We have a list of points on the plane. Find the K closest points to the origin (0, 0).
(Here, the distance between two points on a plane is the Euclidean distance.)
You may return the answer in any order. The answer is guaranteed to be unique (except for the order that it is in.)
Example 1:
Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], K = 1
Output: [[-2,2]]
Explanation: The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest K = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], K = 2
Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]] (The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.)
Note:
1 <= K <= points.length <= 10000-10000 < points[i][0] < 10000-10000 < points[i][1] < 10000
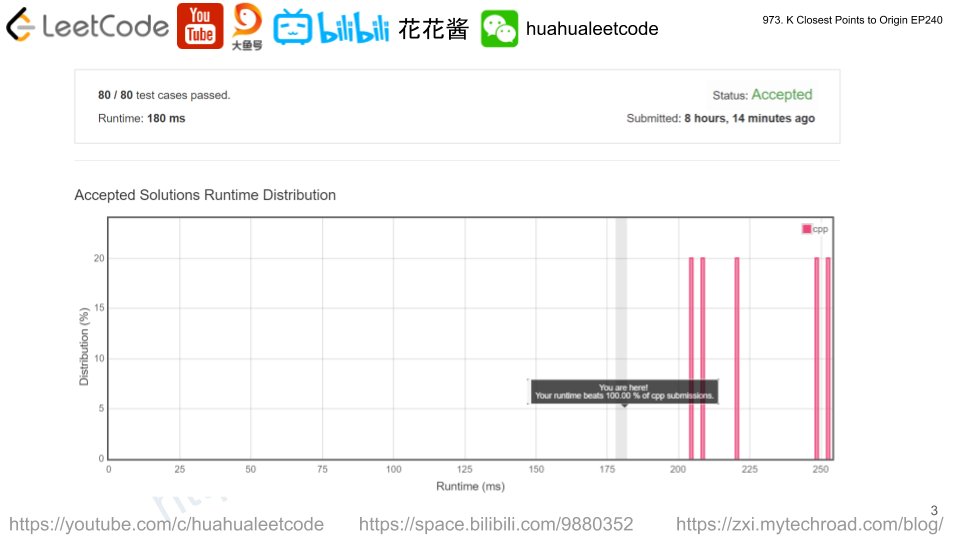
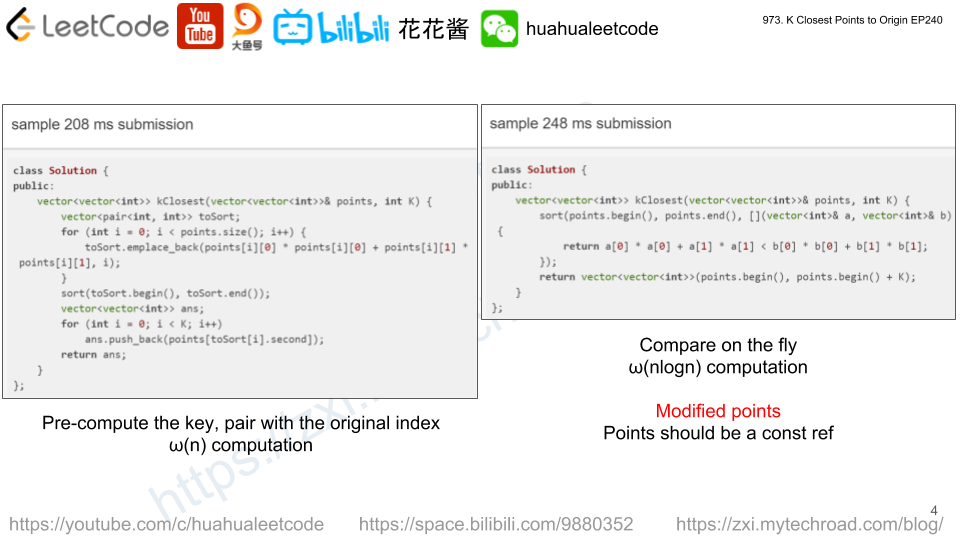
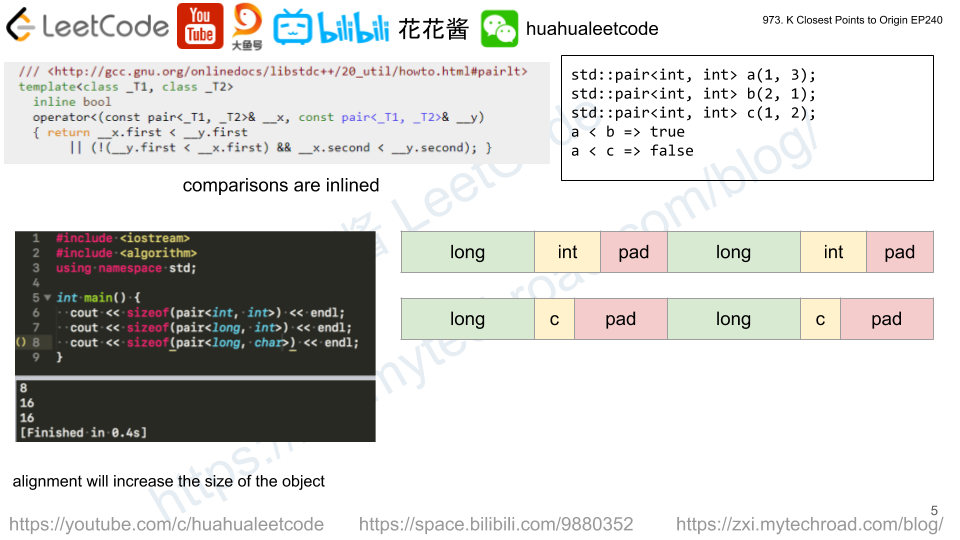
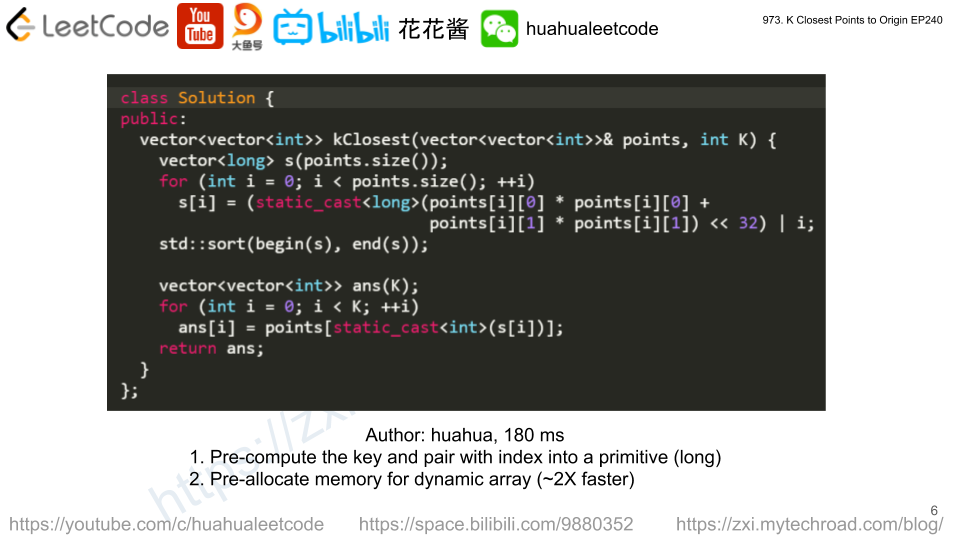
Solution: Sort
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// Author: Huahua, Running time: 180 ms class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int K) { vector<long> s(points.size()); for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) s[i] = (static_cast<long>(points[i][0] * points[i][0] + points[i][1] * points[i][1]) << 32) | i; std::sort(begin(s), end(s)); vector<vector<int>> ans(K); for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) ans[i] = points[static_cast<int>(s[i])]; return ans; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 |
# Author: Huahua, running time: 528 ms class Solution: def kClosest(self, points, K): return sorted(points, key = lambda p: p[0]**2 + p[1]**2)[0:K] |

