You are given the root of a binary search tree and an array queries of size n consisting of positive integers.
Find a 2D array answer of size n where answer[i] = [mini, maxi]:
miniis the largest value in the tree that is smaller than or equal toqueries[i]. If a such value does not exist, add-1instead.maxiis the smallest value in the tree that is greater than or equal toqueries[i]. If a such value does not exist, add-1instead.
Return the array answer.
Example 1:
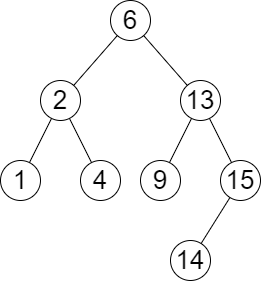
Input: root = [6,2,13,1,4,9,15,null,null,null,null,null,null,14], queries = [2,5,16] Output: [[2,2],[4,6],[15,-1]] Explanation: We answer the queries in the following way: - The largest number that is smaller or equal than 2 in the tree is 2, and the smallest number that is greater or equal than 2 is still 2. So the answer for the first query is [2,2]. - The largest number that is smaller or equal than 5 in the tree is 4, and the smallest number that is greater or equal than 5 is 6. So the answer for the second query is [4,6]. - The largest number that is smaller or equal than 16 in the tree is 15, and the smallest number that is greater or equal than 16 does not exist. So the answer for the third query is [15,-1].
Example 2:
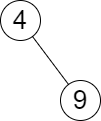
Input: root = [4,null,9], queries = [3] Output: [[-1,4]] Explanation: The largest number that is smaller or equal to 3 in the tree does not exist, and the smallest number that is greater or equal to 3 is 4. So the answer for the query is [-1,4].
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 106n == queries.length1 <= n <= 1051 <= queries[i] <= 106
Solution: Convert to sorted array


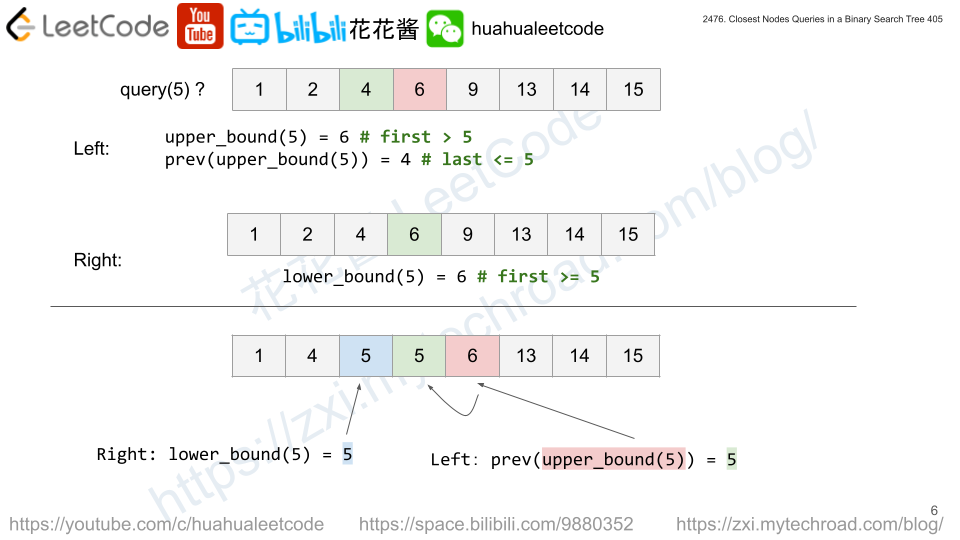

Since we don’t know whether the tree is balanced or not, the safest and easiest way is to convert the tree into a sorted array using inorder traversal. Or just any traversal and sort the array later on.
Once we have a sorted array, we can use lower_bound / upper_bound to query.
Time complexity: O(qlogn)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> closestNodes(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) { vector<int> vals; function<void(TreeNode*)> inorder = [&](TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; inorder(root->left); vals.push_back(root->val); inorder(root->right); }; inorder(root); vector<vector<int>> ans; for (const int q : queries) { vector<int> cur{-1, -1}; auto lit = upper_bound(begin(vals), end(vals), q); if (lit != begin(vals)) cur[0] = *(prev(lit)); auto rit = lower_bound(begin(vals), end(vals), q); if (rit != end(vals)) cur[1] = *rit; ans.push_back(std::move(cur)); } return ans; } }; |
One binary search per query.
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> closestNodes(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) { vector<int> vals; function<void(TreeNode*)> inorder = [&](TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; inorder(root->left); if (vals.empty() || root->val > vals.back()) vals.push_back(root->val); inorder(root->right); }; inorder(root); vector<vector<int>> ans; for (const int q : queries) { vector<int> cur{-1, -1}; auto it = lower_bound(begin(vals), end(vals), q); if (it != end(vals) && *it == q) cur[0] = cur[1] = q; else { if (it != begin(vals)) cur[0] = *prev(it); if (it != end(vals)) cur[1] = *it; } ans.push_back(std::move(cur)); } return ans; } }; |