On a 2-dimensional grid, there are 4 types of squares:
1represents the starting square. There is exactly one starting square.2represents the ending square. There is exactly one ending square.0represents empty squares we can walk over.-1represents obstacles that we cannot walk over.
Return the number of 4-directional walks from the starting square to the ending square, that walk over every non-obstacle square exactly once.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,2,-1]] Output: 2 Explanation: We have the following two paths: 1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2) 2. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2)
Example 2:
Input: [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: We have the following four paths: 1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3) 2. (0,0),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3) 3. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3) 4. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2),(2,3)
Example 3:
Input: [[0,1],[2,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no path that walks over every empty square exactly once. Note that the starting and ending square can be anywhere in the grid.
Note:
1 <= grid.length * grid[0].length <= 20
count how many empty blocks there are and try all possible paths to end point and check whether we visited every empty blocks or not.
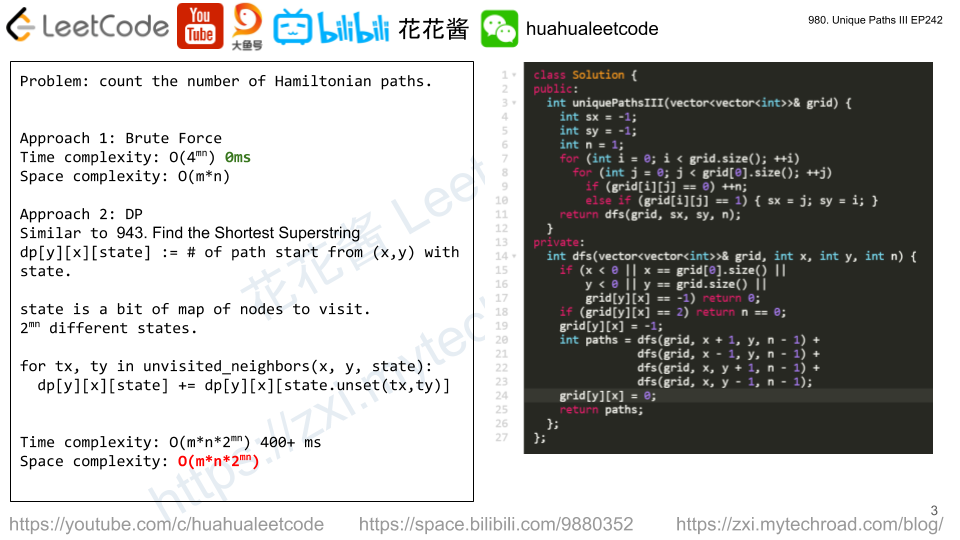
Solution: Brute force / DP
C++/DFS
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
class Solution { public: int uniquePathsIII(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int sx = -1; int sy = -1; int n = 1; for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); ++i) for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); ++j) if (grid[i][j] == 0) ++n; else if (grid[i][j] == 1) { sx = j; sy = i; } return dfs(grid, sx, sy, n); } private: int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y, int n) { if (x < 0 || x == grid[0].size() || y < 0 || y == grid.size() || grid[y][x] == -1) return 0; if (grid[y][x] == 2) return n == 0; grid[y][x] = -1; int paths = dfs(grid, x + 1, y, n - 1) + dfs(grid, x - 1, y, n - 1) + dfs(grid, x, y + 1, n - 1) + dfs(grid, x, y - 1, n - 1); grid[y][x] = 0; return paths; }; }; |
C++/DP
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
class Solution { public: int uniquePathsIII(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { const int n = grid.size(); const int m = grid[0].size(); const vector<int> dirs{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; vector<vector<vector<short>>> cache(n, vector<vector<short>>(m, vector<short>(1 << n * m, -1))); int sx = -1; int sy = -1; int state = 0; auto key = [m](int x, int y) { return 1 << (y * m + x); }; function<short(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int x, int y, int state) { if (cache[y][x][state] != -1) return cache[y][x][state]; if (grid[y][x] == 2) return static_cast<short>(state == 0); int paths = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { const int tx = x + dirs[i]; const int ty = y + dirs[i + 1]; if (tx < 0 || tx == m || ty < 0 || ty == n || grid[ty][tx] == -1) continue; if (!(state & key(tx, ty))) continue; paths += dfs(tx, ty, state ^ key(tx, ty)); } return cache[y][x][state] = paths; }; for (int y = 0; y < n; ++y) for (int x = 0; x < m; ++x) if (grid[y][x] == 0 || grid[y][x] == 2) state |= key(x, y); else if (grid[y][x] == 1) { sx = x; sy = y; } return dfs(sx, sy, state); } }; |