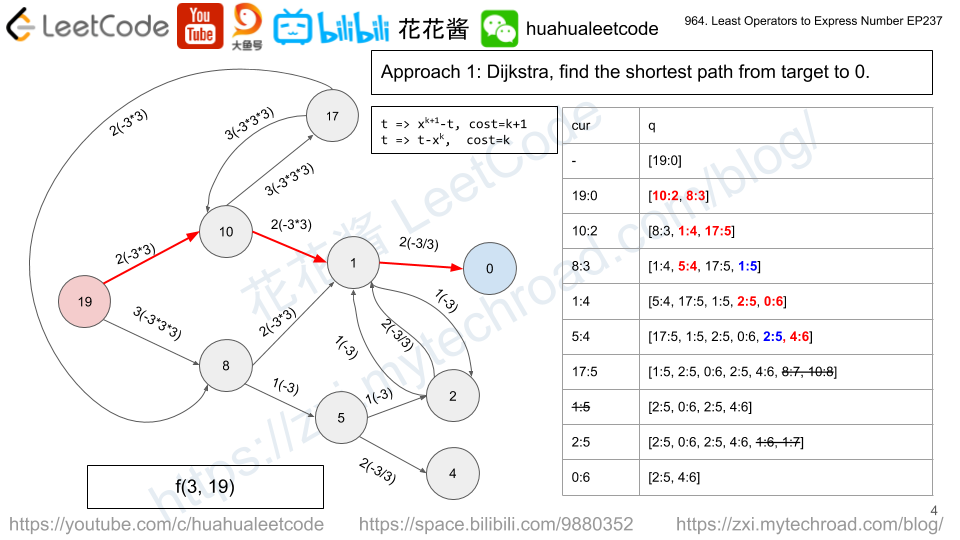
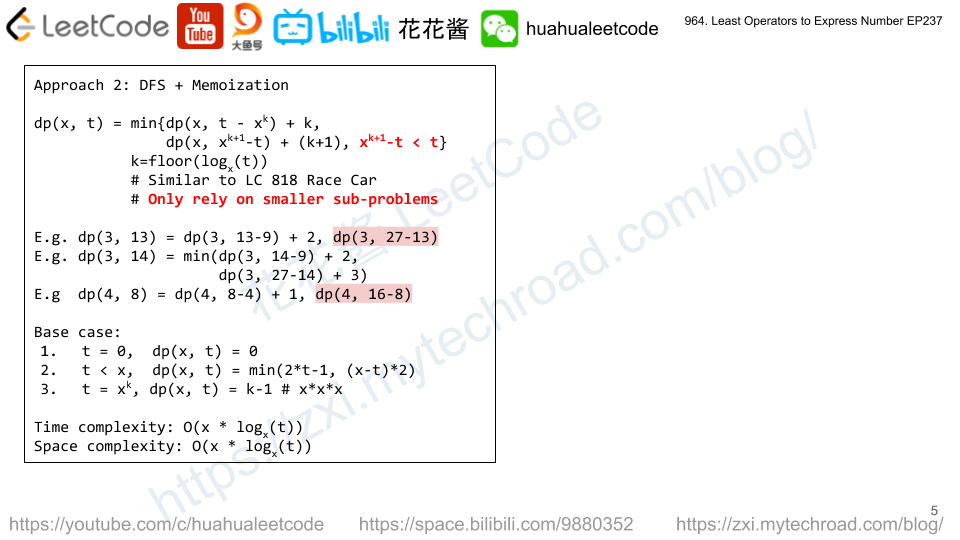
Problem
A binary tree is univalued if every node in the tree has the same value.
Return true if and only if the given tree is univalued.
Example 1:
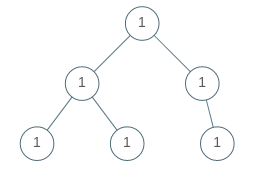
Input: [1,1,1,1,1,null,1] Output: true
Example 2:
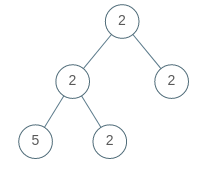
Input: [2,2,2,5,2] Output: false
Note:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. - Each node’s value will be an integer in the range
[0, 99].
Solution: Recursion
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(h)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
// Author: Huahua, running time: 0 ms class Solution { public: bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return true; if (root->left && root->val != root->left->val) return false; if (root->right && root->val != root->right->val) return false; return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right); } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# Author: Huahua, running time: 68 ms class Solution: def isUnivalTree(self, root): if not root: return True if root.left and root.left.val != root.val: return False if root.right and root.right.val != root.val: return False return self.isUnivalTree(root.left) and self.isUnivalTree(root.right) |