Alice and Bob take turns playing a game, with Alice starting first.
There are n stones arranged in a row. On each player’s turn, while the number of stones is more than one, they will do the following:
- Choose an integer
x > 1, and remove the leftmostxstones from the row. - Add the sum of the removed stones’ values to the player’s score.
- Place a new stone, whose value is equal to that sum, on the left side of the row.
The game stops when only one stone is left in the row.
The score difference between Alice and Bob is (Alice's score - Bob's score). Alice’s goal is to maximize the score difference, and Bob’s goal is the minimize the score difference.
Given an integer array stones of length n where stones[i] represents the value of the ith stone from the left, return the score difference between Alice and Bob if they both play optimally.
Example 1:
Input: stones = [-1,2,-3,4,-5] Output: 5 Explanation: - Alice removes the first 4 stones, adds (-1) + 2 + (-3) + 4 = 2 to her score, and places a stone of value 2 on the left. stones = [2,-5]. - Bob removes the first 2 stones, adds 2 + (-5) = -3 to his score, and places a stone of value -3 on the left. stones = [-3]. The difference between their scores is 2 - (-3) = 5.
Example 2:
Input: stones = [7,-6,5,10,5,-2,-6] Output: 13 Explanation: - Alice removes all stones, adds 7 + (-6) + 5 + 10 + 5 + (-2) + (-6) = 13 to her score, and places a stone of value 13 on the left. stones = [13]. The difference between their scores is 13 - 0 = 13.
Example 3:
Input: stones = [-10,-12] Output: -22 Explanation: - Alice can only make one move, which is to remove both stones. She adds (-10) + (-12) = -22 to her score and places a stone of value -22 on the left. stones = [-22]. The difference between their scores is (-22) - 0 = -22.
Constraints:
n == stones.length2 <= n <= 105-104 <= stones[i] <= 104
Solution: Prefix Sum + DP
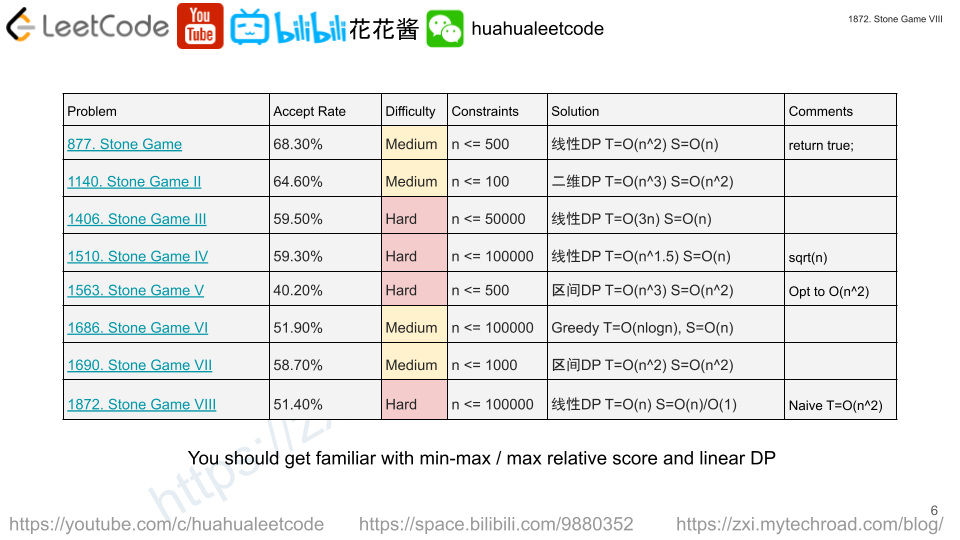



Note: Naive DP (min-max) takes O(n2) which leads to TLE. The key of this problem is that each player takes k stones, but put their sum back as a new stone, so you can assume all the original stones are still there, but opponent has to start from the k+1 th stone.
Let dp[i] denote the max score diff that current player can achieve by taking stones[0~i] (or equivalent)
dp[n-1] = sum(A[0~n-1]) // Alice takes all the stones.
dp[n-2] = sum(A[0~n-2]) – (A[n-1] + sum(A[0~n-2])) = sum(A[0~n-2]) – dp[n-1] // Alice takes n-1 stones, Bob take the last one (A[n-1]) + put-back-stone.
dp[n-3] = sum(A[0~n-3]) – max(dp[n-2], dp[n-1]) // Alice takes n-2 stones, Bob has two options (takes n-1 stones or takes n stones)
…
dp[0] = A[0] – max(dp[n-1], dp[n-1], …, dp[1]) // Alice takes the first stone, Bob has n-1 options.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int stoneGameVIII(vector<int>& stones) { const int n = stones.size(); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) stones[i] += stones[i - 1]; int ans = stones.back(); // take all the stones. for (int i = n - 2; i > 0; --i) ans = max(ans, stones[i] - ans); return ans; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment