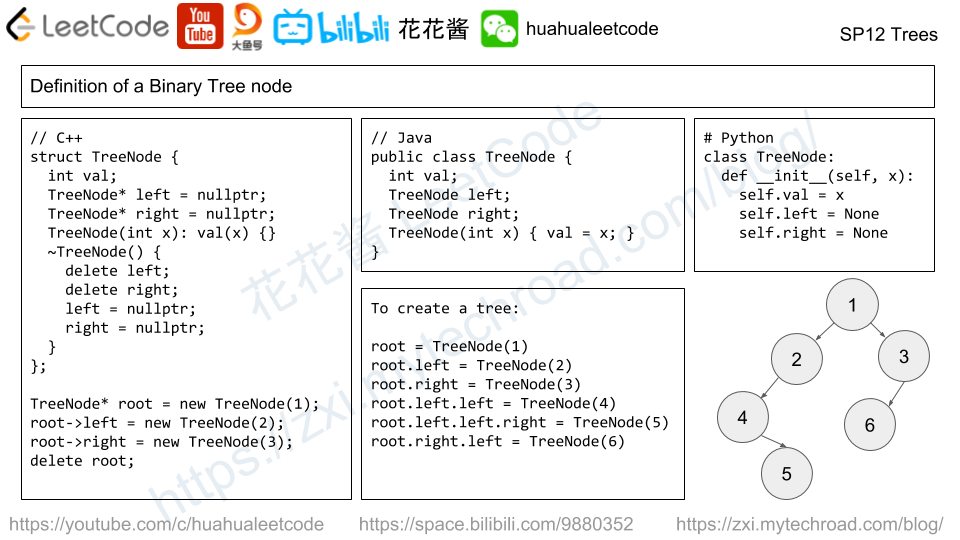
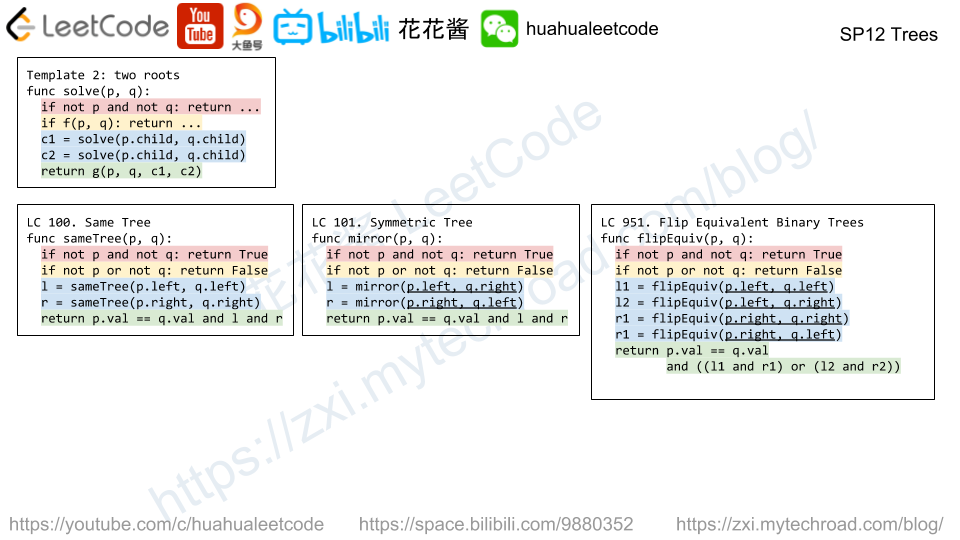
Binary tree is one of the most frequently asked question type during interview.
二叉树是面试中经常会问到的问题。
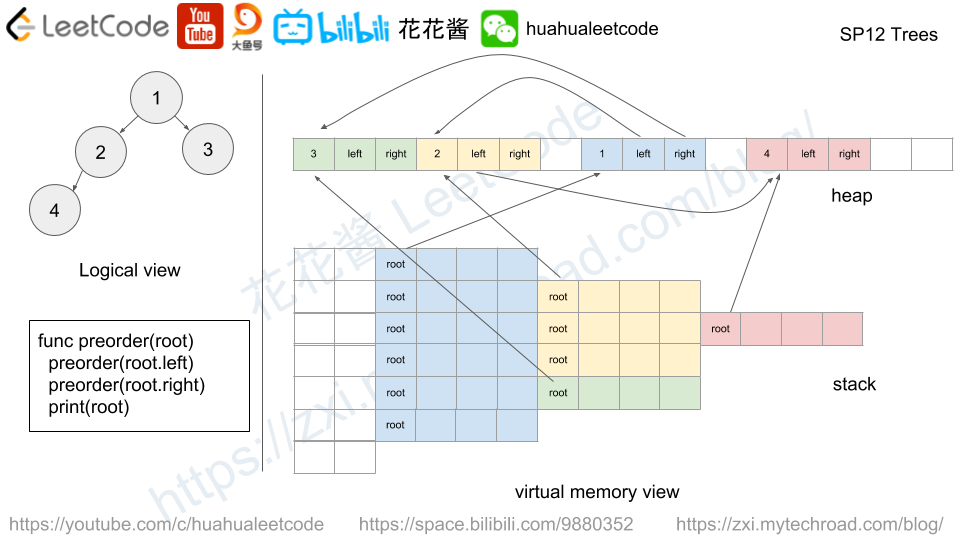
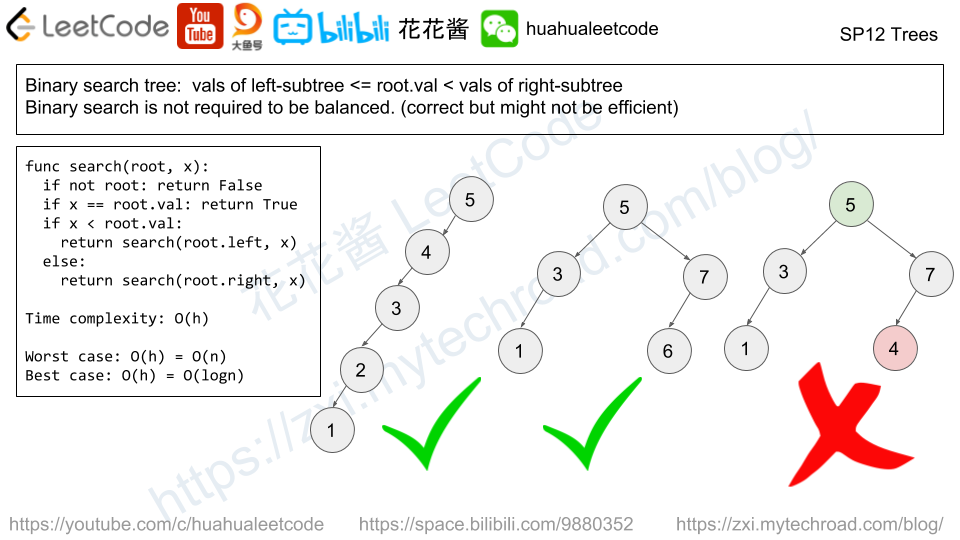
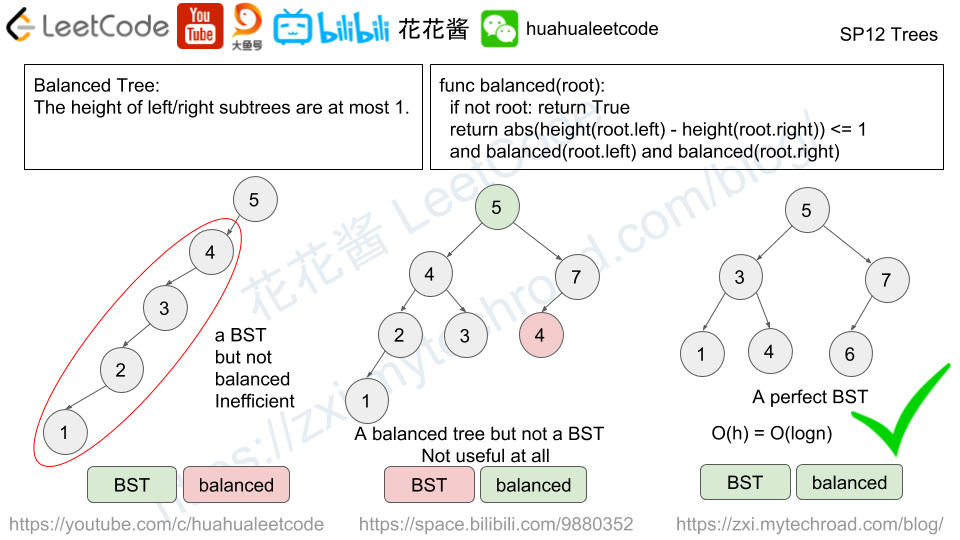
The candidate needs to understand the recursively defined TreeNode and solve the problem through recursion.
面试者需要理解递归定义的TreeNode数据类型,并且通过使用递归的方式来解决问题。

February 21, 2026
Binary tree is one of the most frequently asked question type during interview.
二叉树是面试中经常会问到的问题。
The candidate needs to understand the recursively defined TreeNode and solve the problem through recursion.
面试者需要理解递归定义的TreeNode数据类型,并且通过使用递归的方式来解决问题。










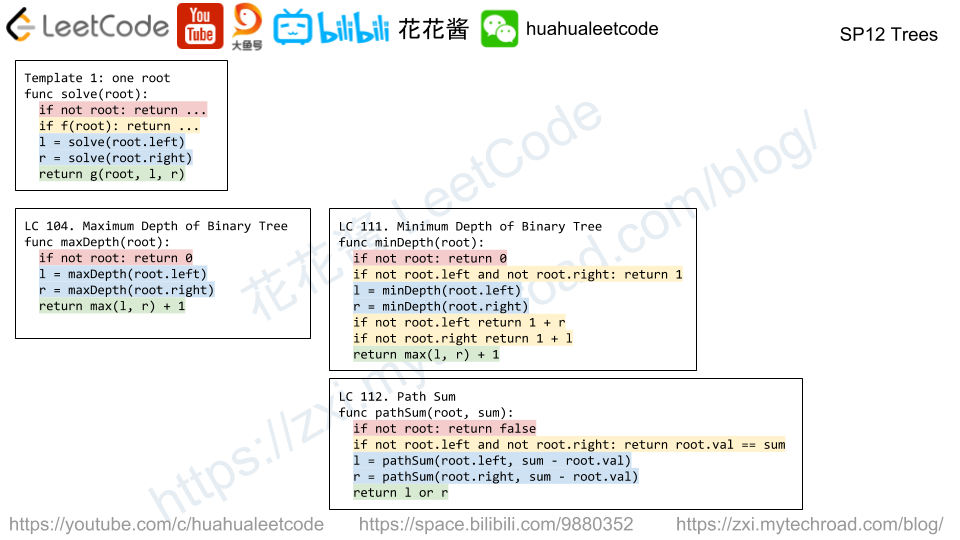
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its minimum depth = 2.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// Author: Huahua, 4 ms class Solution { public: int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; if (!root->left && !root->right) return 1; int l = root->left ? minDepth(root->left) : INT_MAX; int r = root->right ? minDepth(root->right) : INT_MAX; return min(l, r) + 1; } }; |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
class Solution: def minDepth(self, root): if not root: return 0 if not root.left and not root.right: return 1 l = self.minDepth(root.left) r = self.minDepth(root.right) if not root.left: return 1 + r if not root.right: return 1 + l return 1 + min(l, r) |
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its depth = 3.
maxDepth(root) = max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
// Author: Huahua, 4 ms class Solution { public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; int l = maxDepth(root->left); int r = maxDepth(root->right); return max(l, r) + 1; } }; |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# Author: Huahua, 80 ms class Solution: def maxDepth(self, root): if not root: return 0 l = self.maxDepth(root.left) r = self.maxDepth(root.right) return max(l, r) + 1 |
You are installing a billboard and want it to have the largest height. The billboard will have two steel supports, one on each side. Each steel support must be an equal height.
You have a collection of rods which can be welded together. For example, if you have rods of lengths 1, 2, and 3, you can weld them together to make a support of length 6.
Return the largest possible height of your billboard installation. If you cannot support the billboard, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,6] Output: 6 Explanation: We have two disjoint subsets {1,2,3} and {6}, which have the same sum = 6.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 10 Explanation: We have two disjoint subsets {2,3,5} and {4,6}, which have the same sum = 10.
Example 3:
Input: [1,2] Output: 0 Explanation: The billboard cannot be supported, so we return 0.
Note:
0 <= rods.length <= 201 <= rods[i] <= 1000The sum of rods is at most 5000.如果直接暴力搜索的话时间复杂度是O(3^N),铁定超时。对于每一根我们可以选择1、放到左边,2、放到右边,3、不使用。最后再看一下左边和右边是否相同。
题目的数据规模中的这句话非常重要:
The sum of rods is at most 5000.
这句话就是告诉你算法的时间复杂度和sum of rods有关系,通常需要使用DP。
由于每根柱子只能使用一次(让我们想到了 回复 01背包),但是我们怎么去描述放到左边还是放到右边呢?
Naive的方法是用 dp[i] 表示使用前i个柱子能够构成的柱子高度的集合。
e.g. dp[i] = {(h1, h2)}, h1 <= h2
和暴力搜索比起来DP已经对状态进行了压缩,因为我并不需要关心h1, h2是通过哪些(在我之前的)柱子构成了,我只关心它们的当前高度。
然后我可以选择
1、不用第i根柱子
2、放到低的那一堆
3、放到高的那一堆
状态转移的伪代码:
for h1, h2 in dp[i – 1]:
dp[i] += (h1, h2) # not used
dp[i] += (h1, h2 + h) # put on higher
if h1 + h < h2:
dp[i] += (h1 + h, h2) # put on lower
else:
dp[i] += (h2, h1 + h) # put on lower
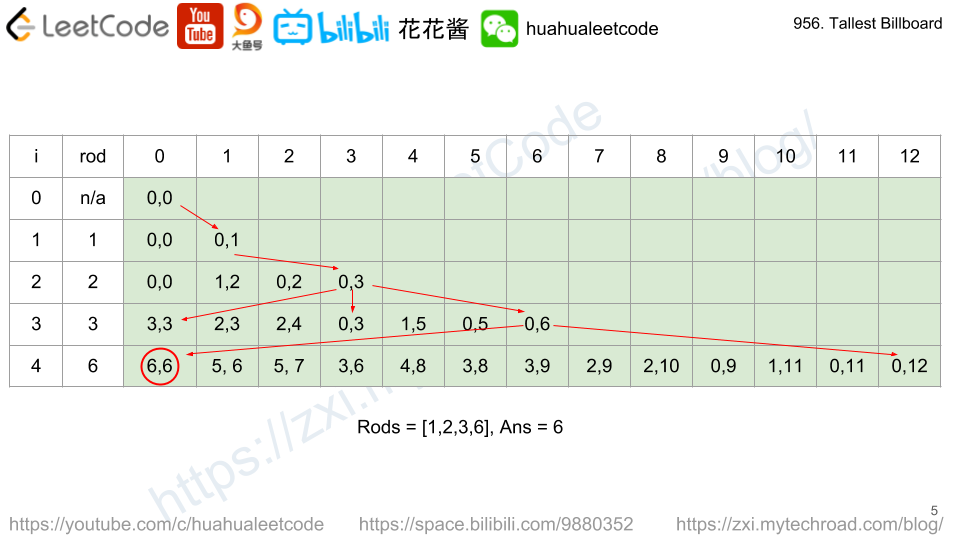
假设 rods=[1,1,2]
dp[0] = {(0,0)}
dp[1] = {(0,0), (0,1)}
dp[2] = {(0,0), (0,1), (0,2), (1,1)}
dp[3] = {(0,0), (0,1), (0,2), (0,3), (0,4), (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (2,2)}
但是dp[i]这个集合的大小可能达到sum^2,所以还是会超时…
时间复杂度 O(n*sum^2)
空间复杂度 O(n*sum^2) 可降维至 O(sum^2)
革命尚未成功,同志仍需努力!
all pairs的cost太大,我们还需要继续压缩状态!
重点来了
通过观察发现,若有2个pairs:
(h1, h2), (h3, h4),
h1 <= h2, h3 <= h4, h1 < h3, h2 – h1 = h4 – h3 即 高度差 相同
如果 min(h1, h2) < min(h3, h4) 那么(h1, h2) 不可能产生最优解,直接舍弃。
因为如果后面的柱子可以构成 h4 – h3/h2 – h1 填补高度差,使得两根柱子一样高,那么答案就是 h2 和 h4。但h2 < h4,所以最优解只能来自后者。
举个例子:我有 (1, 3) 和 (2, 4) 两个pairs,它们的高度差都是2,假设我还有一个长度为2的柱子,那么我可以构成(1+2, 3) 以及 (2+2, 4),虽然这两个都是解。但是后者的高度要大于前者,所以前者无法构成最优解,也就没必要存下来。
所以,我们可以把状态压缩到高度差,对于相同的高度差,我只存h1最大的。
我们用 dp[i][j] 来表示使用前i个柱子,高度差为j的情况下最大的公共高度h1是多少。
状态转移(如下图)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i – 1][j])
dp[i][j+h] = max(dp[i][j + h], dp[i – 1][j])
dp[i][|j-h|] = max(dp[i][|j-h|], dp[i – 1][j] + min(j, h))
时间复杂度 O(nsum)
空间复杂度 O(nsum) 可降维至 O(sum)
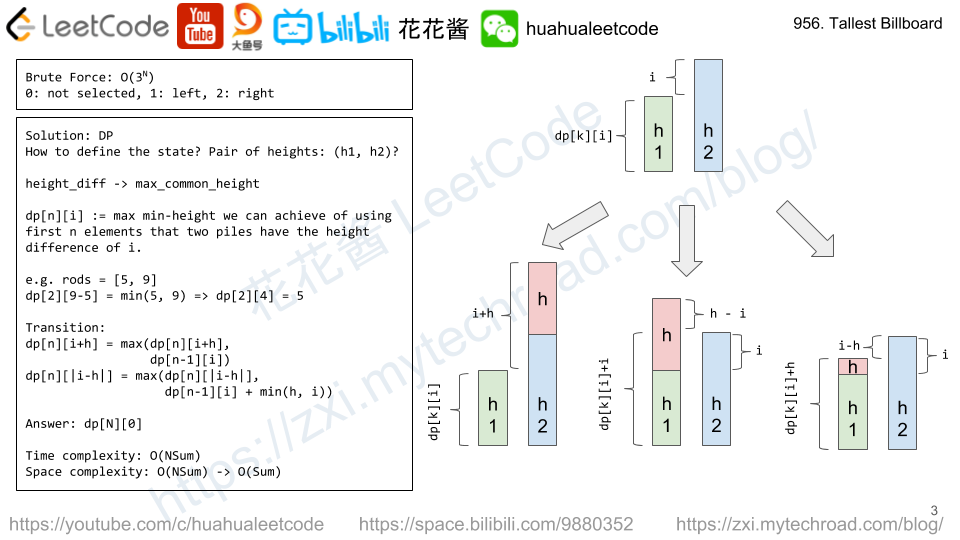
dp[i] := max common height of two piles of height difference i.
e.g. y1 = 5, y2 = 9 => dp[9 – 5] = min(5, 9) => dp[4] = 5.
answer: dp[0]
Time complexity: O(n*Sum)
Space complexity: O(Sum)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
// Author: Huahua, 172 ms class Solution { public: int tallestBillboard(vector<int>& rods) { unordered_map<int, int> dp; dp[0] = 0; for (int rod : rods) { auto cur = dp; for (const auto& kv : cur) { const int k = kv.first; dp[k + rod] = max(dp[k + rod], cur[k]); dp[abs(k - rod)] = max(dp[abs(k - rod)], cur[k] + min(rod, k)); } } return dp[0]; } }; |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua, 8 ms class Solution { public: int tallestBillboard(vector<int>& rods) { const int s = accumulate(begin(rods), end(rods), 0); vector<int> dp(s + 1, -1); dp[0] = 0; for (int rod : rods) { vector<int> cur(dp); for (int i = 0; i <= s - rod; ++i) { if (cur[i] < 0) continue; dp[i + rod] = max(dp[i + rod], cur[i]); dp[abs(i - rod)] = max(dp[abs(i - rod)], cur[i] + min(rod, i)); } } return dp[0]; } }; |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
// Author: Huahua, 12 ms class Solution { public: int tallestBillboard(vector<int>& rods) { const int n = rods.size(); const int s = accumulate(begin(rods), end(rods), 0); // dp[i][j] := min(h1, h2), j = abs(h1 - h2) vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(s + 1, -1)); dp[0][0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { int h = rods[i - 1]; for (int j = 0; j <= s - h; ++j) { if (dp[i - 1][j] < 0) continue; // not used dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]); // put on the taller one dp[i][j + h] = max(dp[i][j + h], dp[i - 1][j]); // put on the shorter one dp[i][abs(j - h)] = max(dp[i][abs(j - h)], dp[i - 1][j] + min(h, j)); } } return dp[n][0]; } }; |
Given an array of integers A with even length, return true if and only if it is possible to reorder it such that A[2 * i + 1] = 2 * A[2 * i] for every 0 <= i < len(A) / 2.
Example 1:
Input: [3,1,3,6] Output: false
Example 2:
Input: [2,1,2,6] Output: false
Example 3:
Input: [4,-2,2,-4] Output: true Explanation: We can take two groups, [-2,-4] and [2,4] to form [-2,-4,2,4] or [2,4,-2,-4].
Example 4:
Input: [1,2,4,16,8,4] Output: false
Note:
0 <= A.length <= 30000A.length is even-100000 <= A[i] <= 100000Time complexity: O(N + 100000 * 2)
Space complexity: O(100000 * 2)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua, 108 ms class Solution { public: bool canReorderDoubled(vector<int>& A) { const int kMaxN = 100000; vector<int> p(kMaxN + 1); vector<int> n(kMaxN + 1); for (int a : A) { if (a >= 0) ++p[a]; else ++n[-a]; } for (int i = 0; i <= kMaxN / 2; ++i) { if (p[i] && (p[i * 2] -= p[i]) < 0) return false; if (n[i] && (n[i * 2] -= n[i]) < 0) return false; } return true; } }; |
Time complexity: O(NlogN)
Space complexity: O(N)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
// Author: Huahua, 108 ms class Solution { public: bool canReorderDoubled(vector<int>& A) { unordered_map<int, int> c; for (int a : A) ++c[a]; vector<int> keys; for (const auto &kv : c) keys.push_back(kv.first); sort(begin(keys), end(keys), [](int a, int b) { return abs(a) < abs(b); }); for (int key : keys) if (c[key] && (c[key * 2] -= c[key]) < 0) return false; return true; } }; |