You are given a directed graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, where each node has exactly one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented by a given 0-indexed integer array edges of length n, where edges[i] indicates that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i].
The edge score of a node i is defined as the sum of the labels of all the nodes that have an edge pointing to i.
Return the node with the highest edge score. If multiple nodes have the same edge score, return the node with the smallest index.
Example 1:
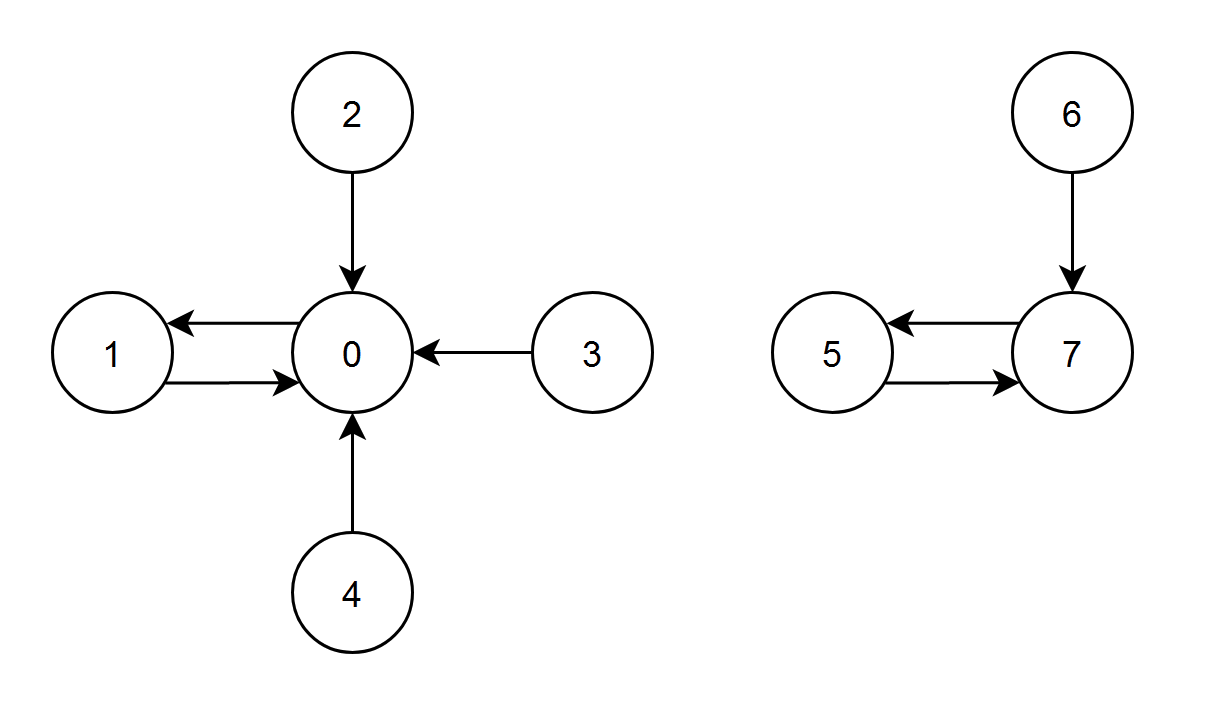
Input: edges = [1,0,0,0,0,7,7,5] Output: 7 Explanation: - The nodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10. - The node 0 has an edge pointing to node 1. The edge score of node 1 is 0. - The node 7 has an edge pointing to node 5. The edge score of node 5 is 7. - The nodes 5 and 6 have an edge pointing to node 7. The edge score of node 7 is 5 + 6 = 11. Node 7 has the highest edge score so return 7.
Example 2:
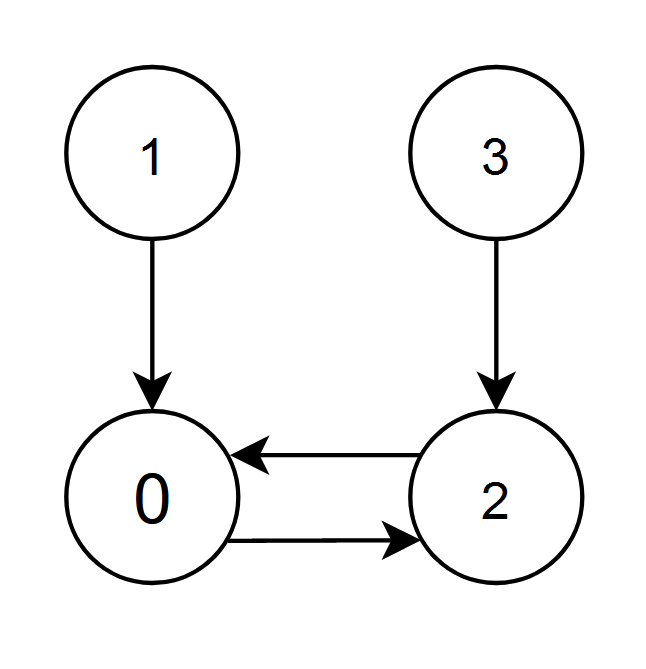
Input: edges = [2,0,0,2] Output: 0 Explanation: - The nodes 1 and 2 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 = 3. - The nodes 0 and 3 have an edge pointing to node 2. The edge score of node 2 is 0 + 3 = 3. Nodes 0 and 2 both have an edge score of 3. Since node 0 has a smaller index, we return 0.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i
Solution:
Use an array to store the score of each node.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
use max_element to find the largest element.
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int edgeScore(vector<int>& edges) { const int n = edges.size(); vector<long> s(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) s[edges[i]] += i; return max_element(begin(s), end(s)) - begin(s); } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment