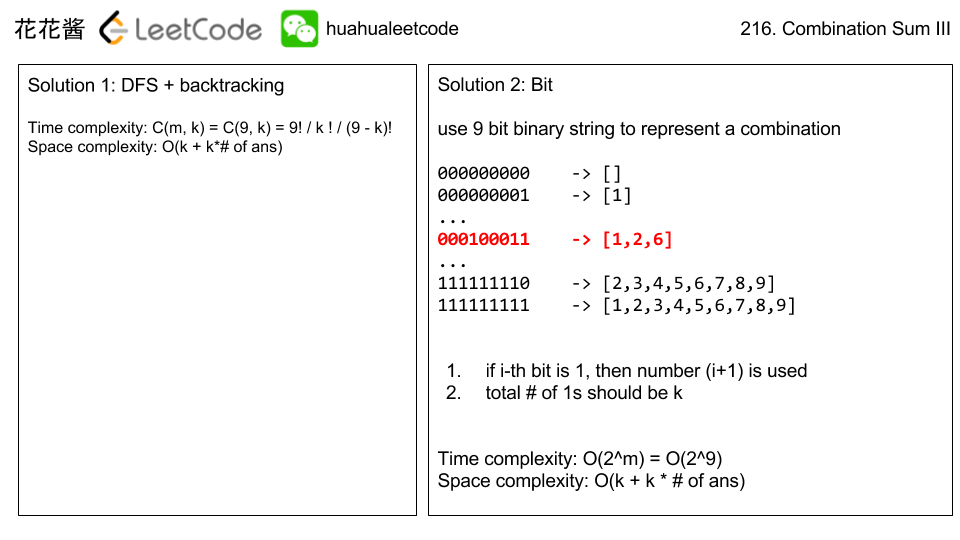
Problem:
Implement a MyCalendar class to store your events. A new event can be added if adding the event will not cause a double booking.
Your class will have the method, book(int start, int end). Formally, this represents a booking on the half open interval [start, end), the range of real numbers x such that start <= x < end.
A double booking happens when two events have some non-empty intersection (ie., there is some time that is common to both events.)
For each call to the method MyCalendar.book, return true if the event can be added to the calendar successfully without causing a double booking. Otherwise, return false and do not add the event to the calendar.
Your class will be called like this: MyCalendar cal = new MyCalendar(); MyCalendar.book(start, end)
Example 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
MyCalendar(); MyCalendar.book(10, 20); // returns true MyCalendar.book(15, 25); // returns false MyCalendar.book(20, 30); // returns true Explanation: The first event can be booked. The second can't because time 15 is already booked by another event. The third event can be booked, as the first event takes every time less than 20, but not including 20. |
Note:
- The number of calls to
MyCalendar.bookper test case will be at most1000. - In calls to
MyCalendar.book(start, end),startandendare integers in the range[0, 10^9].
Idea:
Binary Search
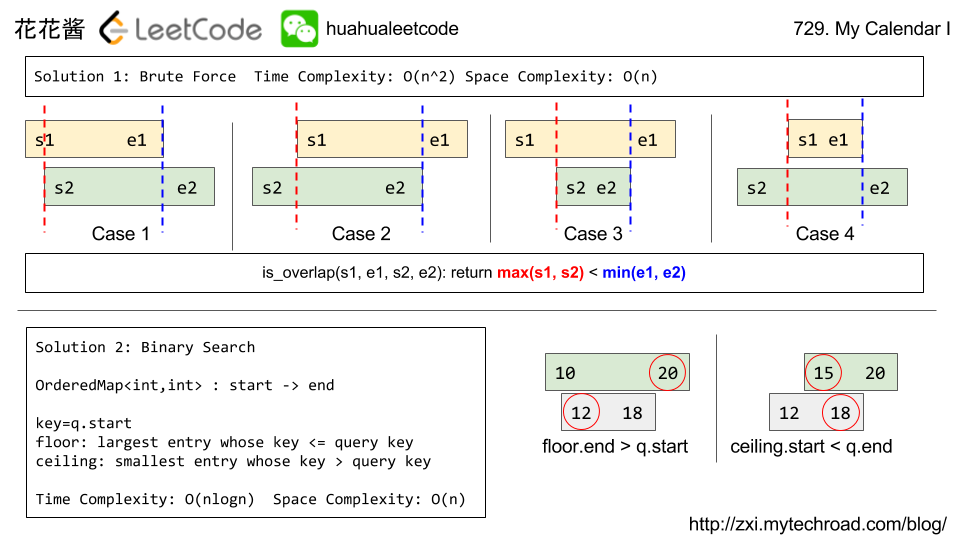
Solution1:
Brute Force: O(n^2)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 99 ms class MyCalendar { public: MyCalendar() {} bool book(int start, int end) { for (const auto& event : booked_) { int s = event.first; int e = event.second; if (max(s, start) < min(e, end)) return false; } booked_.emplace_back(start, end); return true; } private: vector<pair<int, int>> booked_; }; |
Solution 2:
Binary Search O(nlogn)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 82 ms class MyCalendar { public: MyCalendar() {} bool book(int start, int end) { auto it = booked_.lower_bound(start); if (it != booked_.cend() && it->first < end) return false; if (it != booked_.cbegin() && (--it)->second > start) return false; booked_[start] = end; return true; } private: map<int, int> booked_; }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 170 ms class MyCalendar { TreeMap<Integer, Integer> booked_; public MyCalendar() { booked_ = new TreeMap<>(); } public boolean book(int start, int end) { Integer lb = booked_.floorKey(start); if (lb != null && booked_.get(lb) > start) return false; Integer ub = booked_.ceilingKey(start); if (ub != null && ub < end) return false; booked_.put(start, end); return true; } } |
Related Problems: