Problem:
Given a chemical formula (given as a string), return the count of each atom.
An atomic element always starts with an uppercase character, then zero or more lowercase letters, representing the name.
1 or more digits representing the count of that element may follow if the count is greater than 1. If the count is 1, no digits will follow. For example, H2O and H2O2 are possible, but H1O2 is impossible.
Two formulas concatenated together produce another formula. For example, H2O2He3Mg4 is also a formula.
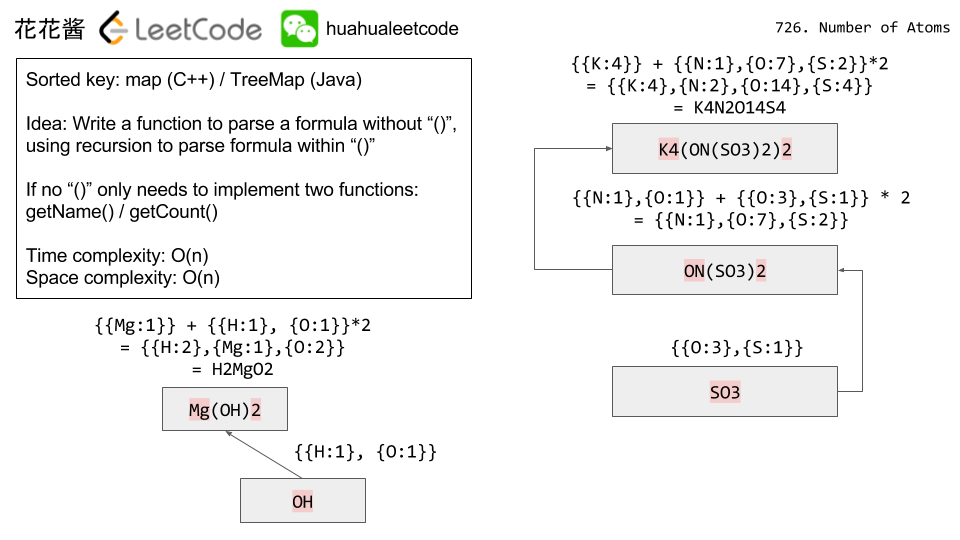
A formula placed in parentheses, and a count (optionally added) is also a formula. For example, (H2O2) and (H2O2)3 are formulas.
Given a formula, output the count of all elements as a string in the following form: the first name (in sorted order), followed by its count (if that count is more than 1), followed by the second name (in sorted order), followed by its count (if that count is more than 1), and so on.
Example 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Input: formula = "H2O" Output: "H2O" Explanation: The count of elements are {'H': 2, 'O': 1}. |
Example 2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Input: formula = "Mg(OH)2" Output: "H2MgO2" Explanation: The count of elements are {'H': 2, 'Mg': 1, 'O': 2}. |
Example 3:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Input: formula = "K4(ON(SO3)2)2" Output: "K4N2O14S4" Explanation: The count of elements are {'K': 4, 'N': 2, 'O': 14, 'S': 4}. |
Note:
- All atom names consist of lowercase letters, except for the first character which is uppercase.
- The length of
formulawill be in the range[1, 1000]. formulawill only consist of letters, digits, and round parentheses, and is a valid formula as defined in the problem.
Idea:
Recursion
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
Solution:
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 3 ms class Solution { public: string countOfAtoms(const string& formula) { int i = 0; string ans; for (const auto& kv : countOfAtoms(formula, i)) { ans += kv.first; if (kv.second > 1) ans += std::to_string(kv.second); } return ans; } private: map<string, int> countOfAtoms(const string& formula, int& i) { map<string, int> counts; while (i != formula.length()) { if (formula[i] == '(') { const auto& tmp_counts = countOfAtoms(formula, ++i); const int count = getCount(formula, i); for (const auto& kv : tmp_counts) counts[kv.first] += kv.second * count; } else if (formula[i] == ')') { ++i; return counts; } else { const string& name = getName(formula, i); counts[name] += getCount(formula, i); } } return counts; } string getName(const string& formula, int& i) { string name; while (isalpha(formula[i]) && (name.empty() || islower(formula[i]))) name += formula[i++]; return name; } int getCount(const string& formula, int& i) { string count_str; while (isdigit(formula[i])) count_str += formula[i++]; return count_str.empty() ? 1 : std::stoi(count_str); } }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 13 ms class Solution { private int i; public String countOfAtoms(String formula) { StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); i = 0; Map<String, Integer> counts = countOfAtoms(formula.toCharArray()); for (String name: counts.keySet()) { ans.append(name); int count = counts.get(name); if (count > 1) ans.append("" + count); } return ans.toString(); } private Map<String, Integer> countOfAtoms(char[] f) { Map<String, Integer> ans = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(); while (i != f.length) { if (f[i] == '(') { ++i; Map<String, Integer> tmp = countOfAtoms(f); int count = getCount(f); for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : tmp.entrySet()) ans.put(entry.getKey(), ans.getOrDefault(entry.getKey(), 0) + entry.getValue() * count); } else if (f[i] == ')') { ++i; return ans; } else { String name = getName(f); ans.put(name, ans.getOrDefault(name, 0) + getCount(f)); } } return ans; } private String getName(char[] f) { String name = "" + f[i++]; while (i < f.length && 'a' <= f[i] && f[i] <= 'z') name += f[i++]; return name; } private int getCount(char[] f) { int count = 0; while (i < f.length && '0' <= f[i] && f[i] <= '9') { count = count * 10 + (f[i] - '0'); ++i; } return count == 0 ? 1 : count; } } |