You are given a square board of characters. You can move on the board starting at the bottom right square marked with the character 'S'.
You need to reach the top left square marked with the character 'E'. The rest of the squares are labeled either with a numeric character 1, 2, ..., 9 or with an obstacle 'X'. In one move you can go up, left or up-left (diagonally) only if there is no obstacle there.
Return a list of two integers: the first integer is the maximum sum of numeric characters you can collect, and the second is the number of such paths that you can take to get that maximum sum, taken modulo 10^9 + 7.
In case there is no path, return [0, 0].
Example 1:
Input: board = ["E23","2X2","12S"] Output: [7,1]
Example 2:
Input: board = ["E12","1X1","21S"] Output: [4,2]
Example 3:
Input: board = ["E11","XXX","11S"] Output: [0,0]
Constraints:
2 <= board.length == board[i].length <= 100
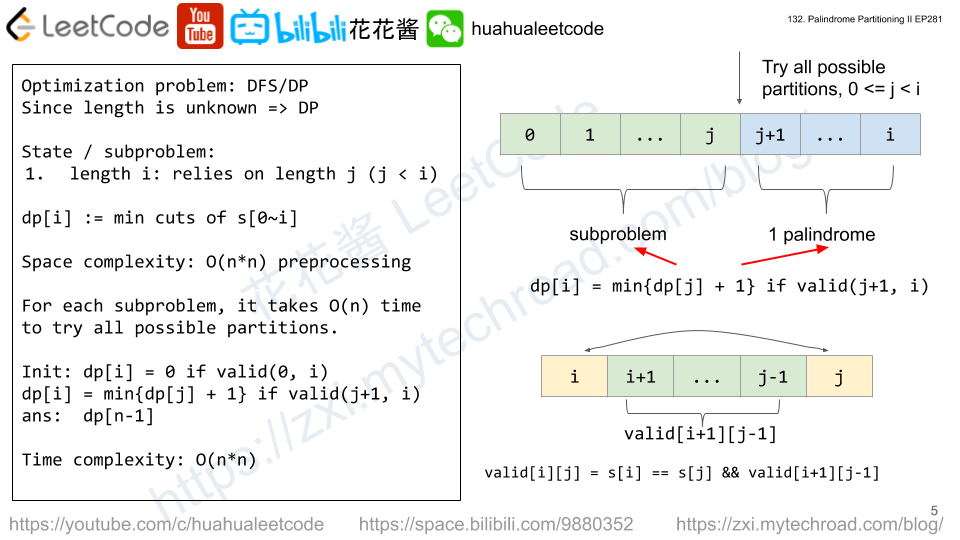
Solution: DP
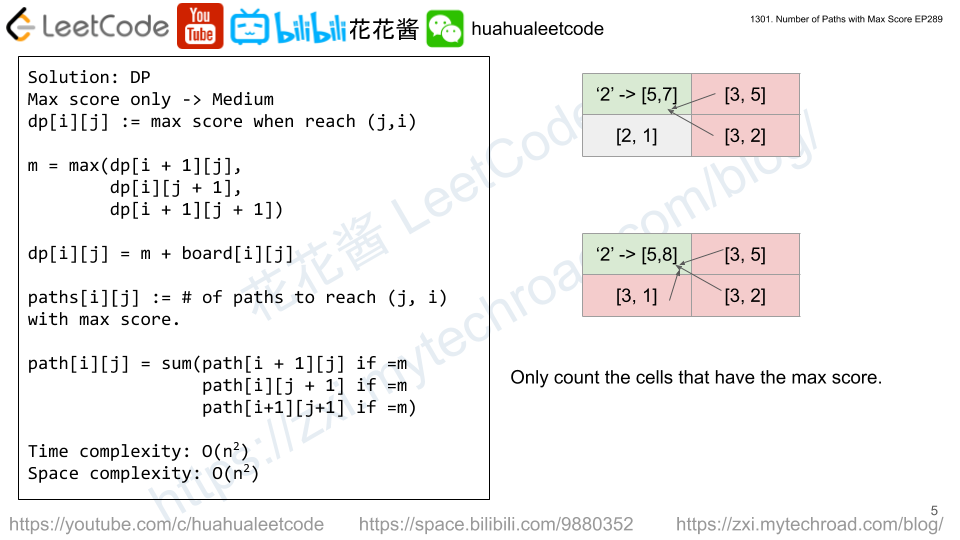
dp[i][j] := max score when reach (j, i)
count[i][j] := path to reach (j, i) with max score
m = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j+1], dp[i+1][j+1])
dp[i][j] = board[i][j] + m
count[i][j] += count[i+1][j] if dp[i+1][j] == m
count[i][j] += count[i][j+1] if dp[i][j+1] == m
count[i][j] += count[i+1][j+1] if dp[i+1][j+1] == m
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n^2)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> pathsWithMaxScore(vector<string>& board) { constexpr int kMod = 1e9 + 7; const int n = board.size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1)); vector<vector<int>> cc(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0)); board[n - 1][n - 1] = board[0][0] = '0'; cc[n - 1][n - 1] = 1; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) { if (board[i][j] != 'X') { int m = max({dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j + 1]}); dp[i][j] = (board[i][j] - '0') + m; if (dp[i + 1][j] == m) cc[i][j] = (cc[i][j] + cc[i + 1][j]) % kMod; if (dp[i][j + 1] == m) cc[i][j] = (cc[i][j] + cc[i][j + 1]) % kMod; if (dp[i + 1][j + 1] == m) cc[i][j] = (cc[i][j] + cc[i + 1][j + 1]) % kMod; } } return {cc[0][0] ? dp[0][0] : 0, cc[0][0]}; } }; |