Given an array nums that represents a permutation of integers from 1 to n. We are going to construct a binary search tree (BST) by inserting the elements of nums in order into an initially empty BST. Find the number of different ways to reorder nums so that the constructed BST is identical to that formed from the original array nums.
For example, given nums = [2,1,3], we will have 2 as the root, 1 as a left child, and 3 as a right child. The array [2,3,1] also yields the same BST but [3,2,1] yields a different BST.
Return the number of ways to reorder nums such that the BST formed is identical to the original BST formed from nums.
Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Example 1:
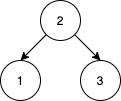
Input: nums = [2,1,3] Output: 1 Explanation: We can reorder nums to be [2,3,1] which will yield the same BST. There are no other ways to reorder nums which will yield the same BST.
Example 2:
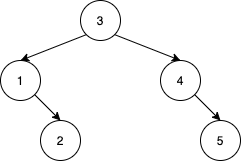
Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2] Output: 5 Explanation: The following 5 arrays will yield the same BST: [3,1,2,4,5] [3,1,4,2,5] [3,1,4,5,2] [3,4,1,2,5] [3,4,1,5,2]
Example 3:
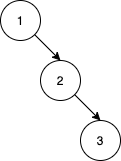
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no other orderings of nums that will yield the same BST.
Example 4:
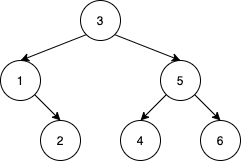
Input: nums = [3,1,2,5,4,6] Output: 19
Example 5:
Input: nums = [9,4,2,1,3,6,5,7,8,14,11,10,12,13,16,15,17,18] Output: 216212978 Explanation: The number of ways to reorder nums to get the same BST is 3216212999. Taking this number modulo 10^9 + 7 gives 216212978.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= nums.length- All integers in
numsare distinct.
Solution: Recursion + Combinatorics
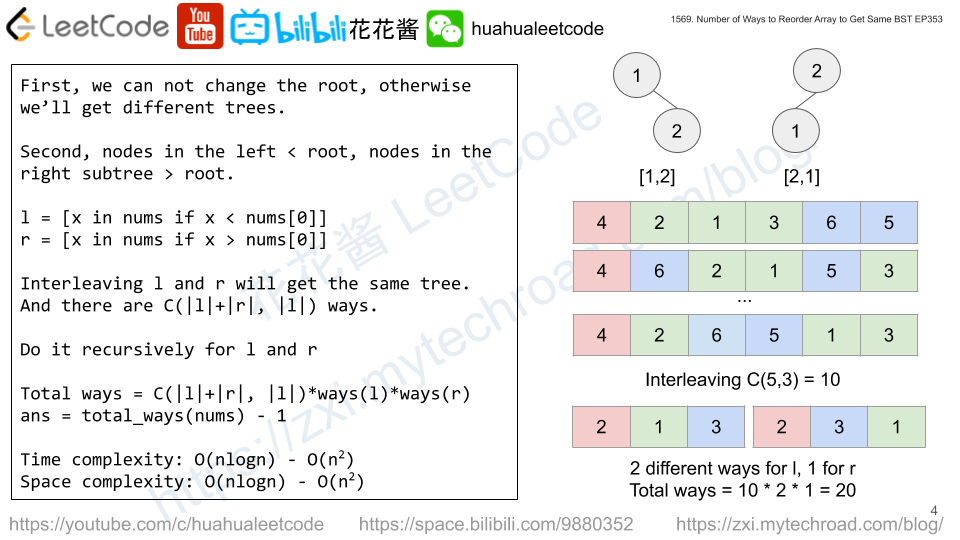
For a given root (first element of the array), we can split the array into left children (nums[i] < nums[0]) and right children (nums[i] > nums[0]). Assuming there are l nodes for the left and r nodes for the right. We have C(l + r, l) different ways to insert l elements into a (l + r) sized array. Within node l / r nodes, we have ways(left) / ways(right) different ways to re-arrange those nodes. So the total # of ways is:
C(l + r, l) * ways(l) * ways(r)
Don’t forget to minus one for the final answer.
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n^2)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
class Solution { public: int numOfWays(vector<int>& nums) { const int n = nums.size(); const int kMod = 1e9 + 7; vector<vector<int>> cnk(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 1)); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) cnk[i][j] = (cnk[i - 1][j] + cnk[i - 1][j - 1]) % kMod; function<int(vector<int>)> trees = [&](const vector<int>& nums) { const int n = nums.size(); if (n <= 2) return 1; vector<int> left; vector<int> right; for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) if (nums[i] < nums[0]) left.push_back(nums[i]); else right.push_back(nums[i]); long ans = cnk[n - 1][left.size()]; ans = (ans * trees(left)) % kMod; ans = (ans * trees(right)) % kMod; return static_cast<int>(ans); }; return trees(nums) - 1; } }; |
python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
class Solution: def numOfWays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: def ways(nums): if len(nums) <= 2: return 1 l = [x for x in nums if x < nums[0]] r = [x for x in nums if x > nums[0]] return comb(len(l) + len(r), len(l)) * ways(l) * ways(r) return (ways(nums) - 1) % (10**9 + 7) |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment