Problem
Given a string S and a string T, count the number of distinct subsequences of S which equals T.
A subsequence of a string is a new string which is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, "ACE" is a subsequence of "ABCDE" while "AEC" is not).
Example 1:
Input: S = "rabbbit", T = "rabbit" Output: 3 Explanation: As shown below, there are 3 ways you can generate "rabbit" from S. (The caret symbol ^ means the chosen letters) rabbbit ^^^^ ^^ rabbbit ^^ ^^^^ rabbbit ^^^ ^^^
Example 2:
Input: S = "babgbag", T = "bag" Output: 5 Explanation: As shown below, there are 5 ways you can generate "bag" from S. (The caret symbol ^ means the chosen letters) babgbag ^^ ^ babgbag ^^ ^ babgbag ^ ^^ babgbag ^ ^^ babgbag ^^^
Solution: DP
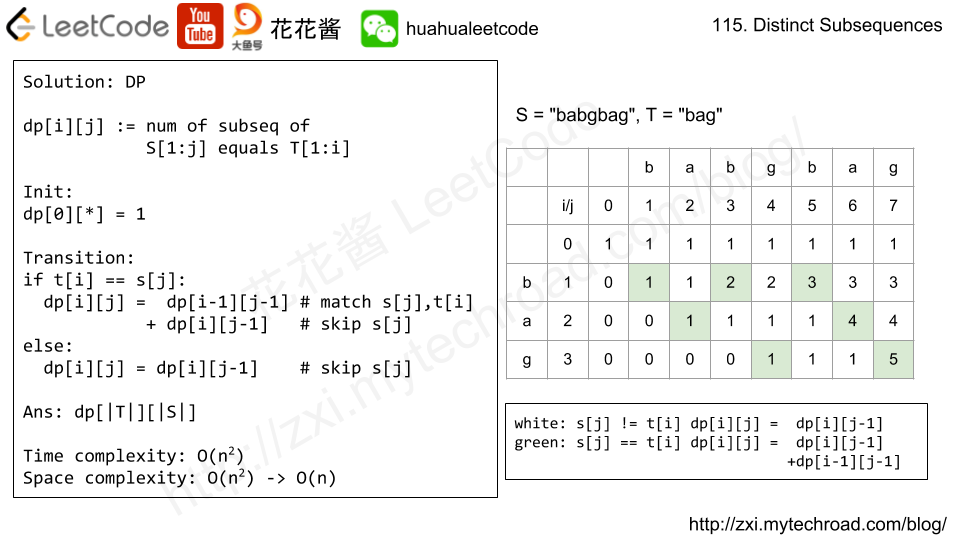
Time complexity: O(|s| * |t|)
Space complexity: O(|s| * |t|)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 4 ms class Solution { public: int numDistinct(string s, string t) { int ls = s.length(); int lt = t.length(); vector<vector<int>> dp(lt + 1, vector<int>(ls + 1)); fill(begin(dp[0]), end(dp[0]), 1); for (int i = 1; i <= lt; ++i) for (int j = 1; j <= ls; ++j) dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + (t[i - 1] == s[j - 1] ? dp[i - 1][j - 1] : 0); return dp[lt][ls]; } }; |


