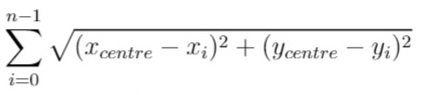Given an integer n, return the decimal value of the binary string formed by concatenating the binary representations of 1 to n in order, modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: "1" in binary corresponds to the decimal value 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3 Output: 27 Explanation: In binary, 1, 2, and 3 corresponds to "1", "10", and "11". After concatenating them, we have "11011", which corresponds to the decimal value 27.
Example 3:
Input: n = 12 Output: 505379714 Explanation: The concatenation results in "1101110010111011110001001101010111100". The decimal value of that is 118505380540. After modulo 109 + 7, the result is 505379714.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105
Solution: Bit Operation
f(n) = (f(n – 1) << length(n)) | n
length(n) increase by 1 whenever n is power of 2.
n = 1, YES, len = 1
n = 2, YES, len = 2
n = 3, NO, len = 2
n = 4, YES, len = 3
n = 5, NO, len = 3
n = 6, NO, len = 3
n = 7, NO, len = 3
n = 8, YES, len = 4
…
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int concatenatedBinary(int n) { constexpr int kMod = 1e9 + 7; long ans = 0; for (int i = 1, len = 0; i <= n; ++i) { if ((i & (i - 1)) == 0) ++len; ans = ((ans << len) % kMod + i) % kMod; } return ans; } }; |