You are given an array nums consisting of non-negative integers. You are also given a queries array, where queries[i] = [xi, mi].
The answer to the ith query is the maximum bitwise XOR value of xi and any element of nums that does not exceed mi. In other words, the answer is max(nums[j] XOR xi) for all j such that nums[j] <= mi. If all elements in nums are larger than mi, then the answer is -1.
Return an integer array answer where answer.length == queries.length and answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,1,2,3,4], queries = [[3,1],[1,3],[5,6]] Output: [3,3,7] Explanation: 1) 0 and 1 are the only two integers not greater than 1. 0 XOR 3 = 3 and 1 XOR 3 = 2. The larger of the two is 3. 2) 1 XOR 2 = 3. 3) 5 XOR 2 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,2,4,6,6,3], queries = [[12,4],[8,1],[6,3]] Output: [15,-1,5]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length, queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 20 <= nums[j], xi, mi <= 109
Solution: Trie on the fly
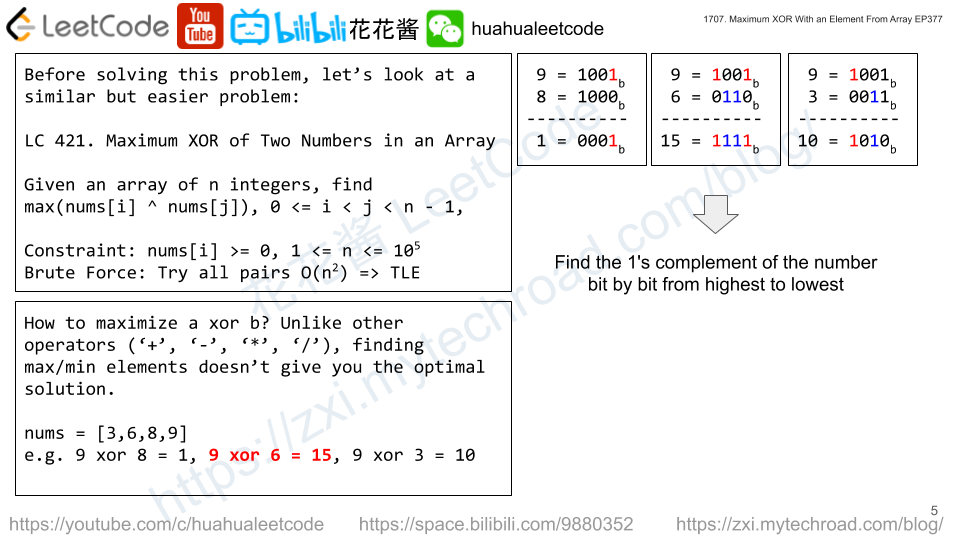
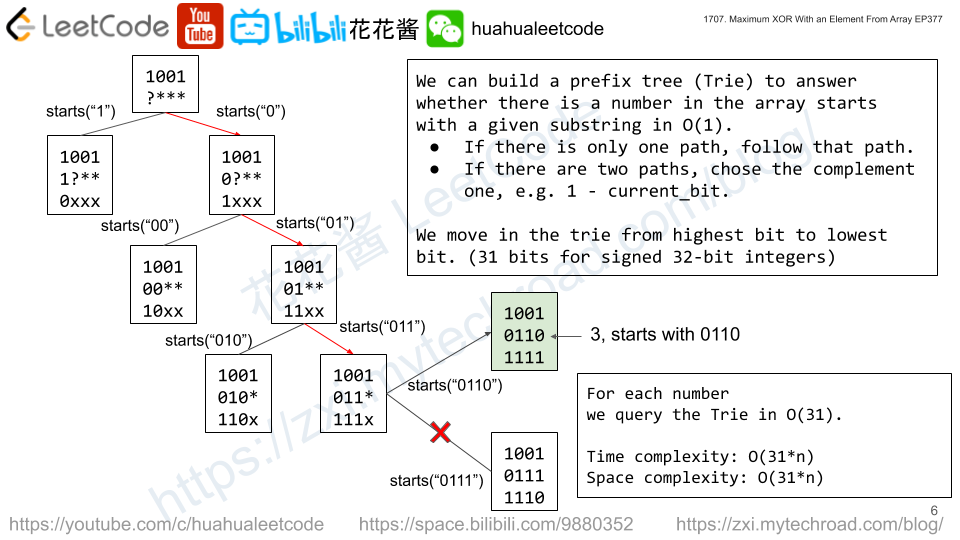
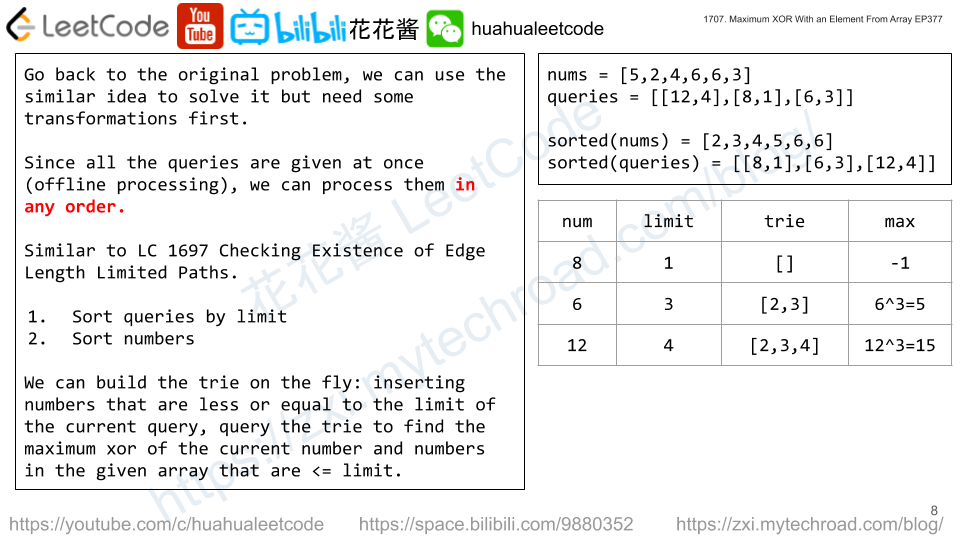
Similar idea to https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/trie/leetcode-421-maximum-xor-of-two-numbers-in-an-array/
We can build the trie on the fly by sorting nums in ascending order and queries by its limit, insert nums into the trie up the limit.
Time complexity: O(nlogn + QlogQ)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
// Author: Huahua class Trie { public: Trie(): children{nullptr, nullptr} {} Trie* children[2]; }; class Solution { public: vector<int> maximizeXor(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { const int n = nums.size(); sort(begin(nums), end(nums)); const int Q = queries.size(); for (int i = 0; i < Q; ++i) queries[i].push_back(i); sort(begin(queries), end(queries), [](const auto& q1, const auto& q2) { return q1[1] < q2[1]; }); Trie root; auto insert = [&](int num) { Trie* node = &root; for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (!node->children[bit]) node->children[bit] = new Trie(); node = node->children[bit]; } }; auto query = [&](int num) { Trie* node = &root; int sum = 0; for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { if (!node) return -1; int bit = (num >> i) & 1; if (node->children[1 - bit]) { sum |= (1 << i); node = node->children[1 - bit]; } else { node = node->children[bit]; } } return sum; }; vector<int> ans(Q); int i = 0; for (const auto& q : queries) { while (i < n && nums[i] <= q[1]) insert(nums[i++]); ans[q[2]] = query(q[0]); } return ans; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment