Given the array queries of positive integers between 1 and m, you have to process all queries[i] (from i=0 to i=queries.length-1) according to the following rules:
- In the beginning, you have the permutation
P=[1,2,3,...,m]. - For the current
i, find the position ofqueries[i]in the permutationP(indexing from 0) and then move this at the beginning of the permutationP.Notice that the position ofqueries[i]inPis the result forqueries[i].
Return an array containing the result for the given queries.
Example 1:
Input: queries = [3,1,2,1], m = 5 Output: [2,1,2,1] Explanation: The queries are processed as follow: For i=0: queries[i]=3, P=[1,2,3,4,5], position of 3 in P is 2, then we move 3 to the beginning of P resulting in P=[3,1,2,4,5]. For i=1: queries[i]=1, P=[3,1,2,4,5], position of 1 in P is 1, then we move 1 to the beginning of P resulting in P=[1,3,2,4,5]. For i=2: queries[i]=2, P=[1,3,2,4,5], position of 2 in P is 2, then we move 2 to the beginning of P resulting in P=[2,1,3,4,5]. For i=3: queries[i]=1, P=[2,1,3,4,5], position of 1 in P is 1, then we move 1 to the beginning of P resulting in P=[1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, the array containing the result is [2,1,2,1].
Example 2:
Input: queries = [4,1,2,2], m = 4 Output: [3,1,2,0]
Example 3:
Input: queries = [7,5,5,8,3], m = 8 Output: [6,5,0,7,5]
Constraints:
1 <= m <= 10^31 <= queries.length <= m1 <= queries[i] <= m
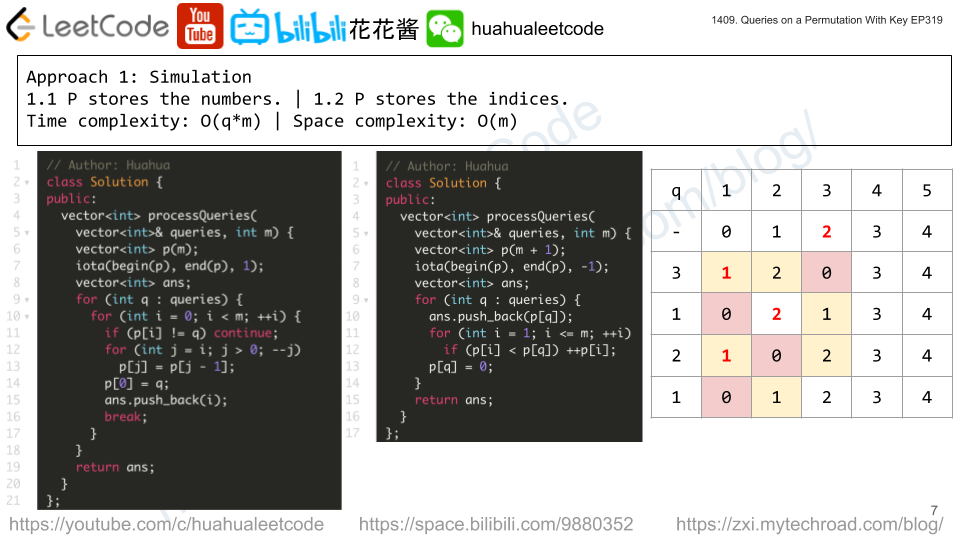
Solution1: Simulation + Hashtable
Use a hashtable to store the location of each key.
For each query q, use h[q] to get the index of q, for each key, if its current index is less than q, increase their indices by 1. (move right). Set h[q] to 0.
Time complexity: O(q*m)
Space complexity: O(m)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
class Solution { public: vector<int> processQueries(vector<int>& queries, int m) { vector<int> p(m + 1); iota(begin(p), end(p), -1); vector<int> ans; for (int q : queries) { ans.push_back(p[q]); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) if (p[i] < p[q]) ++p[i]; p[q] = 0; } return ans; } }; |
Solution 2: Fenwick Tree + HashTable
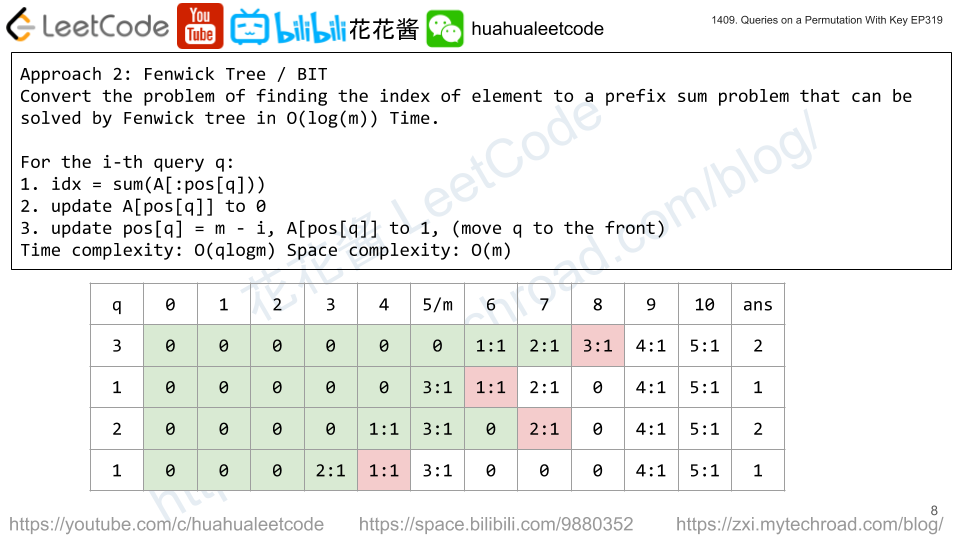
Time complexity: O(qlogm)
Space complexity: O(m)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
// Author: Huahua class Fenwick { public: explicit Fenwick(int n): vals_(n) {} // sum(A[1~i]) int query(int i) const { int s = 0; while (i > 0) { s += vals_[i]; i -= i & -i; } return s; } // A[i] += delta void update(int i, int delta) { while (i < vals_.size()) { vals_[i] += delta; i += i & -i; } } private: vector<int> vals_; }; class Solution { public: vector<int> processQueries(vector<int>& queries, int m) { Fenwick tree(m * 2 + 1); vector<int> pos(m + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) tree.update(pos[i] = i + m, 1); vector<int> ans; for (int q : queries) { ans.push_back(tree.query(pos[q] - 1)); tree.update(pos[q], -1); // set to 0. tree.update(pos[q] = m--, 1); // move to the front. } return ans; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
class Fenwick: def __init__(self, n): self.n = n self.val = [0] * n def query(self, i): s = 0 while i > 0: s += self.val[i] i -= i & -i return s def update(self, i, delta): while i < self.n: self.val[i] += delta i += i & -i class Solution: def processQueries(self, queries: List[int], m: int) -> List[int]: pos = [i + m for i in range(m + 1)] tree = Fenwick(2 * m + 1) for i in range(1, m + 1): tree.update(i + m, 1) ans = [] for q in queries: ans.append(tree.query(pos[q] - 1)) tree.update(pos[q], -1) pos[q] = m m -= 1 tree.update(pos[q], 1) return ans |