There are n cities numbered from 0 to n-1. Given the array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between cities fromi and toi, and given the integer distanceThreshold.
Return the city with the smallest numberof cities that are reachable through some path and whose distance is at most distanceThreshold, If there are multiple such cities, return the city with the greatest number.
Notice that the distance of a path connecting cities i and j is equal to the sum of the edges’ weights along that path.
Example 1:
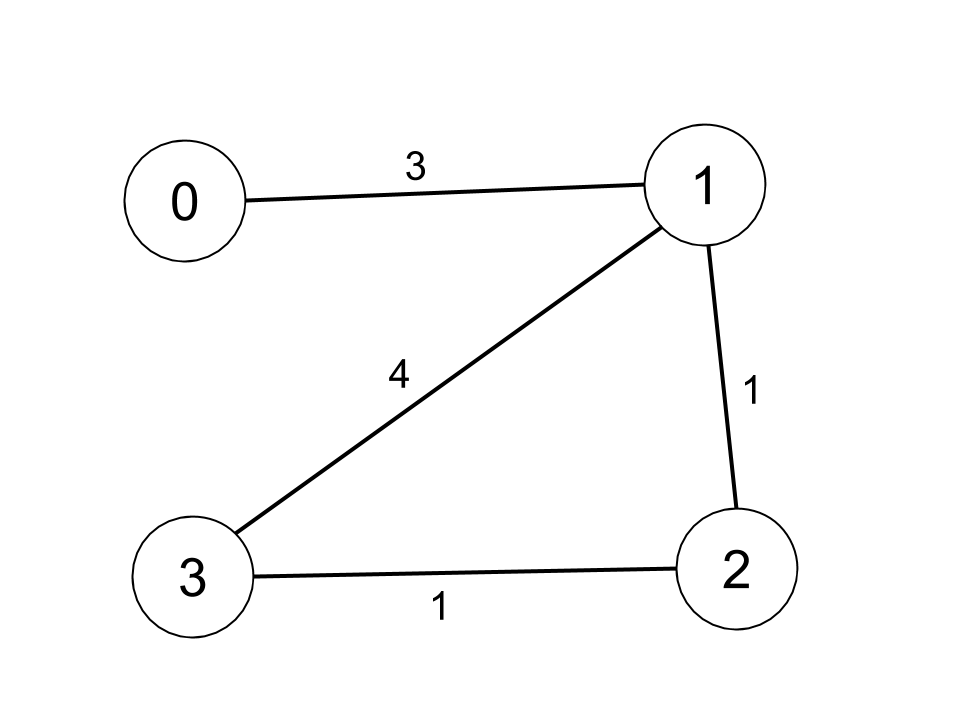
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[1,2,1],[1,3,4],[2,3,1]], distanceThreshold = 4 Output: 3 Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 4 for each city are: City 0 -> [City 1, City 2] City 1 -> [City 0, City 2, City 3] City 2 -> [City 0, City 1, City 3] City 3 -> [City 1, City 2] Cities 0 and 3 have 2 neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 4, but we have to return city 3 since it has the greatest number.
Example 2:
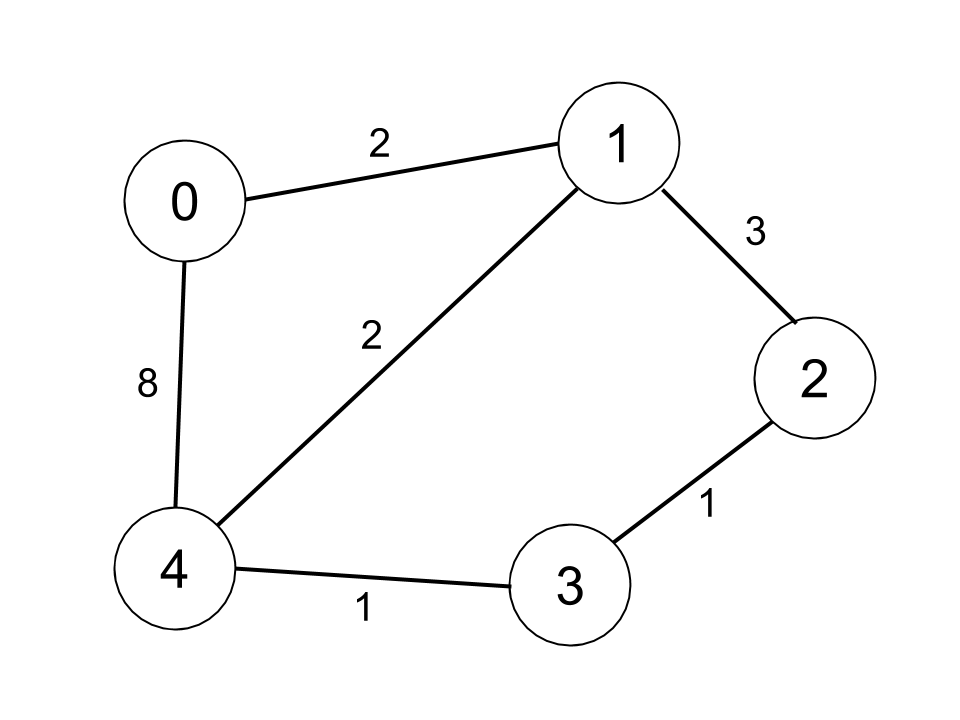
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,4,8],[1,2,3],[1,4,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], distanceThreshold = 2 Output: 0 Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 2 for each city are: City 0 -> [City 1] City 1 -> [City 0, City 4] City 2 -> [City 3, City 4] City 3 -> [City 2, City 4] City 4 -> [City 1, City 2, City 3] The city 0 has 1 neighboring city at a distanceThreshold = 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2edges[i].length == 30 <= fromi < toi < n1 <= weighti, distanceThreshold <= 10^4- All pairs
(fromi, toi)are distinct.
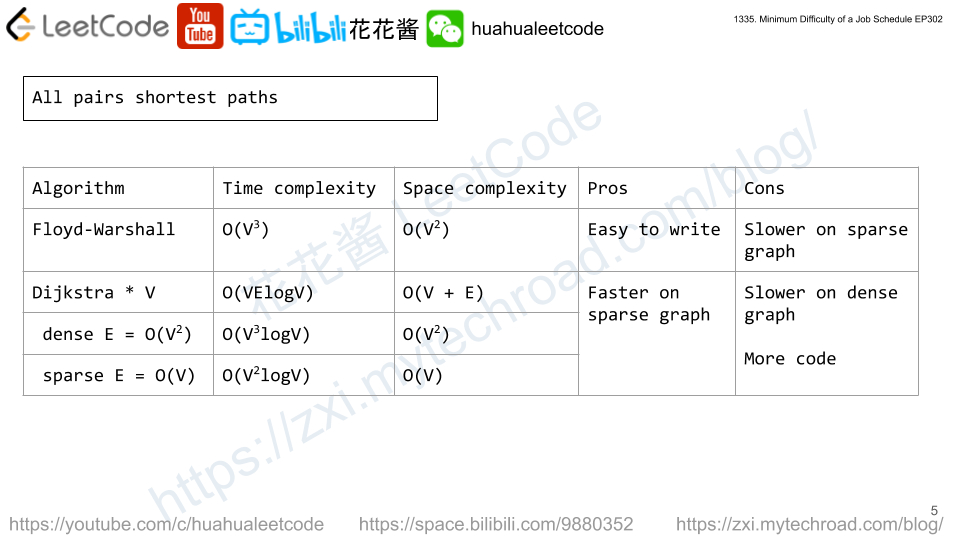
Solution1: Floyd-Warshall
All pair shortest path
Time complexity: O(n^3)
Space complexity: O(n^2)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int findTheCity(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int distanceThreshold) { vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX / 2)); for (const auto& e : edges) dp[e[0]][e[1]] = dp[e[1]][e[0]] = e[2]; for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) for (int u = 0; u < n; ++u) for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) dp[u][v] = min(dp[u][v], dp[u][k] + dp[k][v]); int ans = -1; int min_nb = INT_MAX; for (int u = 0; u < n; ++u) { int nb = 0; for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) if (v != u && dp[u][v] <= distanceThreshold) ++nb; if (nb <= min_nb) { min_nb = nb; ans = u; } } return ans; } }; |
Solution 2: Dijkstra’s Algorithm
Time complexity: O(V * ElogV) / worst O(n^3*logn), best O(n^2*logn)
Space complexity: O(V + E)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
// Author: Huahua // Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int findTheCity(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int t) { vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n); for (const auto& e : edges) { g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]); g[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0], e[2]); } // Returns the number of nodes within t from s. auto dijkstra = [&](int s) { vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX / 2); set<pair<int, int>> q; // <dist, node> vector<set<pair<int, int>>::const_iterator> its(n); dist[s] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) its[i] = q.emplace(dist[i], i).first; while (!q.empty()) { auto it = cbegin(q); int d = it->first; int u = it->second; q.erase(it); if (d > t) break; // pruning for (const auto& p : g[u]) { int v = p.first; int w = p.second; if (dist[v] <= d + w) continue; // Decrease key q.erase(its[v]); its[v] = q.emplace(dist[v] = d + w, v).first; } } return count_if(begin(dist), end(dist), [t](int d) { return d <= t; }); }; int ans = -1; int min_nb = INT_MAX; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int nb = dijkstra(i); if (nb <= min_nb) { min_nb = nb; ans = i; } } return ans; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment