Given a m * n matrix seats that represent seats distributions in a classroom. If a seat is broken, it is denoted by '#' character otherwise it is denoted by a '.' character.
Students can see the answers of those sitting next to the left, right, upper left and upper right, but he cannot see the answers of the student sitting directly in front or behind him. Return the maximum number of students that can take the exam together without any cheating being possible..
Students must be placed in seats in good condition.
Example 1:
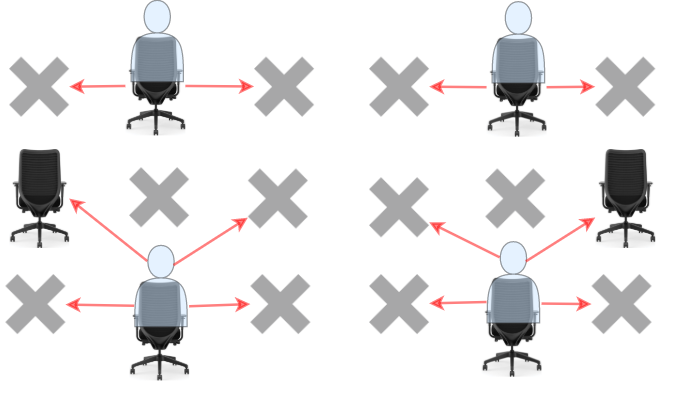
Input: seats = [["#",".","#","#",".","#"], [".","#","#","#","#","."], ["#",".","#","#",".","#"]] Output: 4 Explanation: Teacher can place 4 students in available seats so they don't cheat on the exam.
Example 2:
Input: seats = [[".","#"], ["#","#"], ["#","."], ["#","#"], [".","#"]] Output: 3 Explanation: Place all students in available seats.
Example 3:
Input: seats = [["#",".",".",".","#"], [".","#",".","#","."], [".",".","#",".","."], [".","#",".","#","."], ["#",".",".",".","#"]] Output: 10 Explanation: Place students in available seats in column 1, 3 and 5.
Constraints:
seatscontains only characters'.' and'#'.m == seats.lengthn == seats[i].length1 <= m <= 81 <= n <= 8
Solution 1: DFS (TLE)
Time complexity: O(2^(m*n)) = O(2^64)
Space complexity: O(m*n)
Solution 2: DP
Since how to fill row[i+1] only depends on row[i]’s state, we can define
dp[i][s] as the max # of students after filling i rows and s (as a binary string) is the states i-th row.
dp[i+1][t] = max{dp[i][s] + bits(t)} if row[i] = s && row[i +1] = t is a valid state.
Time complexity: O(m*2^(n+n)*n) = O(2^22)
Space complexity: O(m*2^n) = O(2^11) -> O(2^n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int maxStudents(vector<vector<char>>& seats) { int m = seats.size(); int n = seats[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(1 << n)); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) for (int l = 0; l < (1 << n); ++l) for (int c = 0; c < (1 << n); ++c) { bool flag = true; for (int j = 0; j < n && flag; ++j) { if (!(c & (1 << j))) continue; if (seats[i][j] == '#') flag = false; bool l = j == 0 ? false : (c & (1 << (j - 1))); bool r = j == n - 1 ? false : (c & (1 << (j + 1))); bool ul = (j == 0 || i == 0) ? false : (l & (1 << (j - 1))); bool ur = (j == n - 1 || i == 0) ? false : (l & (1 << (j + 1))); if (l || r || ul || ur) flag = false; } if (flag) dp[i + 1][c] = max(dp[i + 1][c], dp[i][l] + __builtin_popcount(c)); } return *max_element(begin(dp[m]), end(dp[m])); } }; |
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int maxStudents(vector<vector<char>>& seats) { const int m = seats.size(); const int n = seats[0].size(); vector<int> s(m + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) s[i] |= (seats[i - 1][j] == '.') << j; vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(1 << n)); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) for (int c = s[i];;c = (c - 1) & s[i]) { if (c & (c >> 1)) continue; for (int l = s[i - 1];;l = (l - 1) & s[i - 1]) { if (!(l & (c >> 1)) && !((l >> 1) & c)) dp[i][c] = max(dp[i][c], dp[i - 1][l] + __builtin_popcount(c)); if (l == 0) break; } if (c == 0) break; } return *max_element(begin(dp[m]), end(dp[m])); } }; |