Problem
Given an array which consists of non-negative integers and an integer m, you can split the array into m non-empty continuous subarrays. Write an algorithm to minimize the largest sum among these m subarrays.
Note:
If n is the length of array, assume the following constraints are satisfied:
- 1 ≤ n ≤ 1000
- 1 ≤ m ≤ min(50, n)
Examples:
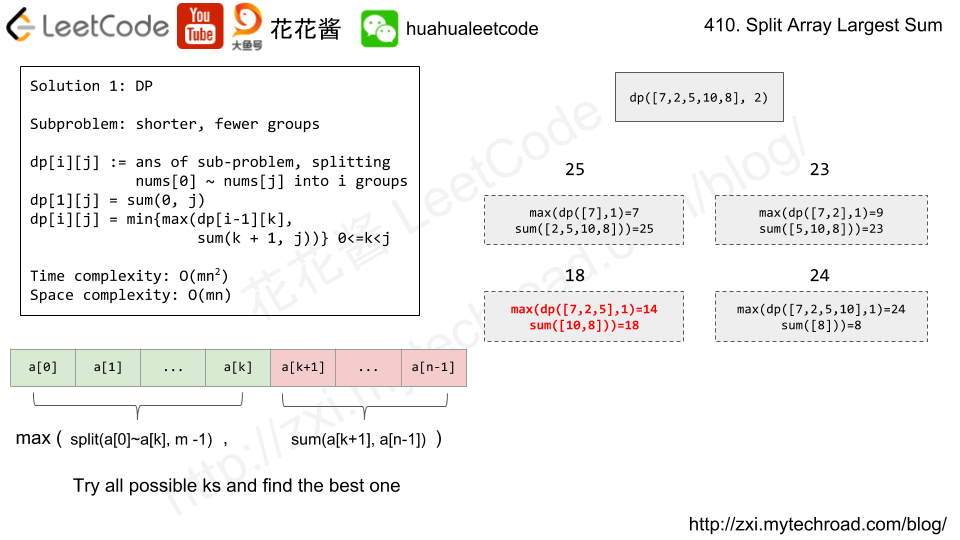
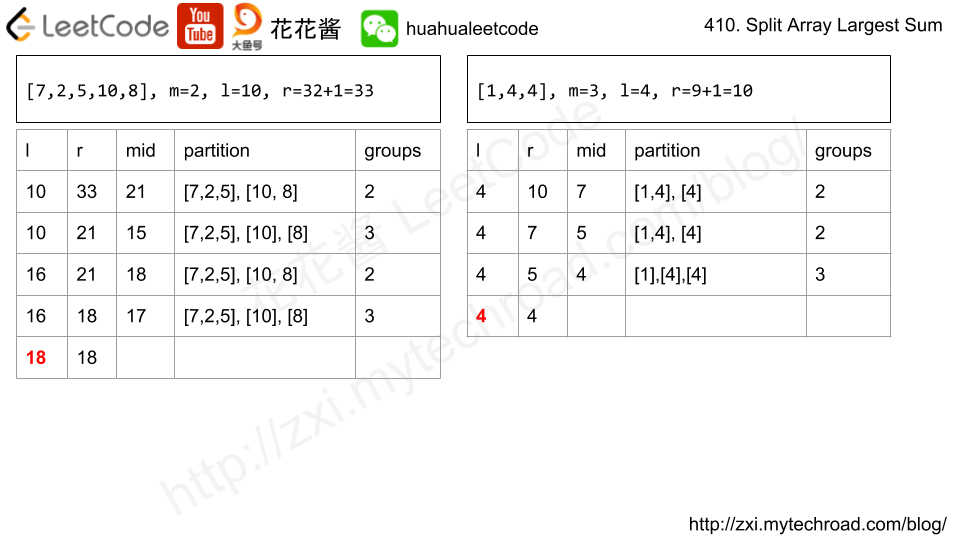
Input: nums = [7,2,5,10,8] m = 2 Output: 18 Explanation: There are four ways to split nums into two subarrays. The best way is to split it into [7,2,5] and [10,8], where the largest sum among the two subarrays is only 18.
