A company has n employees with a unique ID for each employee from 0 to n - 1. The head of the company has is the one with headID.
Each employee has one direct manager given in the manager array where manager[i] is the direct manager of the i-th employee, manager[headID] = -1. Also it’s guaranteed that the subordination relationships have a tree structure.
The head of the company wants to inform all the employees of the company of an urgent piece of news. He will inform his direct subordinates and they will inform their subordinates and so on until all employees know about the urgent news.
The i-th employee needs informTime[i] minutes to inform all of his direct subordinates (i.e After informTime[i] minutes, all his direct subordinates can start spreading the news).
Return the number of minutes needed to inform all the employees about the urgent news.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1, headID = 0, manager = [-1], informTime = [0] Output: 0 Explanation: The head of the company is the only employee in the company.
Example 2:
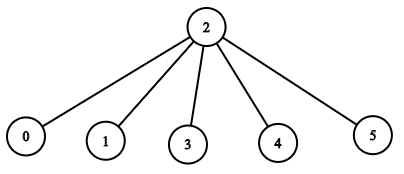
Input: n = 6, headID = 2, manager = [2,2,-1,2,2,2], informTime = [0,0,1,0,0,0] Output: 1 Explanation: The head of the company with id = 2 is the direct manager of all the employees in the company and needs 1 minute to inform them all. The tree structure of the employees in the company is shown.
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, headID = 6, manager = [1,2,3,4,5,6,-1], informTime = [0,6,5,4,3,2,1] Output: 21 Explanation: The head has id = 6. He will inform employee with id = 5 in 1 minute. The employee with id = 5 will inform the employee with id = 4 in 2 minutes. The employee with id = 4 will inform the employee with id = 3 in 3 minutes. The employee with id = 3 will inform the employee with id = 2 in 4 minutes. The employee with id = 2 will inform the employee with id = 1 in 5 minutes. The employee with id = 1 will inform the employee with id = 0 in 6 minutes. Needed time = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 21.
Example 4:
Input: n = 15, headID = 0, manager = [-1,0,0,1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6], informTime = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] Output: 3 Explanation: The first minute the head will inform employees 1 and 2. The second minute they will inform employees 3, 4, 5 and 6. The third minute they will inform the rest of employees.
Example 5:
Input: n = 4, headID = 2, manager = [3,3,-1,2], informTime = [0,0,162,914] Output: 1076
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^50 <= headID < nmanager.length == n0 <= manager[i] < nmanager[headID] == -1informTime.length == n0 <= informTime[i] <= 1000informTime[i] == 0if employeeihas no subordinates.- It is guaranteed that all the employees can be informed.
Solution 1: Build the graph + DFS
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int numOfMinutes(int n, int headID, vector<int>& manager, vector<int>& informTime) { vector<vector<int>> es(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (i != headID) es[manager[i]].push_back(i); function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int cur) { int t = 0; for (int e : es[cur]) t = max(t, dfs(e)); return t + informTime[cur]; }; return dfs(headID); } }; |
Solution 2: Recursion with memoization
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int numOfMinutes(int n, int headID, vector<int>& manager, vector<int>& informTime) { vector<int> cache(n, -1); function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int cur) { if (cur == -1) return 0; if (cache[cur] == -1) cache[cur] = dfs(manager[cur]) + informTime[cur]; return cache[cur]; }; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans = max(ans, dfs(i)); return ans; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# Author: Huahua class Solution: def numOfMinutes(self, n: int, headID: int, manager: List[int], informTime: List[int]) -> int: cache = [-1] * n def dfs(cur): if cur == -1: return 0 if cache[cur] == -1: cache[cur] = dfs(manager[cur]) + informTime[cur] return cache[cur] return max([dfs(i) for i in range(n)]) |