Given a binary tree root and a linked list with head as the first node.
Return True if all the elements in the linked list starting from the head correspond to some downward path connected in the binary tree otherwise return False.
In this context downward path means a path that starts at some node and goes downwards.
Example 1:

Input: head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] Output: true Explanation: Nodes in blue form a subpath in the binary Tree.
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] Output: true
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path in the binary tree that contains all the elements of the linked list from head.
Constraints:
1 <= node.val <= 100for each node in the linked list and binary tree.- The given linked list will contain between
1and100nodes. - The given binary tree will contain between
1and2500nodes.
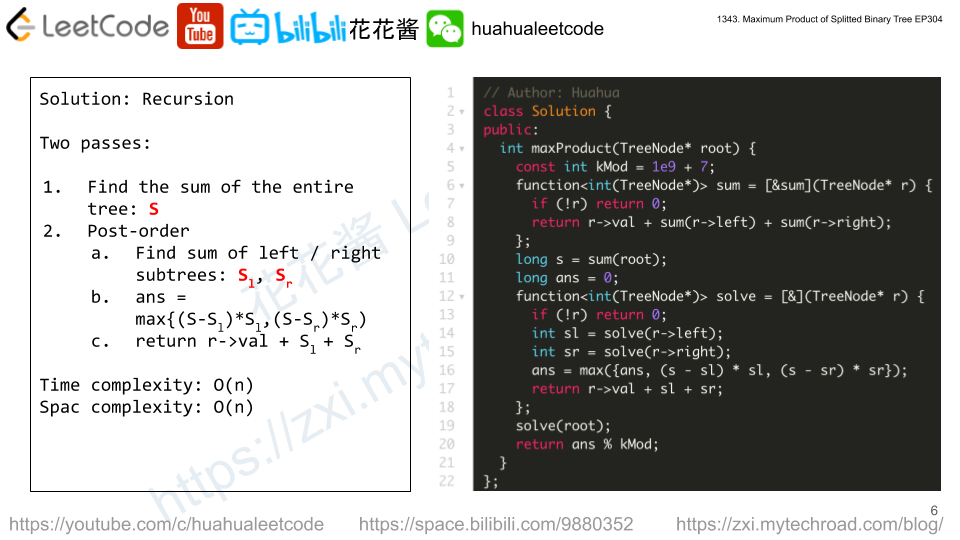
Solution: Recursion
We need two recursion functions: isSubPath / isPath, the later one does a strict match.
Time complexity: O(|L| * |T|)
Space complexity: O(|T|)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
class Solution { public: bool isSubPath(ListNode* head, TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return false; return isPath(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root->left) || isSubPath(head, root->right); } private: bool isPath(ListNode* head, TreeNode* root) { if (!head) return true; if (!root) return false; if (root->val != head->val) return false; return isPath(head->next, root->left) || isPath(head->next, root->right); } }; |