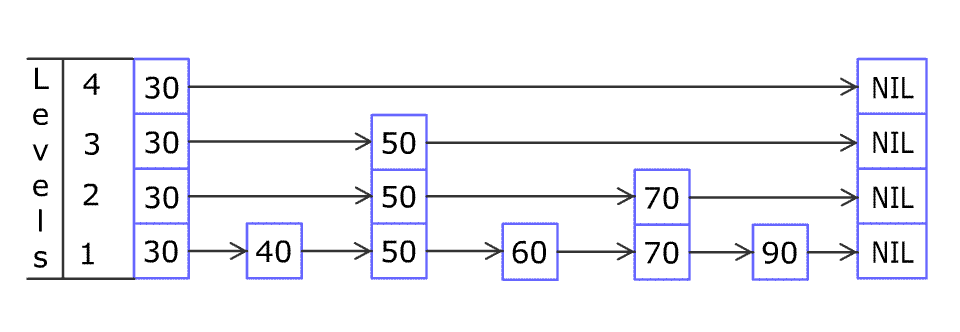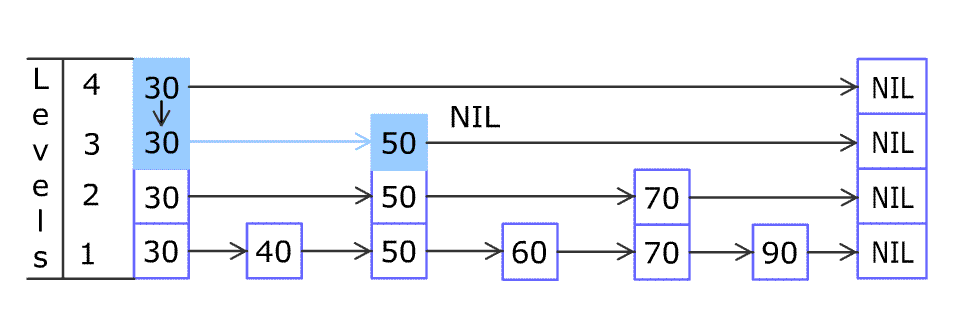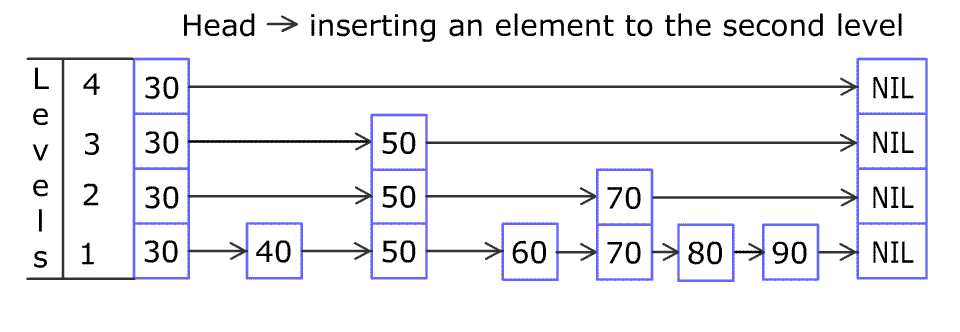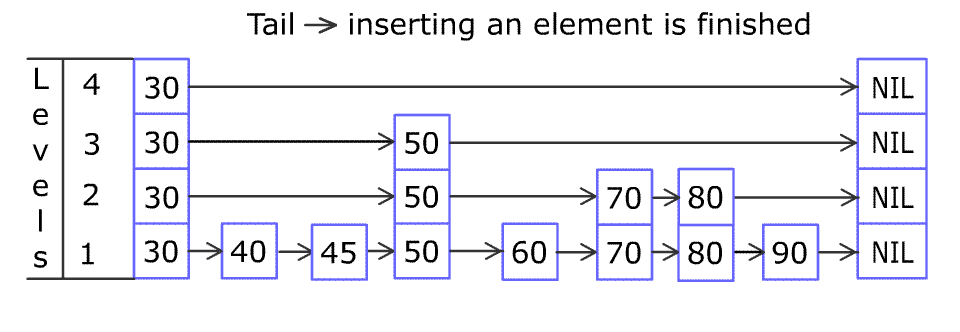
Given an integer array instructions, you are asked to create a sorted array from the elements in instructions. You start with an empty container nums. For each element from left to right in instructions, insert it into nums. The cost of each insertion is the minimum of the following:
- The number of elements currently in
numsthat are strictly less thaninstructions[i]. - The number of elements currently in
numsthat are strictly greater thaninstructions[i].
For example, if inserting element 3 into nums = [1,2,3,5], the cost of insertion is min(2, 1) (elements 1 and 2 are less than 3, element 5 is greater than 3) and nums will become [1,2,3,3,5].
Return the total cost to insert all elements from instructions into nums. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7
Example 1:
Input: instructions = [1,5,6,2] Output: 1 Explanation: Begin with nums = []. Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1]. Insert 5 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,5]. Insert 6 with cost min(2, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,5,6]. Insert 2 with cost min(1, 2) = 1, now nums = [1,2,5,6]. The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 1.
Example 2:
Input: instructions = [1,2,3,6,5,4] Output: 3 Explanation: Begin with nums = []. Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1]. Insert 2 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2]. Insert 3 with cost min(2, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3]. Insert 6 with cost min(3, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3,6]. Insert 5 with cost min(3, 1) = 1, now nums = [1,2,3,5,6]. Insert 4 with cost min(3, 2) = 2, now nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 2 = 3.
Example 3:
Input: instructions = [1,3,3,3,2,4,2,1,2] Output: 4 Explanation: Begin with nums = []. Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1]. Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3]. Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3,3]. Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3,3,3]. Insert 2 with cost min(1, 3) = 1, now nums = [1,2,3,3,3]. Insert 4 with cost min(5, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3,3,3,4]. Insert 2 with cost min(1, 4) = 1, now nums = [1,2,2,3,3,3,4]. Insert 1 with cost min(0, 6) = 0, now nums = [1,1,2,2,3,3,3,4]. Insert 2 with cost min(2, 4) = 2, now nums = [1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4]. The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 2 = 4.
Constraints:
1 <= instructions.length <= 1051 <= instructions[i] <= 105
Solution: Fenwick Tree / Binary Indexed Tree
Time complexity: O(nlogm)
Space complexity: O(m + n)
m is the maximum value, n is number of values.
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
class FenwickTree { public: FenwickTree(int n): sums_(n + 1, 0) {} void update(int i, int delta) { while (i < sums_.size()) { sums_[i] += delta; i += lowbit(i); } } int query(int i) const { int sum = 0; while (i > 0) { sum += sums_[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return sum; } private: static inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); } vector<int> sums_; }; class Solution { public: int createSortedArray(vector<int>& instructions) { const int n = instructions.size(); FenwickTree tree(1e5); long ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int lt = tree.query(instructions[i] - 1); int gt = i - tree.query(instructions[i]); ans += min(lt, gt); tree.update(instructions[i], 1); } return ans % 1000000007; } }; |