You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
Example 1:
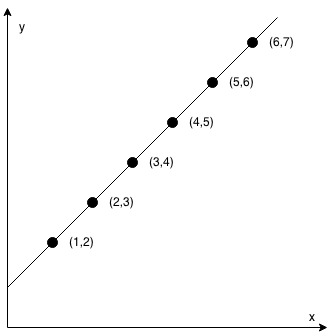
Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]] Output: true
Example 2:
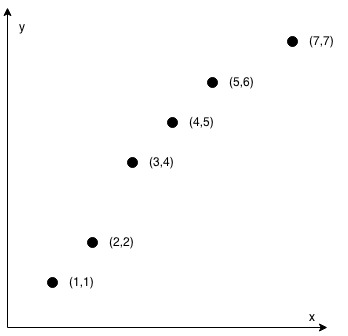
Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]] Output: false
Constraints:
2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000coordinates[i].length == 2-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4coordinatescontains no duplicate point.
Solution: Slope and Hashset
This is not a easy problem, a few corner cases:
- dx == 0
- dy == 0
- dx < 0
Basically we are counting (dx / gcd(dx, dy), dy / gcd(dx, dy)). We will have only ONE entry if all the points are on the same line.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1) w/ early exit.
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) { set<pair<int, int>> s; for (int i = 1; i < coordinates.size(); ++i) { int dx = coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[0][0]; int dy = coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[0][1]; if (dy == 0) s.emplace(1, 0); else if (dx == 0) s.emplace(0, 1); else { if (dx < 0) dx *= -1, dy *= -1; const int d = gcd(dx, dy); s.emplace(dx / d, dy / d); } if (s.size() > 1) return false; } return true; } }; |
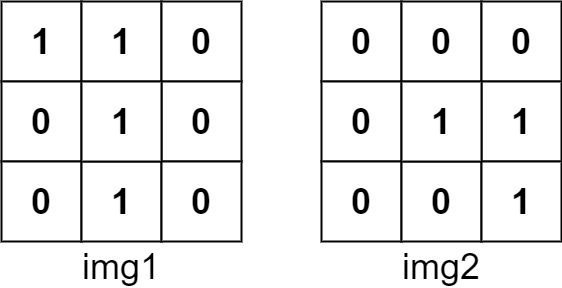
 The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red).
The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red).