Problem
At a lemonade stand, each lemonade costs $5.
Customers are standing in a queue to buy from you, and order one at a time (in the order specified by bills).
Each customer will only buy one lemonade and pay with either a $5, $10, or $20 bill. You must provide the correct change to each customer, so that the net transaction is that the customer pays $5.
Note that you don’t have any change in hand at first.
Return true if and only if you can provide every customer with correct change.
Example 1:
Input: [5,5,5,10,20]
Output: true
Explanation:
From the first 3 customers, we collect three $5 bills in order.
From the fourth customer, we collect a $10 bill and give back a $5.
From the fifth customer, we give a $10 bill and a $5 bill.
Since all customers got correct change, we output true.
Example 2:
Input: [5,5,10]
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: [10,10]
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: [5,5,10,10,20]
Output: false
Explanation:
From the first two customers in order, we collect two $5 bills.
For the next two customers in order, we collect a $10 bill and give back a $5 bill.
For the last customer, we can't give change of $15 back because we only have two $10 bills.
Since not every customer received correct change, the answer is false.
Solution: Simulation + Greedy
Always use 10 bill first.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 18 ms class Solution { public: bool lemonadeChange(vector<int>& bills) { int fives = 0; int tens = 0; for (const int bill : bills) { if (bill == 5) { ++fives; } else if (bill == 10) { if (!fives) return false; ++tens; --fives; } else if (bill == 20) { if (tens && fives) { --tens; --fives; } else if (fives >= 3) { fives -= 3; } else { return false; } } } return true; } }; |
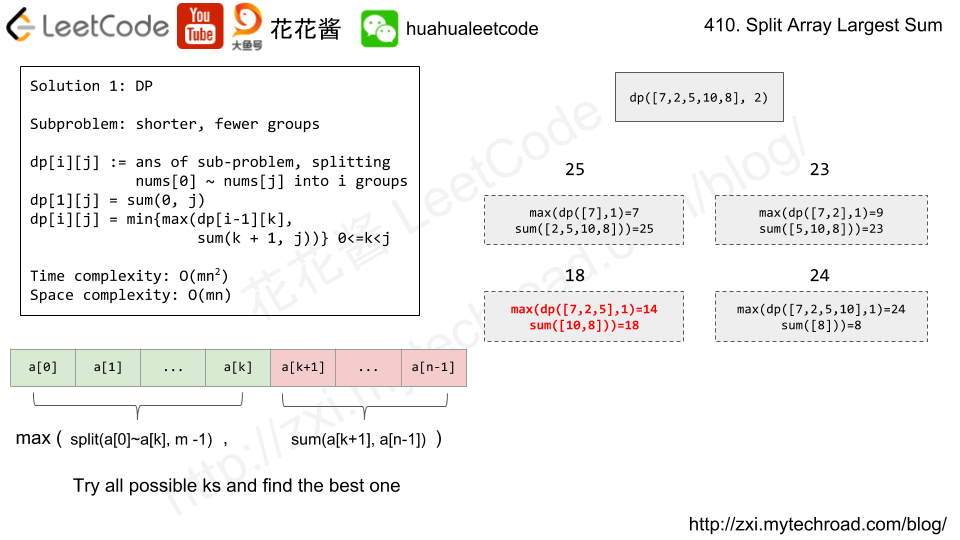
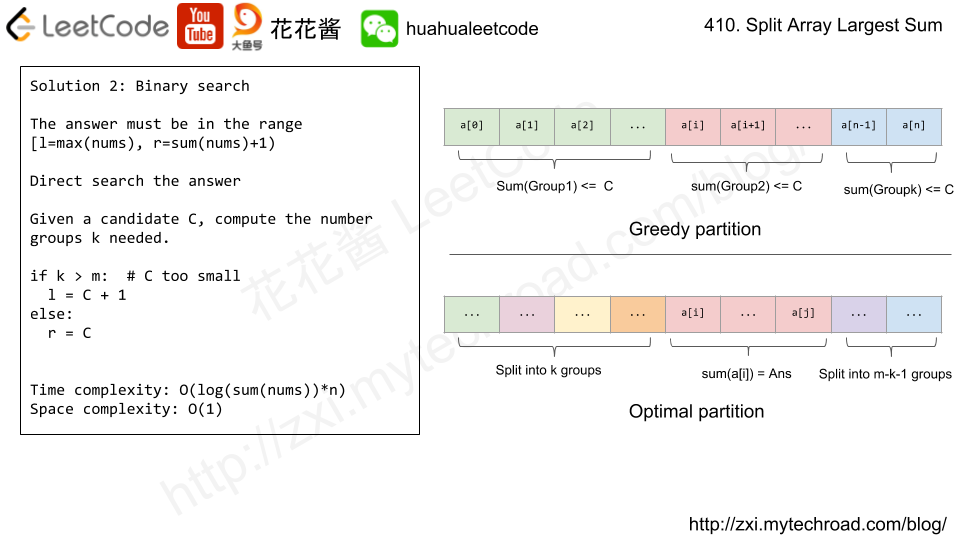
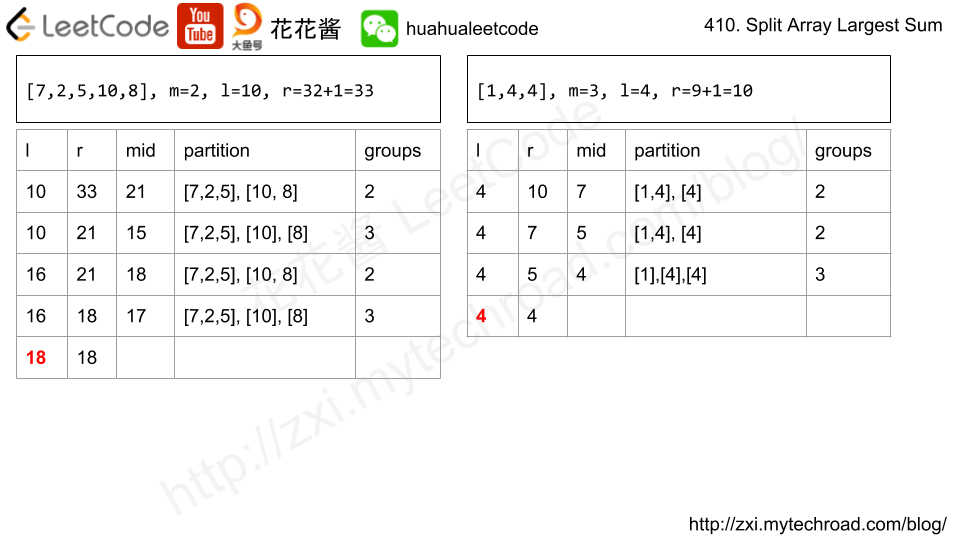
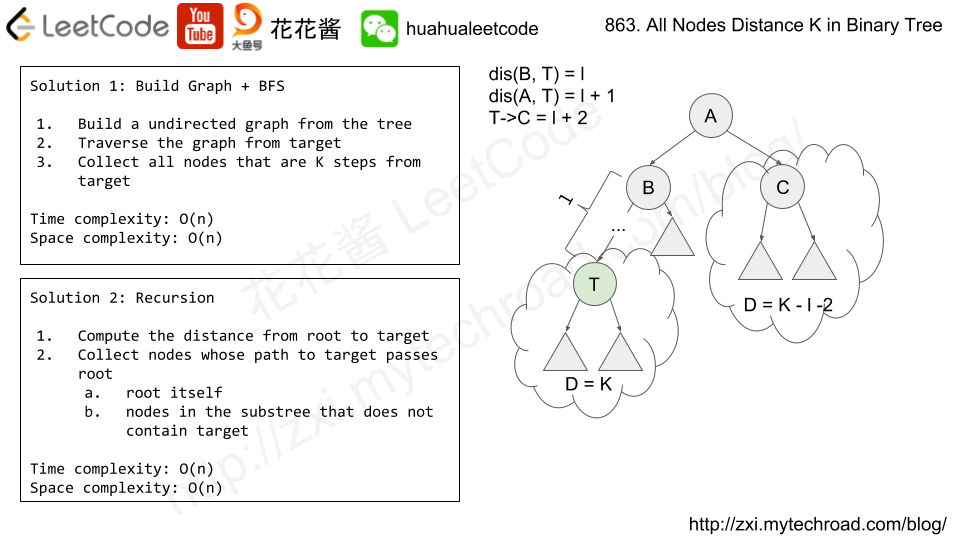
 Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.