Solution: DP
Time complexity: O(n^2*m)
Space complexity: O(n*m)
C++ / Recursion + Memorization
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 111 ms class Solution { public: int splitArray(vector<int>& nums, int m) { const int n = nums.size(); sums_ = vector<int>(n); mem_ = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(m + 1, INT_MAX)); sums_[0] = nums[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) sums_[i] = sums_[i - 1] + nums[i]; return splitArray(nums, n - 1, m); } private: vector<vector<int>> mem_; vector<int> sums_; // min of largest sum of spliting nums[0] ~ nums[k] into m groups int splitArray(const vector<int>& nums, int k, int m) { if (m == 1) return sums_[k]; if (m > k + 1) return INT_MAX; if (mem_[k][m] != INT_MAX) return mem_[k][m]; int ans = INT_MAX; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) ans = min(ans, max(splitArray(nums, i, m - 1), sums_[k] - sums_[i])); return mem_[k][m] = ans; } }; |
C++ / DP
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 90 ms class Solution { public: int splitArray(vector<int>& nums, int m) { const int n = nums.size(); vector<int> sums(n); // dp[i][j] := min of largest sum of splitting nums[0] ~ nums[j] into i groups. vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX)); sums[0] = nums[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + nums[i]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) dp[1][i] = sums[i]; for (int i = 2; i <= m; ++i) for (int j = i - 1; j < n; ++j) for (int k = 0; k < j; ++k) dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], max(dp[i - 1][k], sums[j] - sums[k])); return dp[m][n - 1]; } }; |
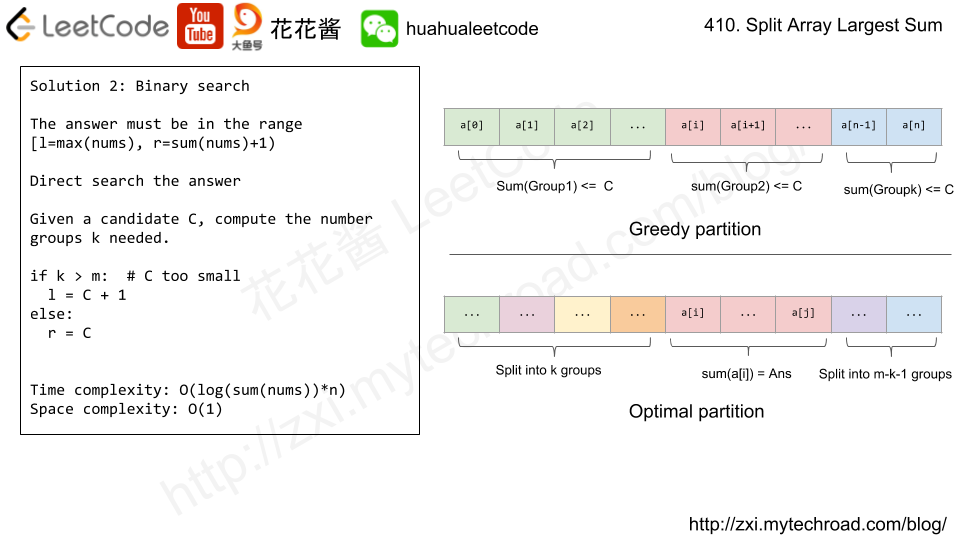
Solution: Binary Search
Time complexity: O(log(sum(nums))*n)
Space complexity: O(1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 3 ms class Solution { public: int splitArray(vector<int>& nums, int m) { long l = *max_element(begin(nums), end(nums)); long r = accumulate(begin(nums), end(nums), 0L) + 1; while (l < r) { long limit = (r - l) / 2 + l; if (min_groups(nums, limit) > m) l = limit + 1; else r = limit; } return l; } private: int min_groups(const vector<int>& nums, long limit) { long sum = 0; int groups = 1; for (int num : nums) { if (sum + num > limit) { sum = num; ++groups; } else { sum += num; } } return groups; } }; |