Given a single positive integer x, we will write an expression of the form x (op1) x (op2) x (op3) x ... where each operator op1, op2, etc. is either addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division (+, -, *, or /). For example, with x = 3, we might write 3 * 3 / 3 + 3 - 3 which is a value of 3.
When writing such an expression, we adhere to the following conventions:
- The division operator (
/) returns rational numbers. - There are no parentheses placed anywhere.
- We use the usual order of operations: multiplication and division happens before addition and subtraction.
- It’s not allowed to use the unary negation operator (
-). For example, “x - x” is a valid expression as it only uses subtraction, but “-x + x” is not because it uses negation.
We would like to write an expression with the least number of operators such that the expression equals the given target. Return the least number of operators used.
Example 1:
Input: x = 3, target = 19
Output: 5
Explanation: 3 * 3 + 3 * 3 + 3 / 3. The expression contains 5 operations.
Example 2:
Input: x = 5, target = 501
Output: 8
Explanation: 5 * 5 * 5 * 5 - 5 * 5 * 5 + 5 / 5. The expression contains 8 operations.
Example 3:
Input: x = 100, target = 100000000
Output: 3
Explanation: 100 * 100 * 100 * 100. The expression contains 3 operations.
Note:
2 <= x <= 1001 <= target <= 2 * 10^8

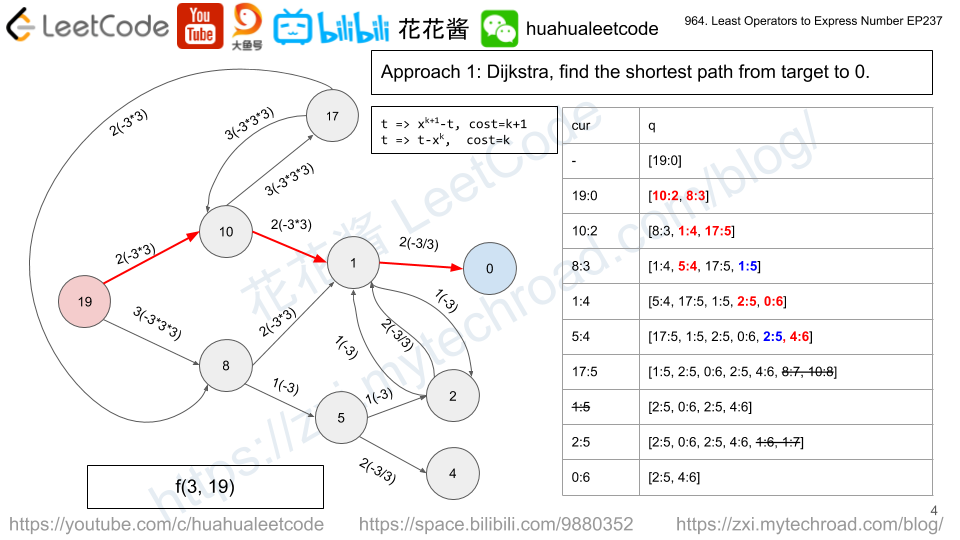
Solution: Dijkstra
Find the shortest path from target to 0 using ops.
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
Space complexity: O(nlogn)
n = x * log(t) / log(x)
C++/set
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
class Solution { public: int leastOpsExpressTarget(int x, int target) { set<pair<int, int>> q; // # x -> number unordered_set<int> s; q.emplace(0, target); while (!q.empty()) { const auto it = begin(q); const int c = it->first; const int t = it->second; q.erase(it); if (t == 0) return c - 1; if (s.count(t)) continue; s.insert(t); int n = log(t) / log(x); int l = t - pow(x, n); q.emplace(c + (n == 0 ? 2 : n), l); int r = pow(x, n + 1) - t; q.emplace(c + n + 1, r); } return -1; } }; |
C++/heap
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
class Solution { public: int leastOpsExpressTarget(int x, int target) { priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q; unordered_set<int> s; q.emplace(0, target); while (!q.empty()) { const int c = q.top().first; const int t = q.top().second; q.pop(); if (t == 0) return c - 1; if (s.count(t)) continue; s.insert(t); int n = log(t) / log(x); int l = t - pow(x, n); q.emplace(c + (n == 0 ? 2 : n), l); int r = pow(x, n + 1) - t; q.emplace(c + n + 1, r); } return -1; } }; |
Solution 2: DFS + Memoization
Time complexity: O(x * log(t)/log(x))
Space complexity: O(x * log(t)/log(x))
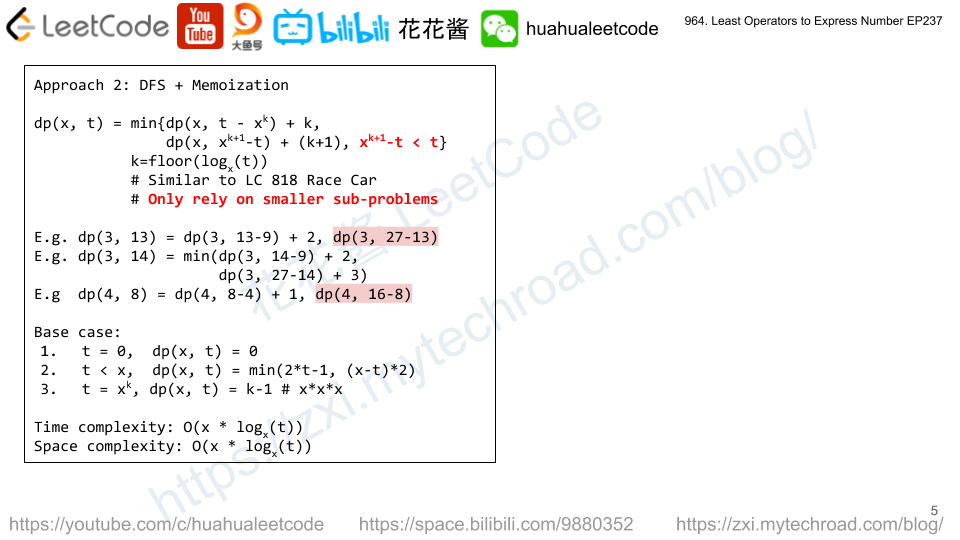
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
// Author: Huahua, running time: 8 ms class Solution { public: int leastOpsExpressTarget(int x, int target) { return dp(x, target); } private: unordered_map<int, int> m_; int dp(int x, int t) { if (t == 0) return 0; if (t < x) return min(2 * t - 1, 2 * (x - t)); if (m_.count(t)) return m_.at(t); int k = log(t) / log(x); long p = pow(x, k); if (t == p) return m_[t] = k - 1; int ans = dp(x, t - p) + k; // t - p < t long left = p * x - t; if (left < t) // only rely on smaller sub-problems ans = min(ans, dp(x, left) + k + 1); return m_[t] = ans; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment