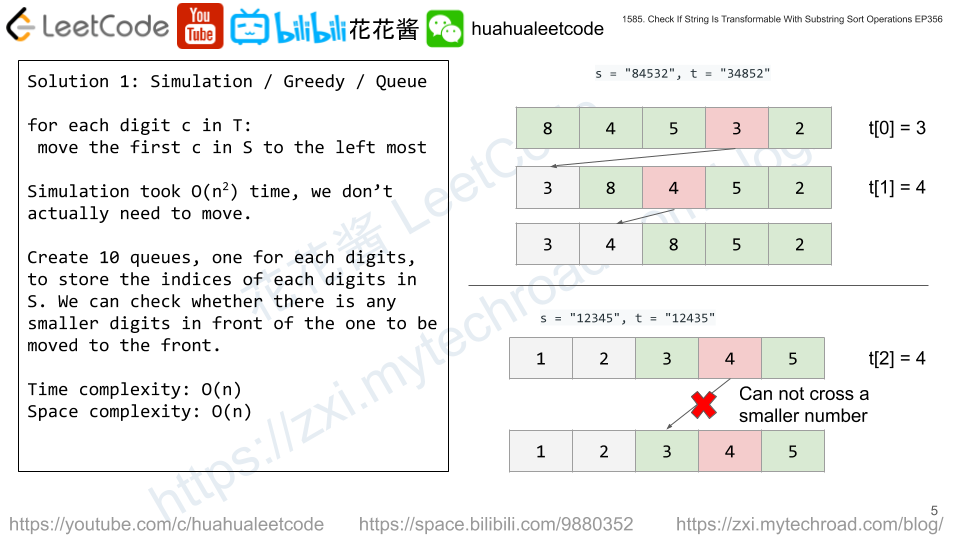
We have an array of integers, nums, and an array of requests where requests[i] = [starti, endi]. The ith request asks for the sum of nums[starti] + nums[starti + 1] + ... + nums[endi - 1] + nums[endi]. Both starti and endi are 0-indexed.
Return the maximum total sum of all requests among all permutations of nums.
Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5], requests = [[1,3],[0,1]] Output: 19 Explanation: One permutation of nums is [2,1,3,4,5] with the following result: requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 1 + 3 + 4 = 8 requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 1 = 3 Total sum: 8 + 3 = 11. A permutation with a higher total sum is [3,5,4,2,1] with the following result: requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 5 + 4 + 2 = 11 requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 3 + 5 = 8 Total sum: 11 + 8 = 19, which is the best that you can do.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6], requests = [[0,1]] Output: 11 Explanation: A permutation with the max total sum is [6,5,4,3,2,1] with request sums [11].
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,10], requests = [[0,2],[1,3],[1,1]] Output: 47 Explanation: A permutation with the max total sum is [4,10,5,3,2,1] with request sums [19,18,10].
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 1051 <= requests.length <= 105requests[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi < n
Solution: Greedy + Sweep line
Sort the numbers, and sort the frequency of each index, it’s easy to show largest number with largest frequency gives us max sum.
ans = sum(nums[i] * freq[i])
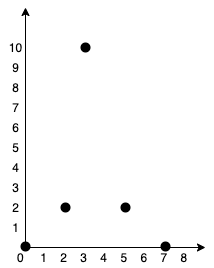
We can use sweep line to compute the frequency of each index in O(n) time and space.
For each request [start, end] : ++freq[start], –freq[end + 1]
Then the prefix sum of freq array is the frequency for each index.
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
class Solution { public: int maxSumRangeQuery(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& requests) { constexpr int kMod = 1e9 + 7; const int n = nums.size(); vector<long> freq(n); for (const auto& r : requests) { ++freq[r[0]]; if (r[1] + 1 < n) --freq[r[1] + 1]; } for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) freq[i] += freq[i - 1]; sort(begin(freq), end(freq)); sort(begin(nums), end(nums)); long ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans += freq[i] * nums[i]; return ans % kMod; } }; |