if (p1.first > 0 && p1.first + speed < 2 * target) q.push(p1); int speed2 = speed > 0 ? -1 : 1; pair<int, int> p2 = {pos, speed2}; int key = (pos << 2) | (speed2 + 1); if (!v.count(key) && p2.first >= target / 2) { q.push(p2); v.insert(key); } } ++steps; } return -1; } }; |
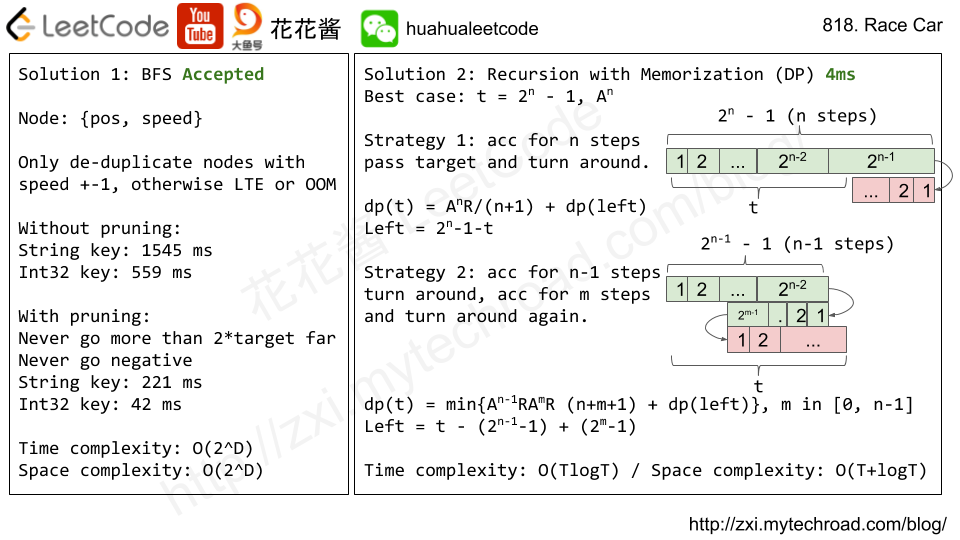
Solution 2: DP O(TlogT)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 4 ms class Solution { public: int racecar(int target) { m_ = vector<int>(target + 1, 0); return dp(target); } private: vector<int> m_; int dp(int t) { if (m_[t] > 0) return m_[t]; int n = ceil(log2(t + 1)); // AA...A (nA) best case if (1 << n == t + 1) return m_[t] = n; // AA...AR (nA + 1R) + dp(left) m_[t] = n + 1 + dp((1 << n) - 1 - t); for (int m = 0; m < n - 1; ++m) { int cur = (1 << (n - 1)) - (1 << m); //AA...ARA...AR (n-1A + 1R + mA + 1R) + dp(left) m_[t] = min(m_[t], n + m + 1 + dp(t - cur)); } return m_[t]; } }; |
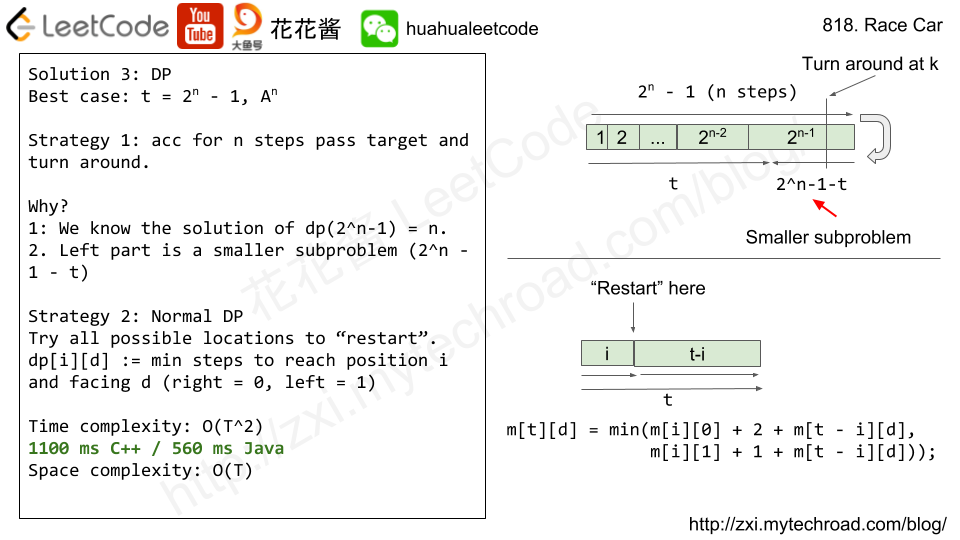
Solution 3: DP O(T^2)
m[t][d] : min steps to reach t and facing d (0 = right, 1 = left)
Time Complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 469 ms constexpr int kMaxT = 10000; int m[kMaxT + 1][2]={0}; class Solution { public: int racecar(int target) { if (m[1][0] == 0) { for (int t = 1; t <= kMaxT; ++t) { const int n = ceil(log2(t + 1)); if (1 << n == t + 1) { m[t][0] = n; m[t][1] = n + 1; continue; } const int l = (1 << n) - 1 - t; m[t][0] = n + 1 + min(m[l][1], m[l][0] + 1); m[t][1] = n + 1 + min(m[l][0], m[l][1] + 1); for (int i = 1; i < t; ++i) { const int mi = min(m[i][0] + 2, m[i][1] + 1); m[t][0] = min(m[t][0], m[t - i][0] + mi); m[t][1] = min(m[t][1], m[t - i][1] + mi); } } } return min(m[target][0], m[target][1]); } }; |
C++/opt
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 361 ms typedef unsigned char uint8; constexpr int kMaxT = 10000; uint8 m[kMaxT + 1][2]={0}; inline uint8 MIN(uint8 a, uint8 b) { return a < b ? a : b; } class Solution { public: int racecar(int target) { if (m[1][0] == 0) { for (int t = 1; t <= kMaxT; ++t) { const int n = ceil(log2(t + 1)); if (1 << n == t + 1) { m[t][0] = n; m[t][1] = n + 1; continue; } const int l = (1 << n) - 1 - t; m[t][0] = n + 1 + MIN(m[l][1], (uint8)(m[l][0] + 1)); m[t][1] = n + 1 + MIN(m[l][0], (uint8)(m[l][1] + 1)); for (int i = 1; i < t; ++i) { const int mi = MIN(m[i][0] + 2, m[i][1] + 1); m[t][0] = MIN(m[t][0], (uint8)(m[t - i][0] + mi)); m[t][1] = MIN(m[t][1], (uint8)(m[t - i][1] + mi)); } } } return min(m[target][0], m[target][1]); } }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 562 ms class Solution { private static int[][] m; public int racecar(int target) { if (m == null) { final int kMaxT = 10000; m = new int[kMaxT + 1][2]; for (int t = 1; t <= kMaxT; ++t) { int n = (int)Math.ceil(Math.log(t + 1) / Math.log(2)); if (1 << n == t + 1) { m[t][0] = n; m[t][1] = n + 1; continue; } int l = (1 << n) - 1 - t; m[t][0] = n + 1 + Math.min(m[l][1], m[l][0] + 1); m[t][1] = n + 1 + Math.min(m[l][0], m[l][1] + 1); for (int i = 1; i < t; ++i) for (int d = 0; d <= 1; d++) m[t][d] = Math.min(m[t][d], Math.min( m[i][0] + 2 + m[t - i][d], m[i][1] + 1 + m[t - i][d])); } } return Math.min(m[target][0], m[target][1]); } } |