Given the array arr of positive integers and the array queries where queries[i] = [Li, Ri], for each query i compute the XOR of elements from Li to Ri (that is, arr[Li] xor arr[Li+1] xor ... xor arr[Ri] ). Return an array containing the result for the given queries.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [1,3,4,8], queries = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3],[3,3]] Output: [2,7,14,8] Explanation: The binary representation of the elements in the array are: 1 = 0001 3 = 0011 4 = 0100 8 = 1000 The XOR values for queries are: [0,1] = 1 xor 3 = 2 [1,2] = 3 xor 4 = 7 [0,3] = 1 xor 3 xor 4 xor 8 = 14 [3,3] = 8
Example 2:
Input: arr = [4,8,2,10], queries = [[2,3],[1,3],[0,0],[0,3]] Output: [8,0,4,4]
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 3 * 10^41 <= arr[i] <= 10^91 <= queries.length <= 3 * 10^4queries[i].length == 20 <= queries[i][0] <= queries[i][1] < arr.length
Solution: Prefix Sum
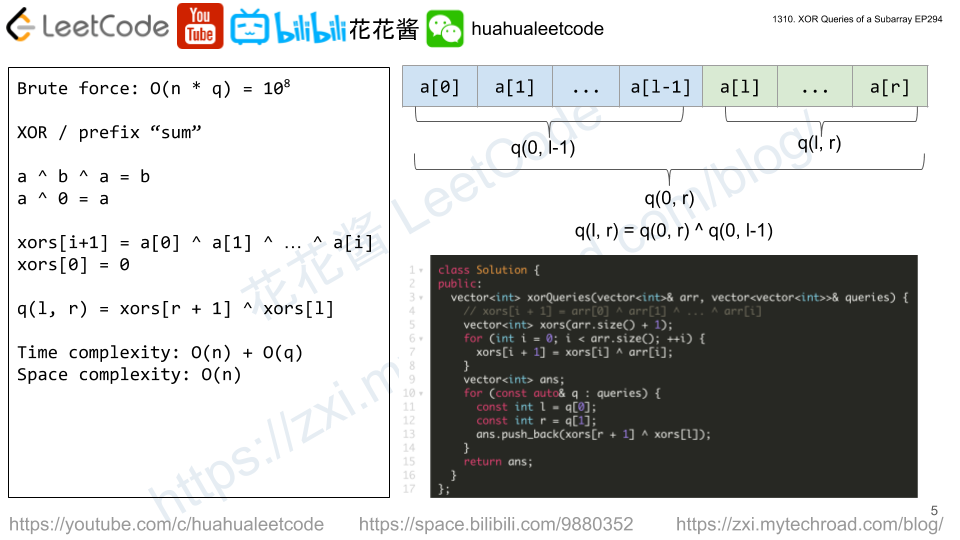
Time complexity: O(n) + O(q)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> xorQueries(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { // xors[i + 1] = arr[0] ^ arr[1] ^ ... ^ arr[i] vector<int> xors(arr.size() + 1); for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); ++i) { xors[i + 1] = xors[i] ^ arr[i]; } vector<int> ans; for (const auto& q : queries) { const int l = q[0]; const int r = q[1]; ans.push_back(xors[r + 1] ^ xors[l]); } return ans; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment