题目大意:给你一些城市之间的机票价格,问从src到dst的最少需要花多少钱,最多可以中转k个机场。
There are n cities connected by m flights. Each fight starts from city u and arrives at v with a price w.
Now given all the cities and fights, together with starting city src and the destination dst, your task is to find the cheapest price from src to dst with up to k stops. If there is no such route, output -1.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
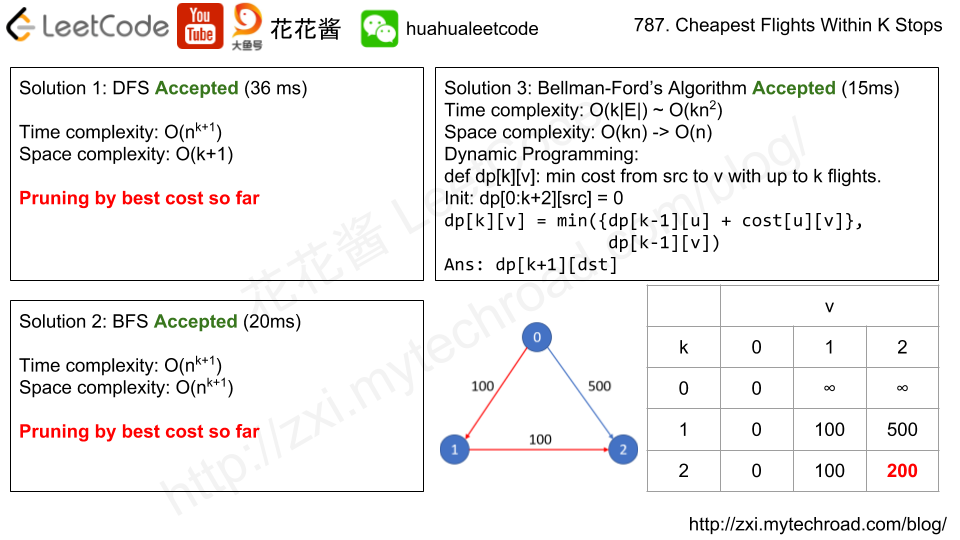
Example 1: Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]] src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 Output: 200 Explanation: The graph looks like this: The cheapest price from city <code>0</code> to city <code>2</code> with at most 1 stop costs 200, as marked red in the picture. |

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Example 2: Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]] src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 Output: 500 Explanation: The graph looks like this: The cheapest price from city <code>0</code> to city <code>2</code> with at most 0 stop costs 500, as marked blue in the picture. |

Note:
- The number of nodes
nwill be in range[1, 100], with nodes labeled from0ton- 1. - The size of
flightswill be in range[0, n * (n - 1) / 2]. - The format of each flight will be
(src,dst, price). - The price of each flight will be in the range
[1, 10000]. kis in the range of[0, n - 1].- There will not be any duplicated flights or self cycles.
Solution 1: DFS
w/o prunning TLE
w/ prunning Accepted
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 36 ms class Solution { public: int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { g_.clear(); for (const auto& e : flights) g_[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]); vector<int> visited(n, 0); visited[src] = 1; int ans = INT_MAX; dfs(src, dst, K + 1, 0, visited, ans); return ans == INT_MAX ? - 1 : ans; } private: unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> g_; void dfs(int src, int dst, int k, int cost, vector<int>& visited, int& ans) { if (src == dst) { ans = cost; return; } if (k == 0) return; for (const auto& p : g_[src]) { if (visited[p.first]) continue; // do not visit the same city twice. if (cost + p.second > ans) continue; // IMPORTANT!!! prunning visited[p.first] = 1; dfs(p.first, dst, k - 1, cost + p.second, visited, ans); visited[p.first] = 0; } } }; |
Solution 2: BFS
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 20 ms class Solution { public: int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> g; for (const auto& e : flights) g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]); int ans = INT_MAX; queue<pair<int,int>> q; q.push({src, 0}); int steps = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); while (size--) { int curr = q.front().first; int cost = q.front().second; q.pop(); if (curr == dst) ans = min(ans, cost); for (const auto& p : g[curr]) { if (cost + p.second > ans) continue; // Important: prunning q.push({p.first, cost + p.second}); } } if (steps++ > K) break; } return ans == INT_MAX ? - 1 : ans; } }; |
Solution 3: Bellman-Ford algorithm
dp[k][i]: min cost from src to i taken up to k flights (k-1 stops)
init: dp[0:k+2][src] = 0
transition: dp[k][i] = min(dp[k-1][j] + price[j][i])
ans: dp[K+1][dst]
Time complexity: O(k * |flights|) / O(k*n^2)
Space complexity: O(k*n) -> O(n)
w/o space compression O(k*n)
C++ O(k*n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 15 ms class Solution { public: int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { constexpr int kInfCost = 1e9; vector<vector<int>> dp(K + 2, vector<int>(n, kInfCost)); dp[0][src] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= K + 1; ++i) { dp[i][src] = 0; for (const auto& p : flights) dp[i][p[1]] = min(dp[i][p[1]], dp[i-1][p[0]] + p[2]); } return dp[K + 1][dst] >= kInfCost ? -1 : dp[K + 1][dst]; } }; |
C++ O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 12 ms class Solution { public: int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { constexpr int kInfCost = 1e9; vector<int> cost(n, kInfCost); cost[src] = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= K; ++i) { vector<int> tmp(cost); for (const auto& p : flights) tmp[p[1]] = min(tmp[p[1]], cost[p[0]] + p[2]); cost.swap(tmp); } return cost[dst] >= kInfCost ? -1 : cost[dst]; } }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 11 ms class Solution { public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) { final int kInfCost = 1<<30; int[] cost = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(cost, kInfCost); cost[src] = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= K; ++i) { int[] tmp = cost.clone(); for(int[] p: flights) tmp[p[1]] = Math.min(tmp[p[1]], cost[p[0]] + p[2]); cost = tmp; } return cost[dst] >= kInfCost ? -1 : cost[dst]; } } |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
""" Author: Huahua Running time: 132 ms """ class Solution: def findCheapestPrice(self, n, flights, src, dst, K): kInfCost = 1e9 cost = [kInfCost for _ in range(n)] cost[src] = 0 for i in range(K + 1): tmp = list(cost) for p in flights: tmp[p[1]] = min(tmp[p[1]], cost[p[0]] + p[2]) cost = tmp return -1 if cost[dst] >= 1e9 else cost[dst] |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment