January 12, 2026
You are given an array nums consisting of non-negative integers. You are also given a queries array, where queries[i] = [xi, mi].
The answer to the ith query is the maximum bitwise XOR value of xi and any element of nums that does not exceed mi. In other words, the answer is max(nums[j] XOR xi) for all j such that nums[j] <= mi. If all elements in nums are larger than mi, then the answer is -1.
Return an integer array answer where answer.length == queries.length and answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,1,2,3,4], queries = [[3,1],[1,3],[5,6]] Output: [3,3,7] Explanation: 1) 0 and 1 are the only two integers not greater than 1. 0 XOR 3 = 3 and 1 XOR 3 = 2. The larger of the two is 3. 2) 1 XOR 2 = 3. 3) 5 XOR 2 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,2,4,6,6,3], queries = [[12,4],[8,1],[6,3]] Output: [15,-1,5]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length, queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 20 <= nums[j], xi, mi <= 109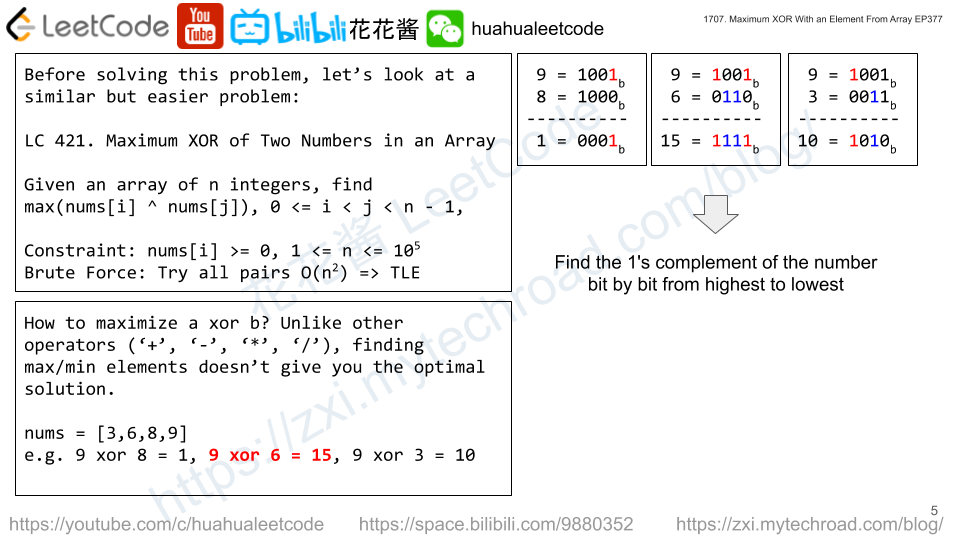
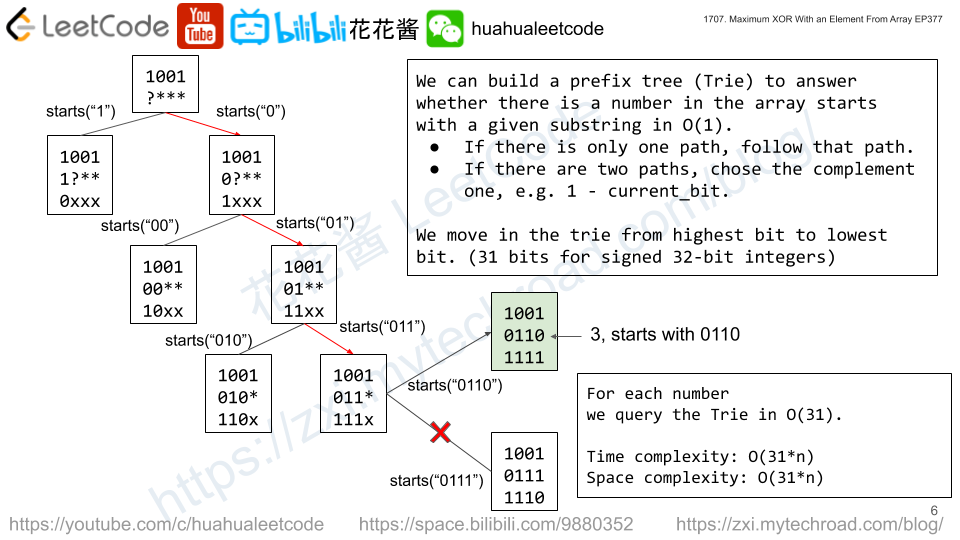
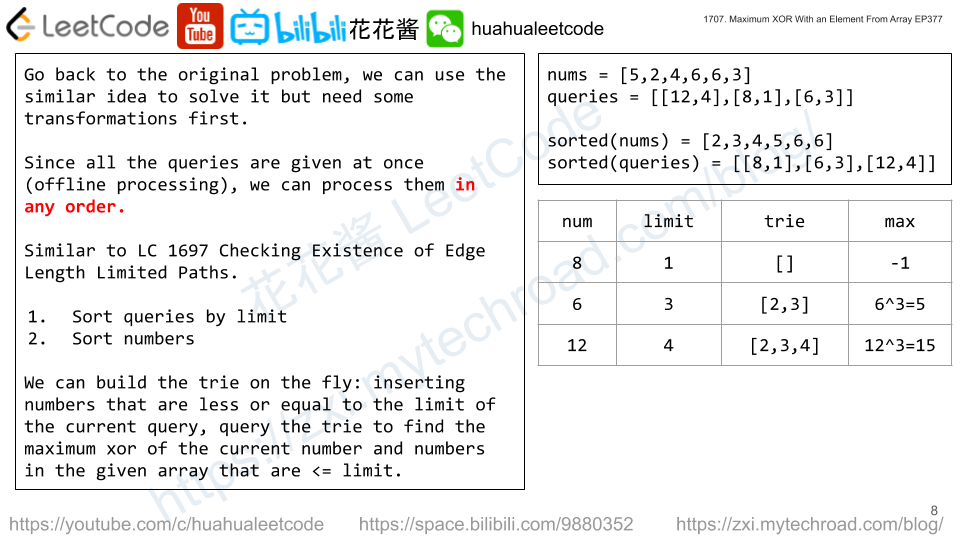
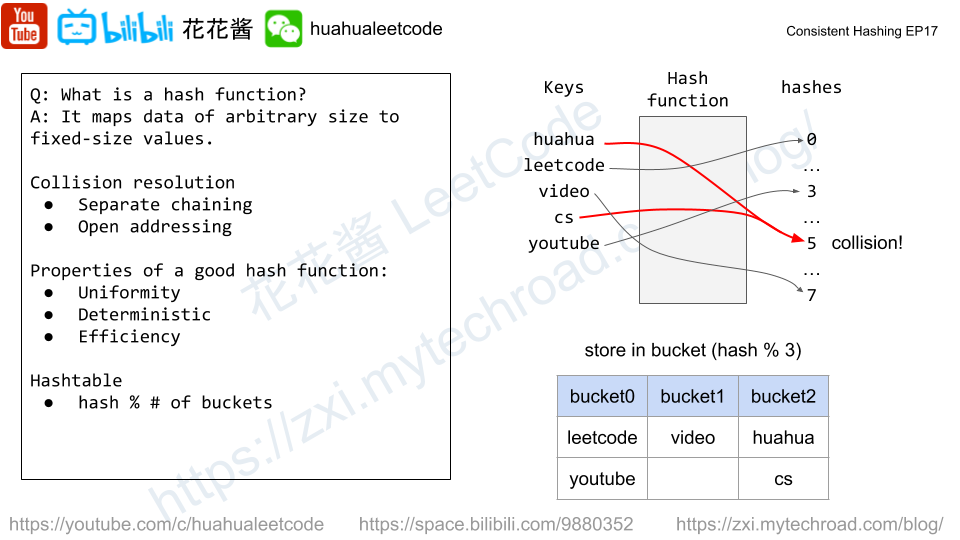
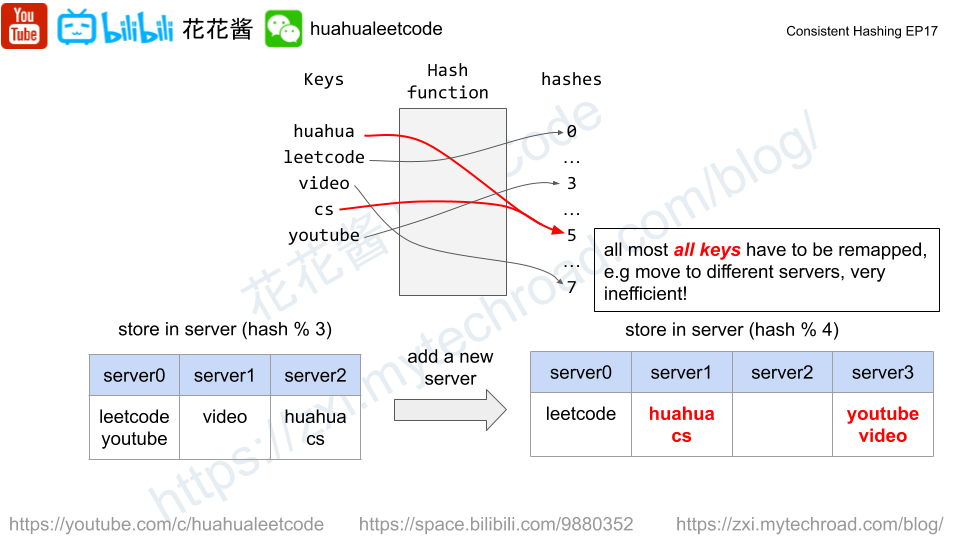
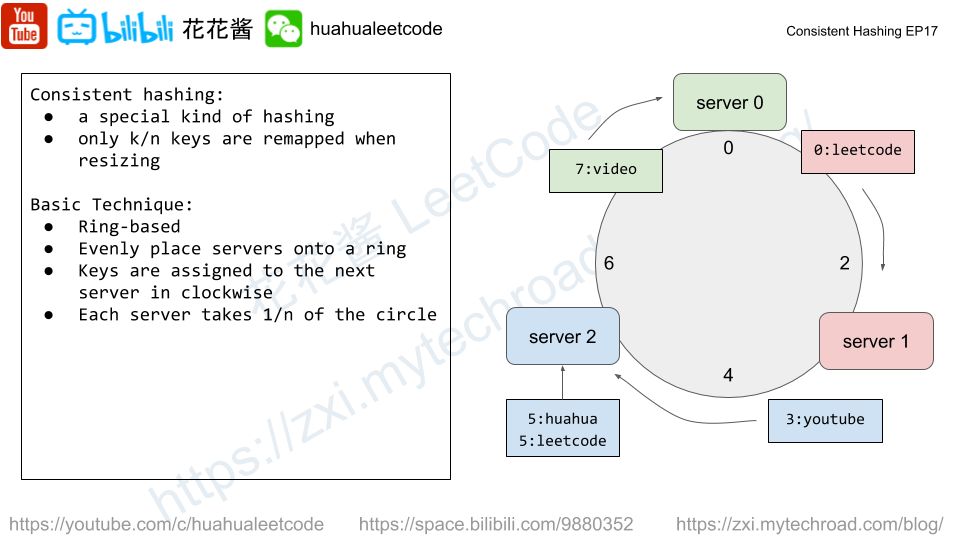
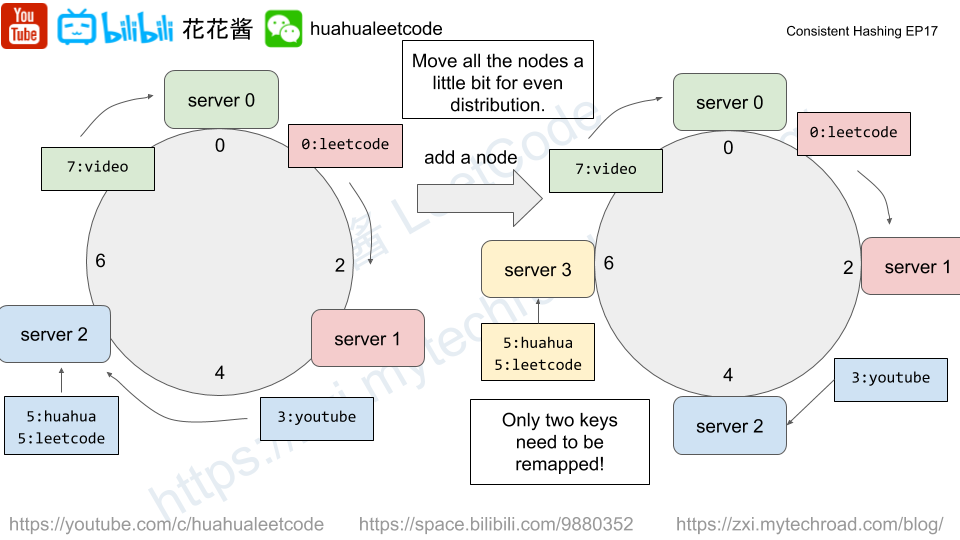
Similar idea to https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/trie/leetcode-421-maximum-xor-of-two-numbers-in-an-array/
We can build the trie on the fly by sorting nums in ascending order and queries by its limit, insert nums into the trie up the limit.
Time complexity: O(nlogn + QlogQ)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
// Author: Huahua class Trie { public: Trie(): children{nullptr, nullptr} {} Trie* children[2]; }; class Solution { public: vector<int> maximizeXor(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { const int n = nums.size(); sort(begin(nums), end(nums)); const int Q = queries.size(); for (int i = 0; i < Q; ++i) queries[i].push_back(i); sort(begin(queries), end(queries), [](const auto& q1, const auto& q2) { return q1[1] < q2[1]; }); Trie root; auto insert = [&](int num) { Trie* node = &root; for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (!node->children[bit]) node->children[bit] = new Trie(); node = node->children[bit]; } }; auto query = [&](int num) { Trie* node = &root; int sum = 0; for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { if (!node) return -1; int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (node->children[1 - bit]) { sum |= (1 << i); node = node->children[1 - bit]; } else { node = node->children[bit]; } } return sum; }; vector<int> ans(Q); int i = 0; for (const auto& q : queries) { while (i < n && nums[i] <= q[1]) insert(nums[i++]); ans[q[2]] = query(q[0]); } return ans; } }; |
Given an integer array nums, return the maximum result of nums[i] XOR nums[j], where 0 ≤ i ≤ j < n.
Follow up: Could you do this in O(n) runtime?
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8] Output: 28 Explanation: The maximum result is 5 XOR 25 = 28.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0] Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,4] Output: 6
Example 4:
Input: nums = [8,10,2] Output: 10
Example 5:
Input: nums = [14,70,53,83,49,91,36,80,92,51,66,70] Output: 127
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1040 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1Time complexity: O(31*2*n)
Space complexity: O(31*2*n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 |
// Author: Huahua class Trie { public: Trie(): children(2) {} vector<unique_ptr<Trie>> children; }; class Solution { public: int findMaximumXOR(vector<int>& nums) { Trie root; // Insert a number into the trie. auto insert = [&](Trie* node, int num) { for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (!node->children[bit]) node->children[bit] = std::make_unique<Trie>(); node = node->children[bit].get(); } }; // Find max xor sum of num and another element in the array. auto query = [&](Trie* node, int num) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (node->children[1 - bit]) { sum += (1 << i); node = node->children[1 - bit].get(); } else { node = node->children[bit].get(); } } return sum; }; // Insert all numbers. for (int x : nums) insert(&root, x); int ans = 0; // For each number find the maximum xor sum. for (int x : nums) ans = max(ans, query(&root, x)); return ans; } }; |
You have a 2-D grid of size m x n representing a box, and you have n balls. The box is open on the top and bottom sides.
Each cell in the box has a diagonal board spanning two corners of the cell that can redirect a ball to the right or to the left.
1.-1.We drop one ball at the top of each column of the box. Each ball can get stuck in the box or fall out of the bottom. A ball gets stuck if it hits a “V” shaped pattern between two boards or if a board redirects the ball into either wall of the box.
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the column that the ball falls out of at the bottom after dropping the ball from the ith column at the top, or -1 if the ball gets stuck in the box.
Example 1:
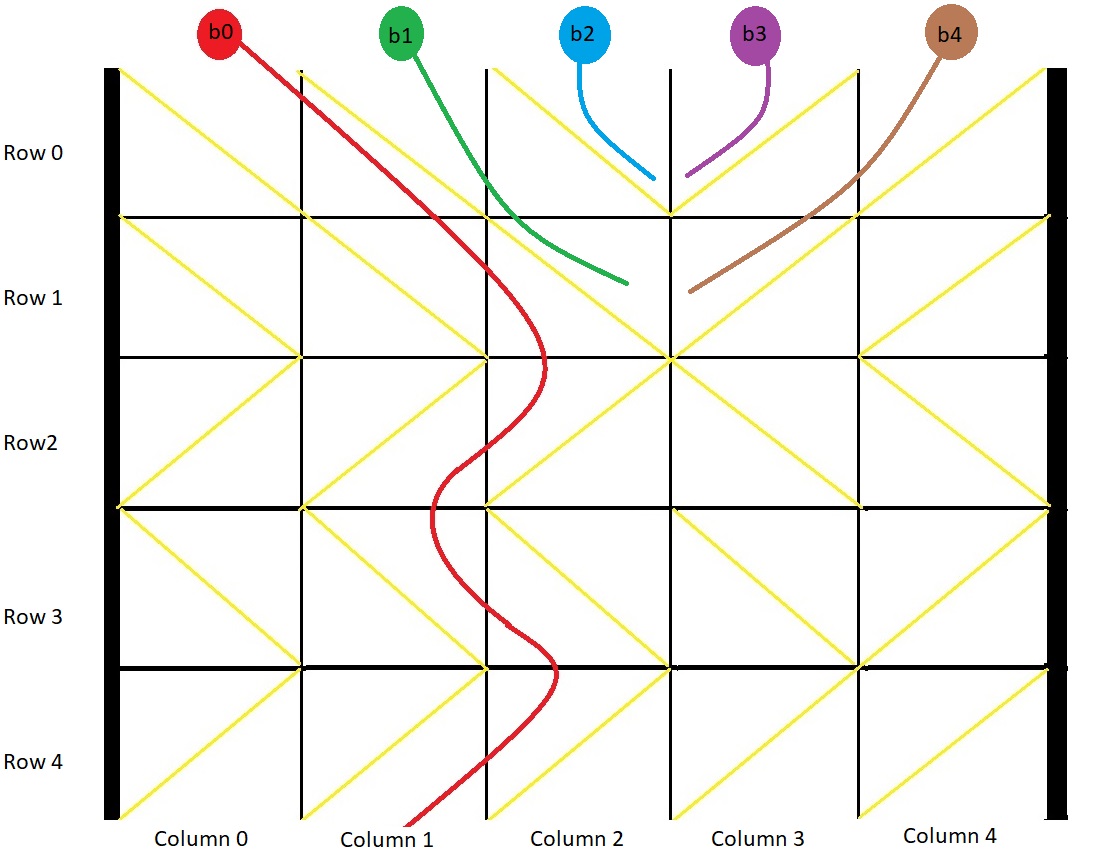
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,-1,-1],[1,1,1,-1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]] Output: [1,-1,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: This example is shown in the photo. Ball b0 is dropped at column 0 and falls out of the box at column 1. Ball b1 is dropped at column 1 and will get stuck in the box between column 2 and 3 and row 1. Ball b2 is dropped at column 2 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 0. Ball b3 is dropped at column 3 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 0. Ball b4 is dropped at column 4 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 1.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[-1]] Output: [-1] Explanation: The ball gets stuck against the left wall.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100grid[i][j] is 1 or -1.Figure out 4 conditions that the ball will get stuck.
Time complexity: O(m*n)
Space complexity: O(1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> findBall(vector<vector<int>>& G) { const int m = G.size(); const int n = G[0].size(); auto fall = [&](int x) -> int { for (int y = 0; y < m; ++y) if ((G[y][x] == -1 && (x == 0 || G[y][x - 1] == 1)) || (G[y][x] == 1 && (x == n - 1 || G[y][x + 1] == -1))) return -1; else x += G[y][x]; return x; }; vector<int> ans(n); for (int x = 0; x < n; ++x) ans[x] = fall(x); return ans; } }; |
There is a special kind of apple tree that grows apples every day for n days. On the ith day, the tree grows apples[i] apples that will rot after days[i] days, that is on day i + days[i] the apples will be rotten and cannot be eaten. On some days, the apple tree does not grow any apples, which are denoted by apples[i] == 0 and days[i] == 0.
You decided to eat at most one apple a day (to keep the doctors away). Note that you can keep eating after the first n days.
Given two integer arrays days and apples of length n, return the maximum number of apples you can eat.
Example 1:
Input: apples = [1,2,3,5,2], days = [3,2,1,4,2] Output: 7 Explanation: You can eat 7 apples: - On the first day, you eat an apple that grew on the first day. - On the second day, you eat an apple that grew on the second day. - On the third day, you eat an apple that grew on the second day. After this day, the apples that grew on the third day rot. - On the fourth to the seventh days, you eat apples that grew on the fourth day.
Example 2:
Input: apples = [3,0,0,0,0,2], days = [3,0,0,0,0,2] Output: 5 Explanation: You can eat 5 apples: - On the first to the third day you eat apples that grew on the first day. - Do nothing on the fouth and fifth days. - On the sixth and seventh days you eat apples that grew on the sixth day.
Constraints:
apples.length == ndays.length == n1 <= n <= 2 * 1040 <= apples[i], days[i] <= 2 * 104days[i] = 0 if and only if apples[i] = 0.Sort by rotten day in ascending order, only push onto the queue when that day has come (be able to grow apples).
Time complexity: O((n+ d)logn)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int eatenApples(vector<int>& apples, vector<int>& days) { const int n = apples.size(); using P = pair<int, int>; priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> q; // {rotten_day, index} int ans = 0; for (int d = 0; d < n || !q.empty(); ++d) { if (d < n && apples[d]) q.emplace(d + days[d], d); while (!q.empty() && (q.top().first <= d || apples[q.top().second] == 0)) q.pop(); if (q.empty()) continue; --apples[q.top().second]; ++ans; } return ans; } }; |