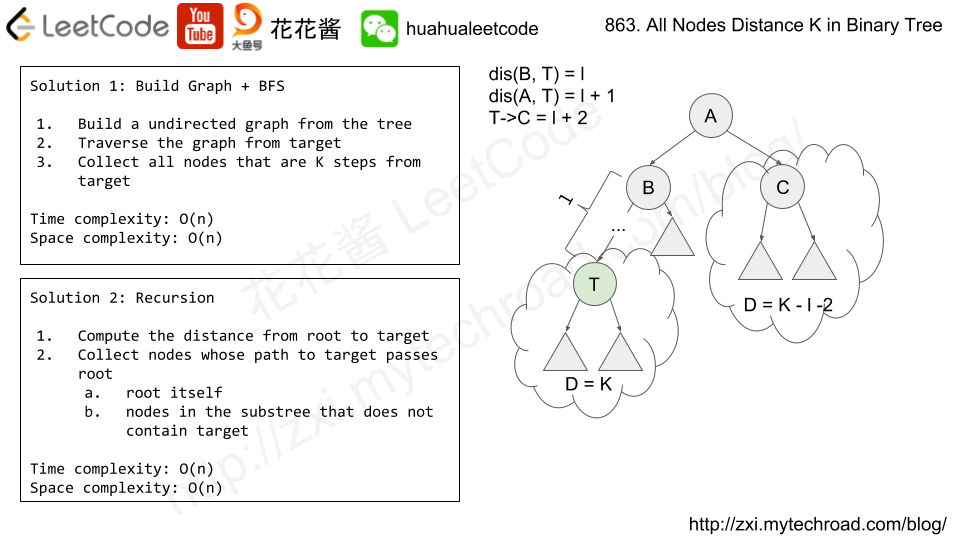
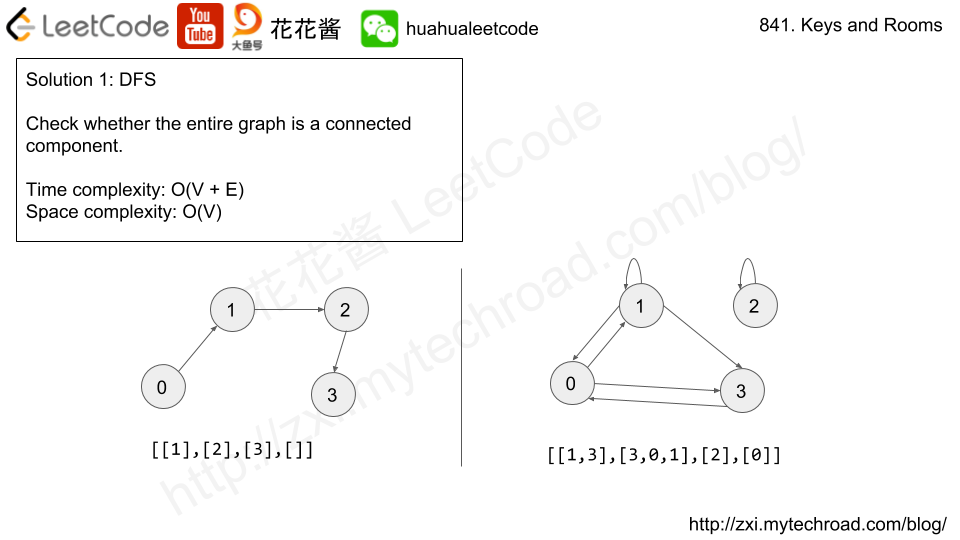
Video is for 花花酱 LeetCode 886. Possible Bipartition, but the algorithm is exact the same.
Problem
https://leetcode.com/problems/is-graph-bipartite/
Given an undirected graph, return true if and only if it is bipartite.
Recall that a graph is bipartite if we can split it’s set of nodes into two independent subsets A and B such that every edge in the graph has one node in A and another node in B.
The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of indexes j for which the edge between nodes i and j exists. Each node is an integer between 0 and graph.length - 1. There are no self edges or parallel edges: graph[i] does not contain i, and it doesn’t contain any element twice.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,3], [0,2], [1,3], [0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:
0----1
| |
| |
3----2
We can divide the vertices into two groups: {0, 2} and {1, 3}.
Example 2: Input: [[1,2,3], [0,2], [0,1,3], [0,2]] Output: false Explanation: The graph looks like this: 0----1 | \ | | \ | 3----2 We cannot find a way to divide the set of nodes into two independent subsets.
Note:
graphwill have length in range[1, 100].graph[i]will contain integers in range[0, graph.length - 1].graph[i]will not containior duplicate values.- The graph is undirected: if any element
jis ingraph[i], theniwill be ingraph[j].
Solution: Graph Coloring
For each node
- If has not been colored, color it to RED(1).
- Color its neighbors with a different color RED(1) to BLUE(-1) or BLUE(-1) to RED(-1).
If we can finish the coloring then the graph is bipartite. All red nodes on the left no connections between them and all blues nodes on the right, again no connections between them. red and blue nodes are neighbors.
Time complexity: O(V+E)
Space complexity: O(V)
C++ / DFS
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 12 ms class Solution { public: bool isBipartite(vector<vector<int>>& graph) { const int n = graph.size(); vector<int> colors(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (!colors[i] && !coloring(graph, colors, 1, i)) return false; return true; } private: bool coloring(const vector<vector<int>>& graph, vector<int>& colors, int color, int node) { if (colors[node]) return colors[node] == color; colors[node] = color; for (int nxt : graph[node]) if (!coloring(graph, colors, -color, nxt)) return false; return true; } }; |
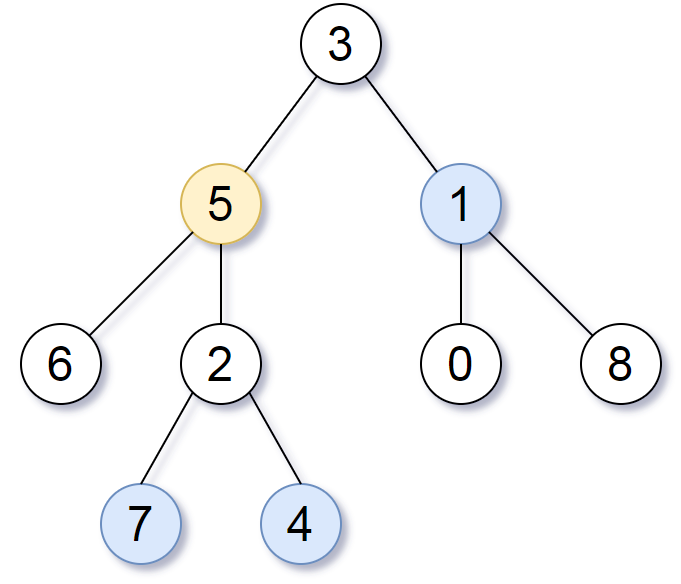 Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.