We are given an array A of N lowercase letter strings, all of the same length.
Now, we may choose any set of deletion indices, and for each string, we delete all the characters in those indices.
For example, if we have an array A = ["babca","bbazb"] and deletion indices {0, 1, 4}, then the final array after deletions is ["bc","az"].
Suppose we chose a set of deletion indices D such that after deletions, the final array has every element (row) in lexicographic order.
For clarity, A[0] is in lexicographic order (ie. A[0][0] <= A[0][1] <= ... <= A[0][A[0].length - 1]), A[1] is in lexicographic order (ie. A[1][0] <= A[1][1] <= ... <= A[1][A[1].length - 1]), and so on.
Return the minimum possible value of D.length.
Example 1:
Input: ["babca","bbazb"] Output: 3 Explanation: After deleting columns 0, 1, and 4, the final array is A = ["bc", "az"]. Both these rows are individually in lexicographic order (ie. A[0][0] <= A[0][1] and A[1][0] <= A[1][1]). Note that A[0] > A[1] - the array A isn't necessarily in lexicographic order.
Example 2:
Input: ["edcba"] Output: 4 Explanation: If we delete less than 4 columns, the only row won't be lexicographically sorted.
Example 3:
Input: ["ghi","def","abc"] Output: 0 Explanation: All rows are already lexicographically sorted.
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 1001 <= A[i].length <= 100
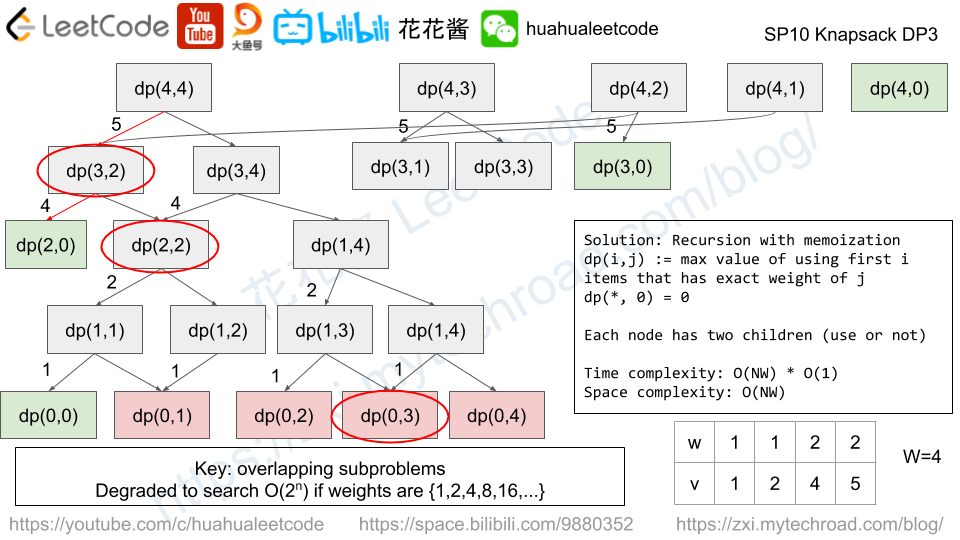
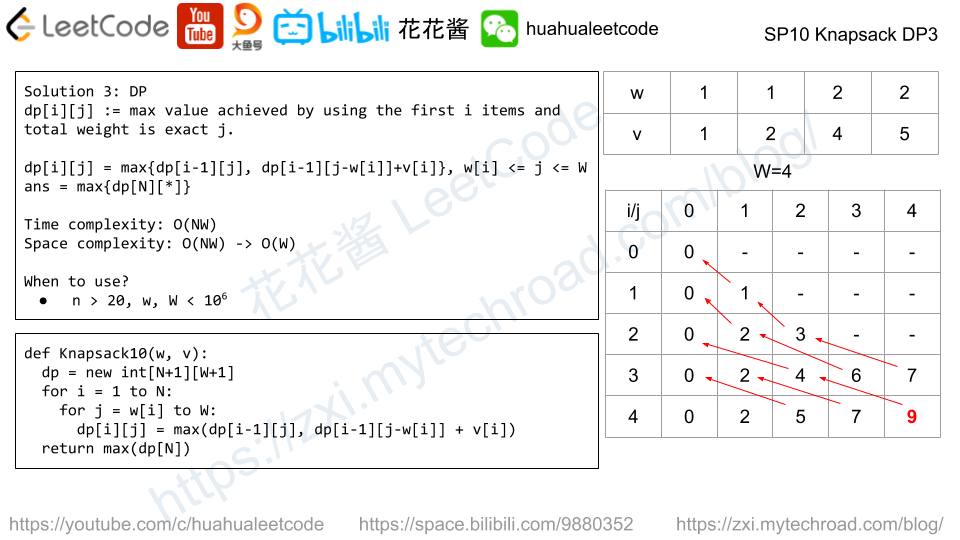
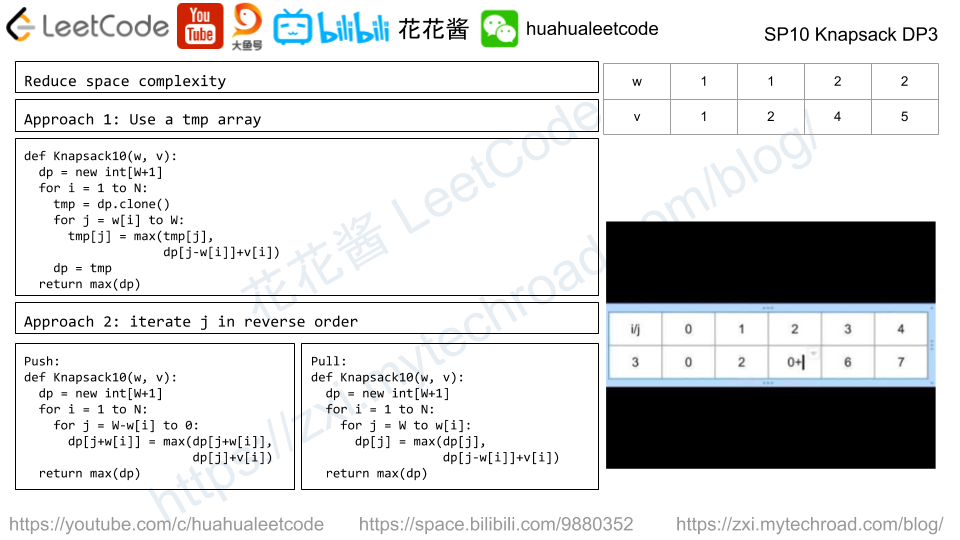
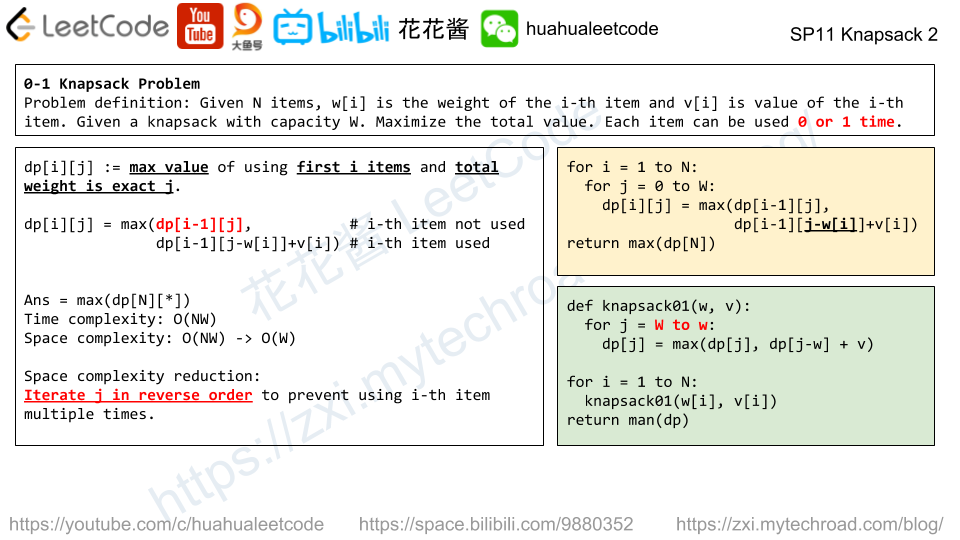
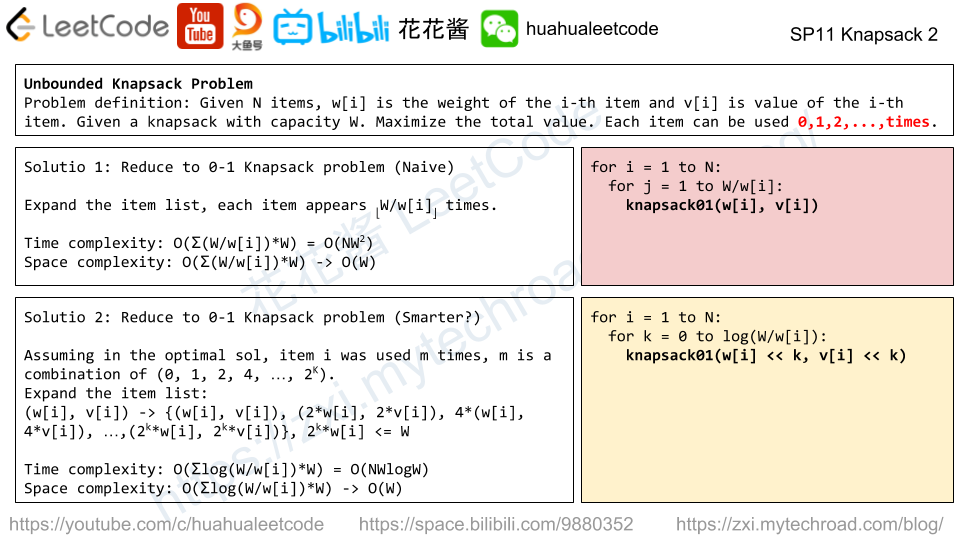
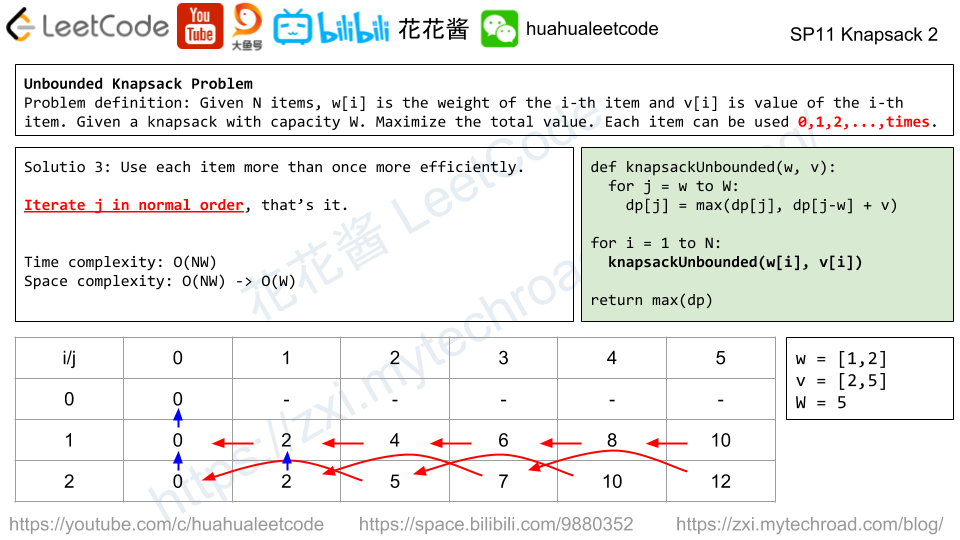
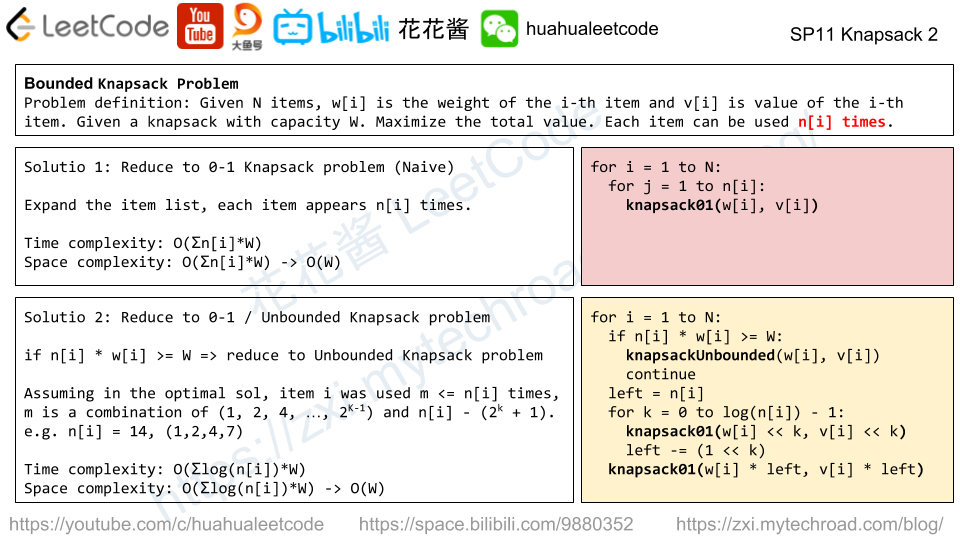
Solution: DP
dp[i] := max length of increasing sub-sequence (of all strings) ends with i-th letter.
dp[i] = max(dp[j] + 1) if all A[*][j] <= A[*][i], j < i
Time complexity: (n*L^2)
Space complexity: O(L)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua, running time: 24 ms class Solution { public: int minDeletionSize(vector<string>& A) { vector<int> dp(A[0].length(), 1); for (int i = 0; i < A[0].length(); ++i) for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) { bool valid = true; for (const auto& a : A) if (a[j] > a[i]) { valid = false; break; } if (valid) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1); } return A[0].length() - *max_element(begin(dp), end(dp)); } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
// Author: Huahua, running time: 176 ms class Solution: def minDeletionSize(self, A): n = len(A[0]) dp = [1] * n for i in range(1, n): for j in range(i): valid = True for a in A: if a[j] > a[i]: valid = False break if valid: dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1) return n - max(dp) |
 .
.