Given a string s. An awesome substring is a non-empty substring of s such that we can make any number of swaps in order to make it palindrome.
Return the length of the maximum length awesome substring of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "3242415" Output: 5 Explanation: "24241" is the longest awesome substring, we can form the palindrome "24142" with some swaps.
Example 2:
Input: s = "12345678" Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: s = "213123" Output: 6 Explanation: "213123" is the longest awesome substring, we can form the palindrome "231132" with some swaps.
Example 4:
Input: s = "00" Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 10^5sconsists only of digits.
Solution: Prefix mask + Hashtable
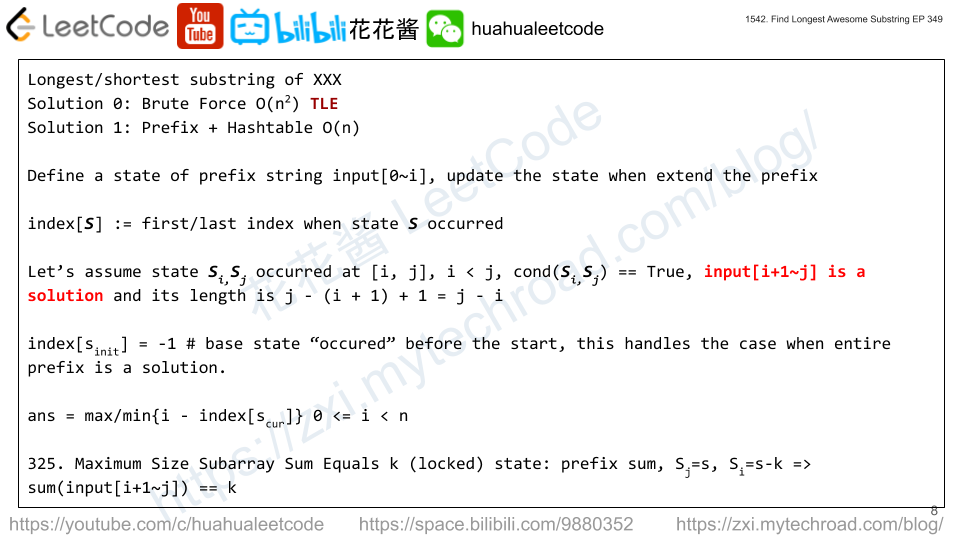
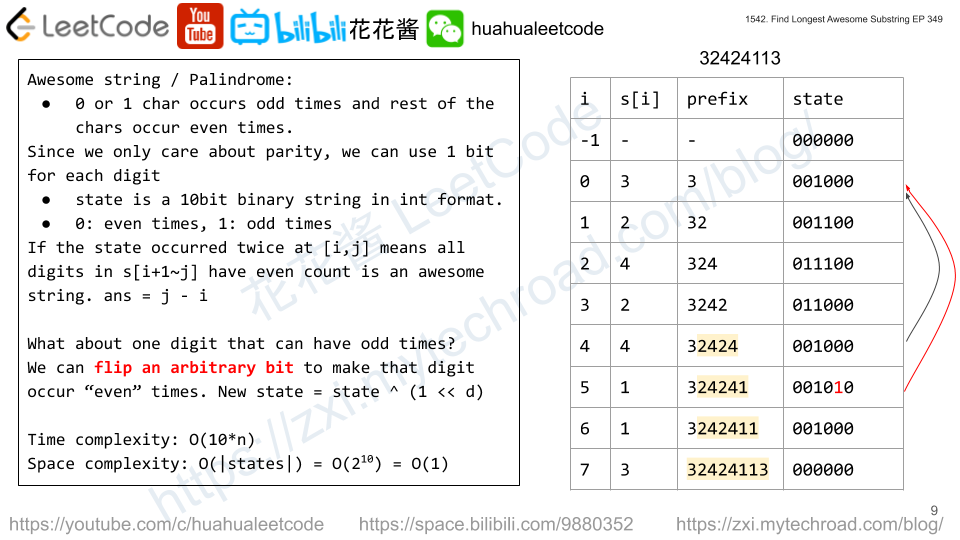
For a palindrome all digits must occurred even times expect one. We can use a 10 bit mask to track the occurrence of each digit for prefix s[0~i]. 0 is even, 1 is odd.
We use a hashtable to track the first index of each prefix state.
If s[0~i] and s[0~j] have the same state which means every digits in s[i+1~j] occurred even times (zero is also even) and it’s an awesome string. Then (j – (i+1) + 1) = j – i is the length of the palindrome. So far so good.
But we still need to consider the case when there is a digit with odd occurrence. We can enumerate all possible ones from 0 to 9, and temporarily flip the bit of the digit and see whether that state happened before.
fisrt_index[0] = -1, first_index[*] = inf
ans = max(ans, j – first_index[mask])
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(2^10) = O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
class Solution { public: int longestAwesome(string s) { constexpr int kInf = 1e9; vector<int> idx(1024, kInf); idx[0] = -1; int mask = 0; // prefix's state 0:even, 1:odd int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) { mask ^= (1 << (s[i] - '0')); ans = max(ans, i - idx[mask]); // One digit with odd count is allowed. for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) ans = max(ans, i - idx[mask ^ (1 << j)]); idx[mask] = min(idx[mask], i); } return ans; } }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public int longestAwesome(String s) { final int n = s.length(); int[] idx = new int[1024]; Arrays.fill(idx, n); idx[0] = -1; int mask = 0; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { mask ^= (1 << (s.charAt(i) - '0')); ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[mask]); for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[mask ^ (1 << j)]); idx[mask] = Math.min(idx[mask], i); } return ans; } } |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# Author: Huahua class Solution: def longestAwesome(self, s: str) -> int: idx = [-1] + [len(s)] * 1023 ans, mask = 0, 0 for i, c in enumerate(s): mask ^= 1 << (ord(c) - ord('0')) ans = max([ans, i - idx[mask]] + [i - idx[mask ^ (1 << j)] for j in range(10)]) idx[mask] = min(idx[mask], i) return ans |