You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a digit between 0 and 9 (inclusive).
The triangular sum of nums is the value of the only element present in nums after the following process terminates:
- Let
numscomprise ofnelements. Ifn == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer arraynewNumsof lengthn - 1. - For each index
i, where0 <= i < n - 1, assign the value ofnewNums[i]as(nums[i] + nums[i+1]) % 10, where%denotes modulo operator. - Replace the array
numswithnewNums. - Repeat the entire process starting from step 1.
Return the triangular sum of nums.
Example 1:
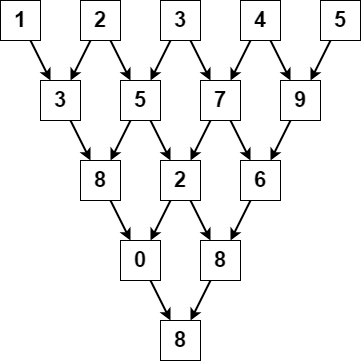
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 8 Explanation: The above diagram depicts the process from which we obtain the triangular sum of the array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5] Output: 5 Explanation: Since there is only one element in nums, the triangular sum is the value of that element itself.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 9
Solution 1: Simulation
Time complexity: O(n2)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int triangularSum(vector<int>& nums) { while (nums.size() != 1) { vector<int> next(nums.size() - 1); for (size_t i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; ++i) next[i] = (nums[i] + nums[i + 1]) % 10; swap(next, nums); } return nums[0]; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment