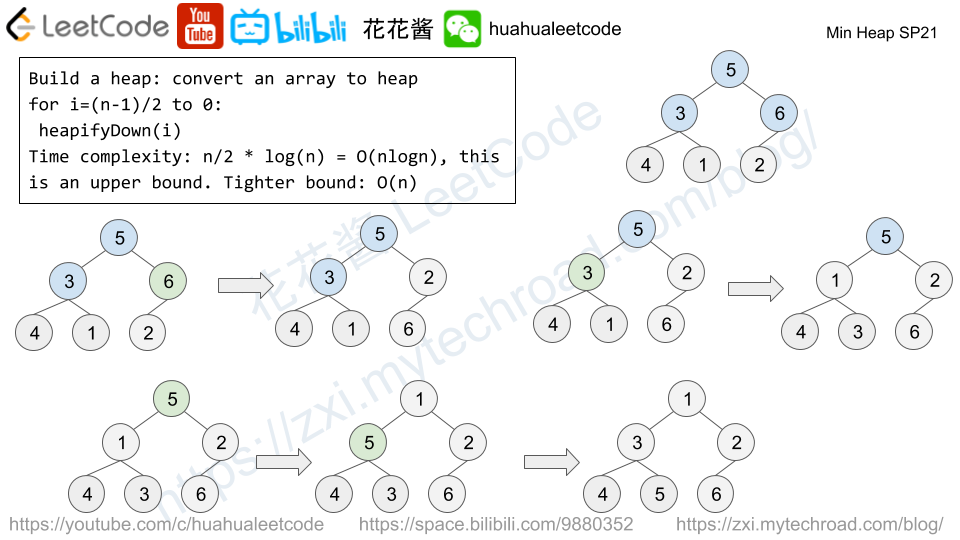
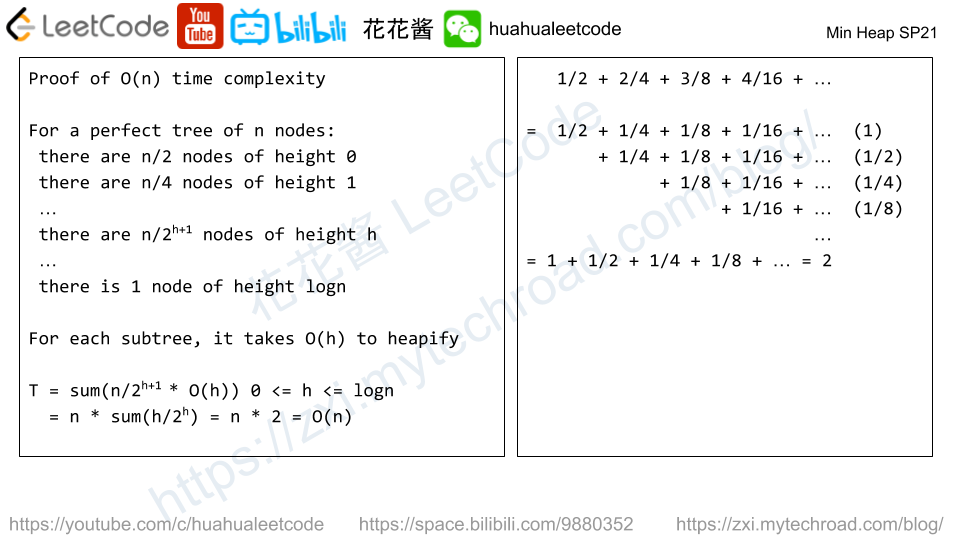
You are given an integer array nums. You can choose exactly one index (0-indexed) and remove the element. Notice that the index of the elements may change after the removal.
For example, if nums = [6,1,7,4,1]:
- Choosing to remove index
1results innums = [6,7,4,1]. - Choosing to remove index
2results innums = [6,1,4,1]. - Choosing to remove index
4results innums = [6,1,7,4].
An array is fair if the sum of the odd-indexed values equals the sum of the even-indexed values.
Return the number of indices that you could choose such that after the removal, numsis fair.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,1,6,4] Output: 1 Explanation: Remove index 0: [1,6,4] -> Even sum: 1 + 4 = 5. Odd sum: 6. Not fair. Remove index 1: [2,6,4] -> Even sum: 2 + 4 = 6. Odd sum: 6. Fair. Remove index 2: [2,1,4] -> Even sum: 2 + 4 = 6. Odd sum: 1. Not fair. Remove index 3: [2,1,6] -> Even sum: 2 + 6 = 8. Odd sum: 1. Not fair. There is 1 index that you can remove to make nums fair.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1] Output: 3 Explanation: You can remove any index and the remaining array is fair.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: 0 Explanation: You cannot make a fair array after removing any index.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 104
Solution: Prefix Sum
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int waysToMakeFair(vector<int>& nums) { int n = nums.size(); vector<int> odds(n + 1); vector<int> evens(n + 1); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { odds[i + 1] = odds[i] + (i % 2 == 1) * nums[i]; evens[i + 1] = evens[i] + (i % 2 == 0) * nums[i]; } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { const int odd = odds[i] + (evens[n] - evens[i + 1]); const int even = evens[i] + (odds[n] - odds[i + 1]); ans += odd == even; } return ans; } }; |