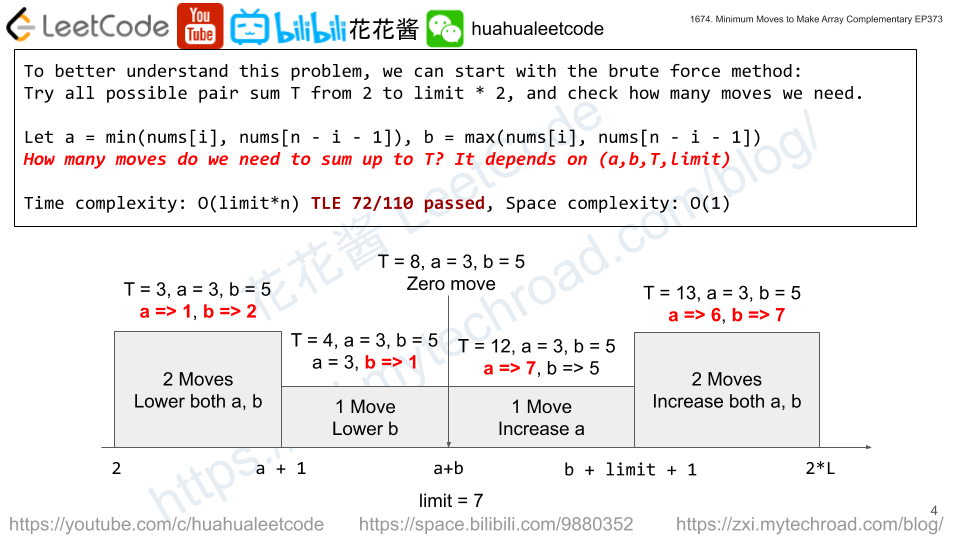
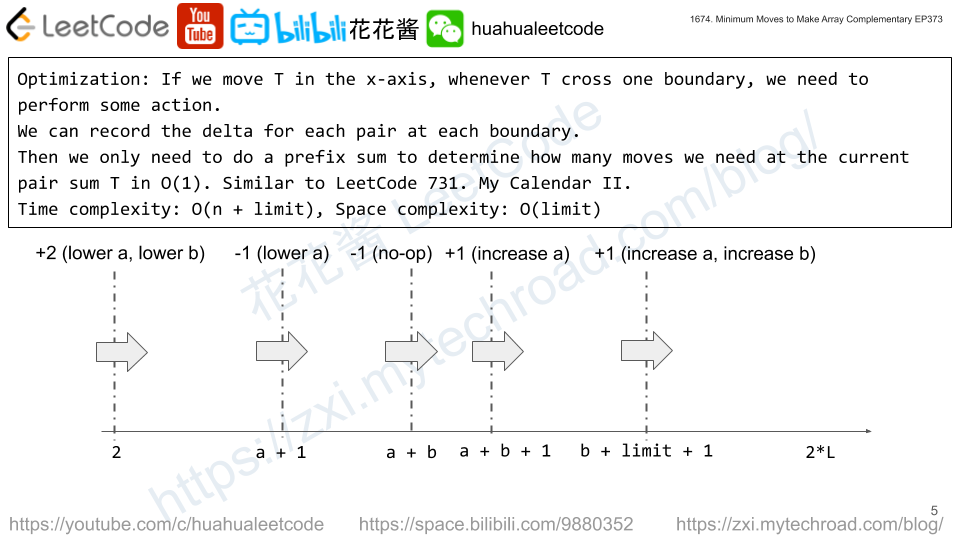
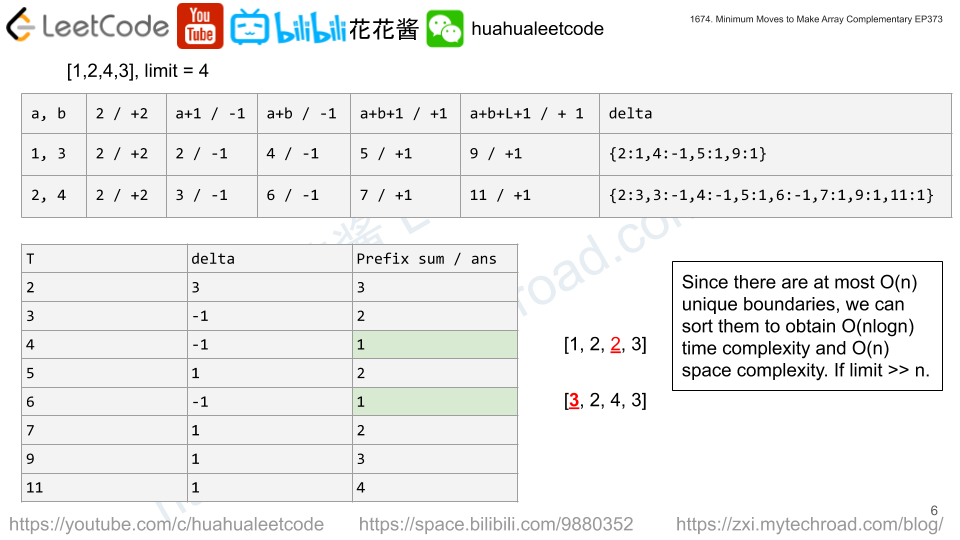
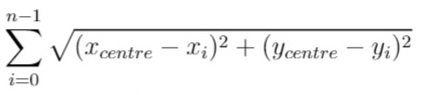You own a Goal Parser that can interpret a string command. The command consists of an alphabet of "G", "()" and/or "(al)" in some order. The Goal Parser will interpret "G" as the string "G", "()" as the string "o", and "(al)" as the string "al". The interpreted strings are then concatenated in the original order.
Given the string command, return the Goal Parser‘s interpretation of command.
Example 1:
Input: command = "G()(al)" Output: "Goal" Explanation: The Goal Parser interprets the command as follows: G -> G () -> o (al) -> al The final concatenated result is "Goal".
Example 2:
Input: command = "G()()()()(al)" Output: "Gooooal"
Example 3:
Input: command = "(al)G(al)()()G" Output: "alGalooG"
Constraints:
1 <= command.length <= 100commandconsists of"G","()", and/or"(al)"in some order.
Solution: String
If we encounter ‘(‘ check the next character to determine whether it’s ‘()’ or ‘(al’)
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
class Solution { public: string interpret(string command) { string ans; for (int i = 0; i < command.size(); ++i) { if (command[i] == 'G') ans += "G"; else if (command[i] == '(') { if (command[i + 1] == ')') ans += "o"; else ans += "al"; } } return ans; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
class Solution: def interpret(self, command: str) -> str: ans = [] for i, c in enumerate(command): if c == 'G': ans.append('G') elif c == '(': ans.append('o' if command[i + 1] == ')' else 'al') return ''.join(ans) |