You are given the root of a binary tree and an integer k.
Return an integer denoting the size of the kth largest perfect binary
subtree, or -1 if it doesn’t exist.
A perfect binary tree is a tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children.
Example 1:
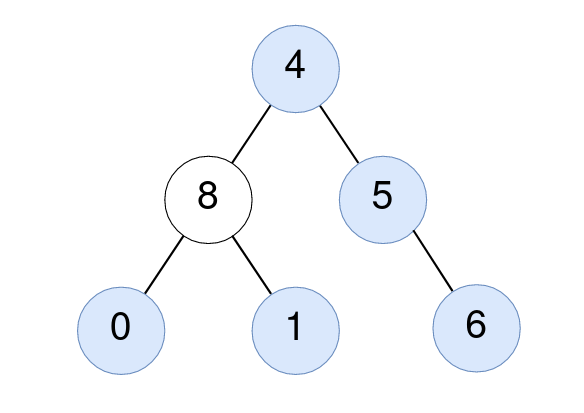
Input: root = [5,3,6,5,2,5,7,1,8,null,null,6,8], k = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
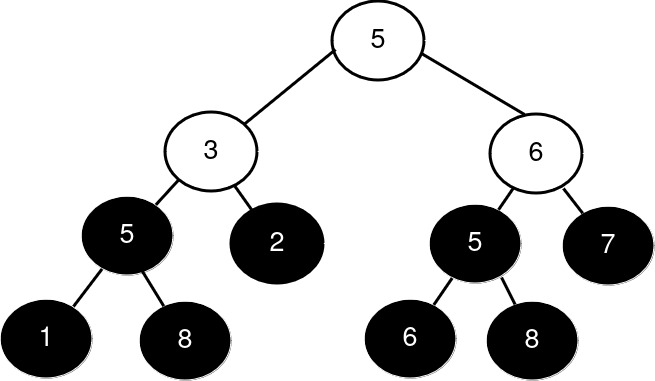
The roots of the perfect binary subtrees are highlighted in black. Their sizes, in decreasing order are [3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1].
The 2nd largest size is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 1
Output: 7
Explanation:
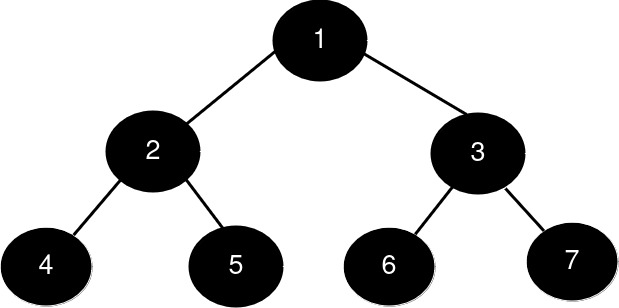
The sizes of the perfect binary subtrees in decreasing order are [7, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1]. The size of the largest perfect binary subtree is 7.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], k = 3
Output: -1
Explanation:
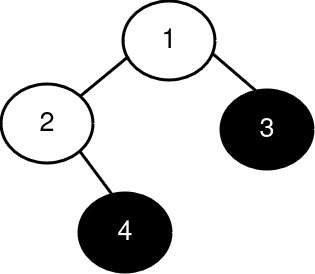
The sizes of the perfect binary subtrees in decreasing order are [1, 1]. There are fewer than 3 perfect binary subtrees.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 2000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 20001 <= k <= 1024
Solution: DFS
Write a function f() to return the perfect subtree size at node n.
def f(TreeNode n):
if not n: return 0
l, r = f(n.left), f(n.right)
return l + r + 1 if l == r && l != -1 else -1
Time complexity: O(n + KlogK)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
class Solution { public: int kthLargestPerfectSubtree(TreeNode* root, int k) { vector<int> ss; function<int(TreeNode*)> PerfectSubtree = [&](TreeNode* node) -> int { if (node == nullptr) return 0; int l = PerfectSubtree(node->left); int r = PerfectSubtree(node->right); if (l == r && l != -1) { ss.push_back(l + r + 1); return ss.back(); } return -1; }; PerfectSubtree(root); sort(rbegin(ss), rend(ss)); return k <= ss.size() ? ss[k - 1] : -1; } }; |