Problem
Given a binary tree rooted at root, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
A node is deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Return the node with the largest depth such that it contains all the deepest nodes in it’s subtree.
Example 1:
Input: [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation:We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree. The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree. The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2. Both the input and output have TreeNode type.
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be between 1 and 500.
- The values of each node are unique.
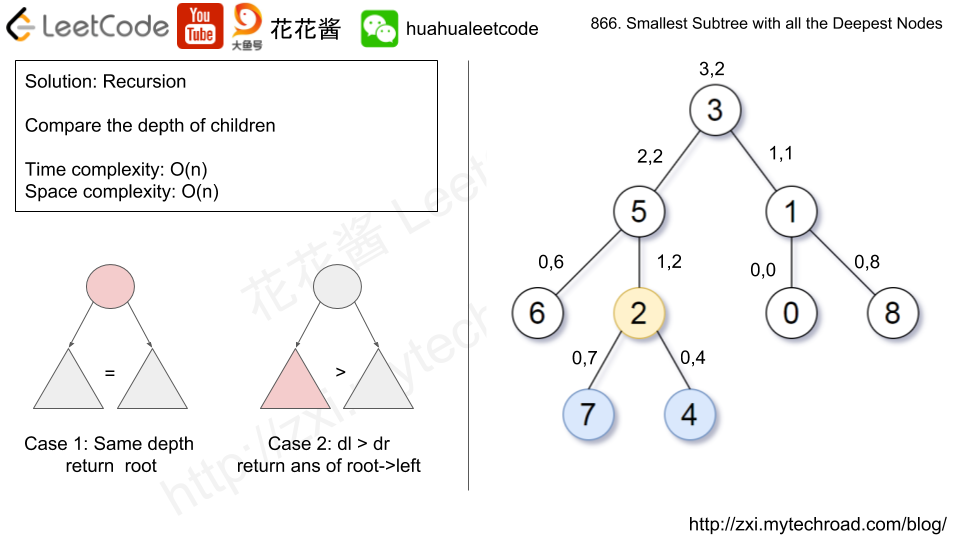
Solution: Recursion
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 0 ms class Solution { public: TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) { return depth(root).second; } private: pair<int, TreeNode*> depth(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return {-1, nullptr}; auto l = depth(root->left); auto r = depth(root->right); int dl = l.first; int dr = r.first; return { max(dl, dr) + 1, dl == dr ? root : (dl > dr) ? l.second : r.second}; } }; |
v2
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 0 ms class Solution { public: TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* ans; depth(root, &ans); return ans; } private: int depth(TreeNode* root, TreeNode** s) { if (root == nullptr) return -1; TreeNode* sl; TreeNode* sr; int l = depth(root->left, &sl); int r = depth(root->right, &sr); *s = (l == r) ? root : ((l > r) ? sl : sr); return max(l, r) + 1; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
""" Author: Huahua Running time: 40 ms """ class Solution: def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root): def solve(root): if not root: return (-1, None) dl, sl = solve(root.left) dr, sr = solve(root.right) if dl == dr: return (dl + 1, root) return (dl + 1, sl) if dl > dr else (dr + 1, sr) return solve(root)[1] |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.
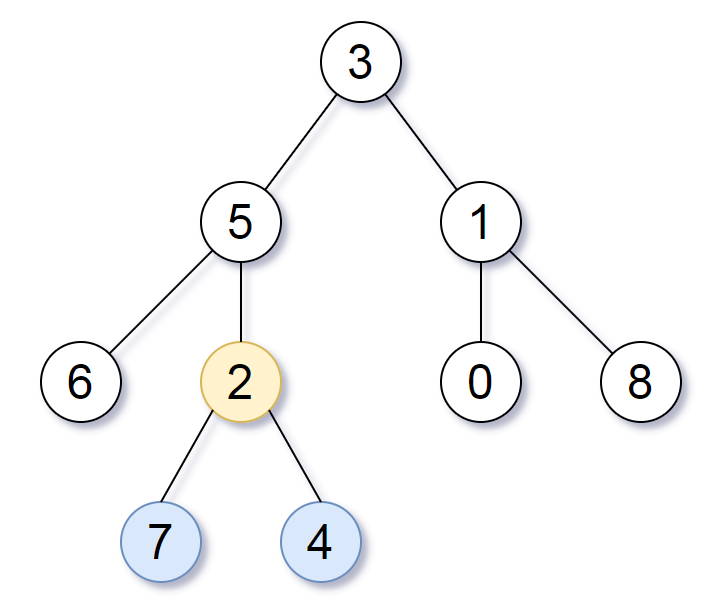 We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree.
The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2.
Both the input and output have TreeNode type.
We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree.
The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2.
Both the input and output have TreeNode type.



Be First to Comment