Write a program to find the n-th ugly number.
Ugly numbers are positive integers which are divisible by a or b or c.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, a = 2, b = 3, c = 5 Output: 4 Explanation: The ugly numbers are 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10... The 3rd is 4.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, a = 2, b = 3, c = 4 Output: 6 Explanation: The ugly numbers are 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12... The 4th is 6.
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, a = 2, b = 11, c = 13 Output: 10 Explanation: The ugly numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13... The 5th is 10.
Example 4:
Input: n = 1000000000, a = 2, b = 217983653, c = 336916467 Output: 1999999984
Constraints:
1 <= n, a, b, c <= 10^91 <= a * b * c <= 10^18- It’s guaranteed that the result will be in range
[1, 2 * 10^9]
Solution: Binary Search
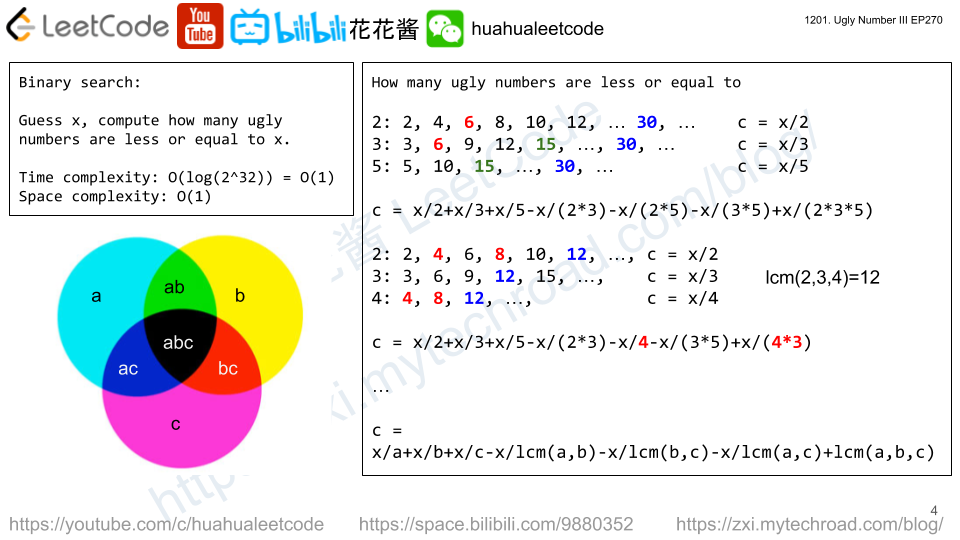
Number of ugly numbers that are <= m are:
m / a + m / b + m / c – (m / LCM(a,b) + m / LCM(a, c) + m / LCM(b, c) + m / LCM(a, LCM(b, c))
Time complexity: O(logn)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int nthUglyNumber(int n, long a, long b, long c) { long l = 1; long r = INT_MAX; long ab = lcm(a, b); long ac = lcm(a, c); long bc = lcm(b, c); long abc = lcm(a, bc); while (l < r) { long m = l + (r - l) / 2; long k = m / a + m / b + m / c - m / ab - m / ac - m / bc + m / abc; if (k >= n) r = m; else l = m + 1; } return l; } }; |