There are n piles of coins on a table. Each pile consists of a positive number of coins of assorted denominations.
In one move, you can choose any coin on top of any pile, remove it, and add it to your wallet.
Given a list piles, where piles[i] is a list of integers denoting the composition of the ith pile from top to bottom, and a positive integer k, return the maximum total value of coins you can have in your wallet if you choose exactly k coins optimally.
Example 1:
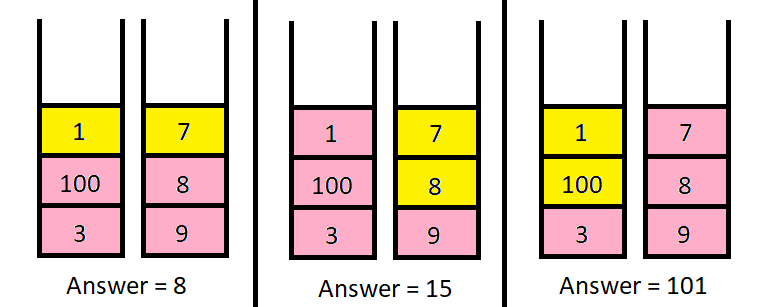
Input: piles = [[1,100,3],[7,8,9]], k = 2 Output: 101 Explanation: The above diagram shows the different ways we can choose k coins. The maximum total we can obtain is 101.
Example 2:
Input: piles = [[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[1,1,1,1,1,1,700]], k = 7 Output: 706 Explanation: The maximum total can be obtained if we choose all coins from the last pile.
Constraints:
n == piles.length1 <= n <= 10001 <= piles[i][j] <= 1051 <= k <= sum(piles[i].length) <= 2000
Solution: DP
let dp(i, k) be the maximum value of picking k elements using piles[i:n].
dp(i, k) = max(dp(i + 1, k), sum(piles[i][0~j]) + dp(i + 1, k – j – 1)), 0 <= j < len(piles[i])
Time complexity: O(n * m), m = sum(piles[i]) <= 2000
Space complexity: O(n * k)
Python
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# Author: Huahua class Solution: def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int: n = len(piles) @cache def dp(i: int, k: int) -> int: """Max value of picking k elements using piles[i:n].""" if i == n: return 0 ans, cur = dp(i + 1, k), 0 for j in range(min(len(piles[i]), k)): ans = max(ans, (cur := cur + piles[i][j]) + dp(i + 1, k - j - 1)) return ans return dp(0, k) |