You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Example 1:
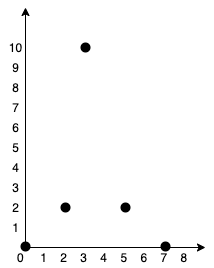
Input: points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]] Output: 20 Explanation: We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20. Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]] Output: 18
Example 3:
Input: points = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[-1,1]] Output: 4
Example 4:
Input: points = [[-1000000,-1000000],[1000000,1000000]] Output: 4000000
Example 5:
Input: points = [[0,0]] Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 1000-106 <= xi, yi <= 106- All pairs
(xi, yi)are distinct.
Solution: Minimum Spanning Tree
Kruskal’s algorithm
Time complexity: O(n^2logn)
Space complexity: O(n^2)
using vector of vector, array, pair of pair, or tuple might lead to TLE…
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
struct Edge { int cost; int x; int y; bool operator<(const Edge& e) const { return cost < e.cost; } }; class Solution { public: int minCostConnectPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) { const int n = points.size(); vector<Edge> edges(n * (n - 1) / 2); // {cost, i, j} for (int i = 0, idx = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) edges[idx++] = {abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1]), i, j}; std::sort(begin(edges), end(edges)); vector<int> p(n); std::iota(begin(p), end(p), 0); vector<int> rank(n, 0); int ans = 0; int count = 0; for (const auto& e : edges) { int rx = find(p, e.x); int ry = find(p, e.y); if (rx == ry) continue; ans += e.cost; if (rank[rx] < rank[ry]) swap(rx, ry); p[rx] = ry; rank[ry] += rank[rx] == rank[ry]; if (++count == n - 1) break; } return ans; } private: int find(vector<int>& p, int x) const { while (p[x] != x) { int tp = p[x]; p[x] = p[p[x]]; x = tp; } return x; } }; |
Prim’s Algorithm
ds[i] := min distance from i to ANY nodes in the tree.
Time complexity: O(n^2) Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
class Solution { public: int minCostConnectPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) { const int n = points.size(); auto dist = [](const vector<int>& pi, const vector<int>& pj) { return abs(pi[0] - pj[0]) + abs(pi[1] - pj[1]); }; vector<int> ds(n, INT_MAX); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) ds[i] = dist(points[0], points[i]); int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { auto it = min_element(begin(ds), end(ds)); const int v = distance(begin(ds), it); ans += ds[v]; ds[v] = INT_MAX; // done for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (ds[i] == INT_MAX) continue; ds[i] = min(ds[i], dist(points[i], points[v])); } } return ans; } }; |