You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
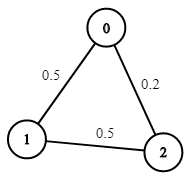
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
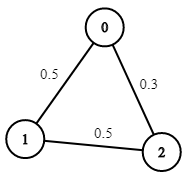
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
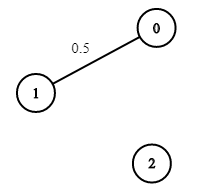
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.00000 Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
Solution: Dijkstra’s Algorithm
max(P1*P2*…*Pn) => max(log(P1*P2…*Pn)) => max(log(P1) + log(P2) + … + log(Pn) => min(-(log(P1) + log(P2) … + log(Pn)).
Thus we can convert this problem to the classic single source shortest path problem that can be solved with Dijkstra’s algorithm.
Time complexity: O(ElogV)
Space complexity: O(E+V)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// Author: Huahua // Author: Huahua class Solution { public: double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) { vector<vector<pair<int, double>>> g(n); // u -> {v, -log(w)} for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) { const double w = -log(succProb[i]); g[edges[i][0]].emplace_back(edges[i][1], w); g[edges[i][1]].emplace_back(edges[i][0], w); } vector<double> dist(n, FLT_MAX); priority_queue<pair<double, int>> q; q.emplace(-0.0, start); vector<int> seen(n); while (!q.empty()) { const double d = -q.top().first; const int u = q.top().second; q.pop(); seen[u] = 1; if (u == end) return exp(-d); for (const auto& [v, w] : g[u]) { if (seen[v] || d + w > dist[v]) continue; q.emplace(-(dist[v] = d + w), v); } } return 0; } }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
// Author: Huahua import java.util.AbstractMap; class Solution { public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) { var g = new ArrayList<List<Map.Entry<Integer, Double>>>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) g.add(new ArrayList<Map.Entry<Integer, Double>>()); for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; ++i) { g.get(edges[i][0]).add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(edges[i][1], -Math.log(succProb[i]))); g.get(edges[i][1]).add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(edges[i][0], -Math.log(succProb[i]))); } var seen = new boolean[n]; var dist = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(dist, Double.MAX_VALUE); seen[start] = true; dist[start] = 0.0; // {u, dist[u]} var q = new PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Double>>(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()); q.offer(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(start, 0.0)); while (!q.isEmpty()) { var node = q.poll(); final int u = node.getKey(); if (u == end) return Math.exp(-dist[end]); seen[u] = true; for (var e : g.get(u)) { final int v = e.getKey(); final double w = e.getValue(); if (seen[v] || dist[u] + w > dist[v]) continue; dist[v] = dist[u] + w; q.offer(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(v, dist[v])); } } return 0; } } |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
# Author: Huahua class Solution: def maxProbability(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], succProb: List[float], start: int, end: int) -> float: g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for i, e in enumerate(edges): g[e[0]].append((e[1], -math.log(succProb[i]))) g[e[1]].append((e[0], -math.log(succProb[i]))) seen = [False] * n dist = [float('inf')] * n dist[start] = 0.0 q = [(dist[start], start)] while q: _, u = heapq.heappop(q) if seen[u]: continue seen[u] = True if u == end: return math.exp(-dist[u]) for v, w in g[u]: if seen[v] or dist[u] + w > dist[v]: continue dist[v] = dist[u] + w heapq.heappush(q, (dist[v], v)) return 0 |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment