You are given an m x n matrix maze (0-indexed) with empty cells (represented as '.') and walls (represented as '+'). You are also given the entrance of the maze, where entrance = [entrancerow, entrancecol] denotes the row and column of the cell you are initially standing at.
In one step, you can move one cell up, down, left, or right. You cannot step into a cell with a wall, and you cannot step outside the maze. Your goal is to find the nearest exit from the entrance. An exit is defined as an empty cell that is at the border of the maze. The entrance does not count as an exit.
Return the number of steps in the shortest path from the entrance to the nearest exit, or -1 if no such path exists.
Example 1:
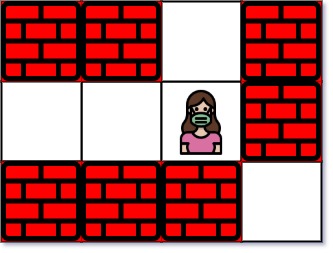
Input: maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2] Output: 1 Explanation: There are 3 exits in this maze at [1,0], [0,2], and [2,3]. Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,2]. - You can reach [1,0] by moving 2 steps left. - You can reach [0,2] by moving 1 step up. It is impossible to reach [2,3] from the entrance. Thus, the nearest exit is [0,2], which is 1 step away.
Example 2:
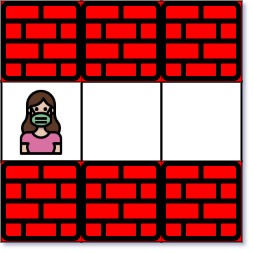
Input: maze = [["+","+","+"],[".",".","."],["+","+","+"]], entrance = [1,0] Output: 2 Explanation: There is 1 exit in this maze at [1,2]. [1,0] does not count as an exit since it is the entrance cell. Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,0]. - You can reach [1,2] by moving 2 steps right. Thus, the nearest exit is [1,2], which is 2 steps away.
Example 3:

Input: maze = [[".","+"]], entrance = [0,0] Output: -1 Explanation: There are no exits in this maze.
Constraints:
maze.length == mmaze[i].length == n1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is either'.'or'+'.entrance.length == 20 <= entrancerow < m0 <= entrancecol < nentrancewill always be an empty cell.
Solution: BFS
Use BFS to find the shortest path. We can re-use the board for visited array.
Time complexity: O(m*n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) { const int m = maze.size(); const int n = maze[0].size(); const vector<int> dirs{0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.emplace(entrance[1], entrance[0]); for (int steps = 0; !q.empty(); ++steps) { for (int s = q.size(); s; --s) { const auto [x, y] = q.front(); q.pop(); if (x == 0 || x == n - 1 || y == 0 || y == m - 1) if (x != entrance[1] || y != entrance[0]) return steps; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { const int tx = x + dirs[i]; const int ty = y + dirs[i + 1]; if (tx < 0 || tx >= n || ty < 0 || ty >= m || maze[ty][tx] != '.') continue; maze[ty][tx] = '*'; q.emplace(tx, ty); } } } return -1; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment