Problem:
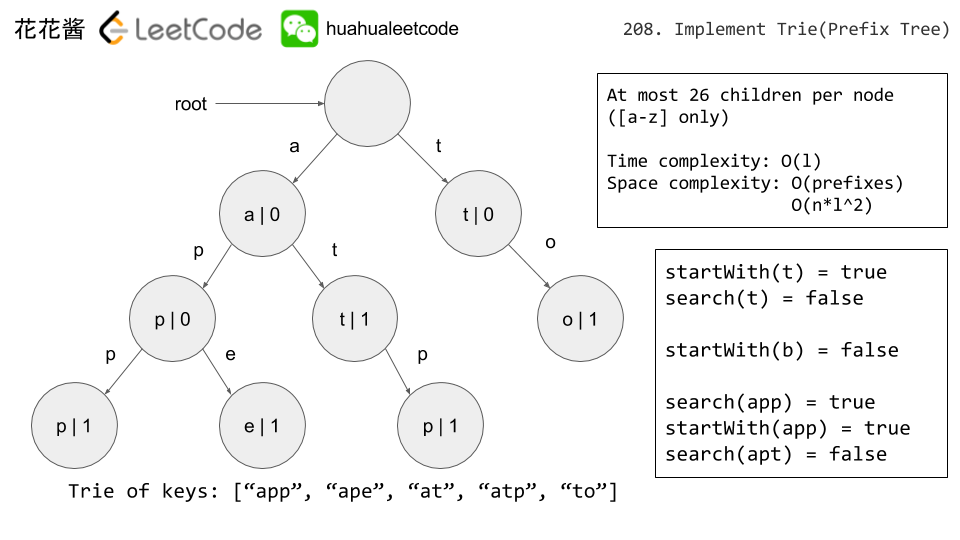
Implement a trie with insert, search, and startsWith methods.
Note:
You may assume that all inputs are consist of lowercase letters a-z.
Idea:
Tree/children array
Solution:
C++ / Array
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 99 ms class Trie { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ Trie(): root_(new TrieNode()) {} /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ void insert(const string& word) { TrieNode* p = root_.get(); for (const char c : word) { if (!p->children[c - 'a']) p->children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode(); p = p->children[c - 'a']; } p->is_word = true; } /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ bool search(const string& word) const { const TrieNode* p = find(word); return p && p->is_word; } /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ bool startsWith(const string& prefix) const { return find(prefix) != nullptr; } private: struct TrieNode { TrieNode():is_word(false), children(26, nullptr){} ~TrieNode() { for (TrieNode* child : children) if (child) delete child; } bool is_word; vector<TrieNode*> children; }; const TrieNode* find(const string& prefix) const { const TrieNode* p = root_.get(); for (const char c : prefix) { p = p->children[c - 'a']; if (p == nullptr) break; } return p; } std::unique_ptr<TrieNode> root_; }; |
C++ / hashmap
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 98 ms class Trie { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ Trie(): root_(new TrieNode()) {} /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ void insert(const string& word) { TrieNode* p = root_.get(); for (const char c : word) { if (!p->children.count(c)) p->children[c] = new TrieNode(); p = p->children[c]; } p->is_word = true; } /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ bool search(const string& word) const { const TrieNode* p = find(word); return p && p->is_word; } /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ bool startsWith(const string& prefix) const { return find(prefix) != nullptr; } private: struct TrieNode { TrieNode():is_word(false){} ~TrieNode() { for (auto& kv : children) if (kv.second) delete kv.second; } bool is_word; unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children; }; const TrieNode* find(const string& prefix) const { const TrieNode* p = root_.get(); for (const char c : prefix) { if (!p->children.count(c)) return nullptr; p = p->children.at(c); } return p; } std::unique_ptr<TrieNode> root_; }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 184 ms class Trie { class TrieNode { public TrieNode() { children = new TrieNode[26]; is_word = false; } public boolean is_word; public TrieNode[] children; } private TrieNode root; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public Trie() { root = new TrieNode(); } /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ public void insert(String word) { TrieNode p = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { int index = (int)(word.charAt(i) - 'a'); if (p.children[index] == null) p.children[index] = new TrieNode(); p = p.children[index]; } p.is_word = true; } /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ public boolean search(String word) { TrieNode node = find(word); return node != null && node.is_word; } /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { TrieNode node = find(prefix); return node != null; } private TrieNode find(String prefix) { TrieNode p = root; for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) { int index = (int)(prefix.charAt(i) - 'a'); if (p.children[index] == null) return null; p = p.children[index]; } return p; } } |
Python 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
""" Author: Huahua Running time: 469 ms """ class Trie(object): class TrieNode(object): def __init__(self): self.is_word = False self.children = [None] * 26 def __init__(self): self.root = Trie.TrieNode() def insert(self, word): p = self.root for c in word: index = ord(c) - ord('a') if not p.children[index]: p.children[index] = Trie.TrieNode() p = p.children[index] p.is_word = True def search(self, word): node = self.find(word) return node is not None and node.is_word def startsWith(self, prefix): return self.find(prefix) is not None def find(self, prefix): p = self.root for c in prefix: index = ord(c) - ord('a') if not p.children[index]: return None p = p.children[index] return p |
Python 2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
""" Author: Huahua Running time: 212 ms """ class Trie(object): def __init__(self): self.root = {} def insert(self, word): p = self.root for c in word: if c not in p: p[c] = {} p = p[c] p['#'] = True def search(self, word): node = self.find(word) return node is not None and '#' in node def startsWith(self, prefix): return self.find(prefix) is not None def find(self, prefix): p = self.root for c in prefix: if c not in p: return None p = p[c] return p |