Problem
Given a balanced parentheses string S, compute the score of the string based on the following rule:
()has score 1ABhas scoreA + B, where A and B are balanced parentheses strings.(A)has score2 * A, where A is a balanced parentheses string.
Example 1:
Input: "()" Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: "(())" Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: "()()" Output: 2
Example 4:
Input: "(()(()))" Output: 6
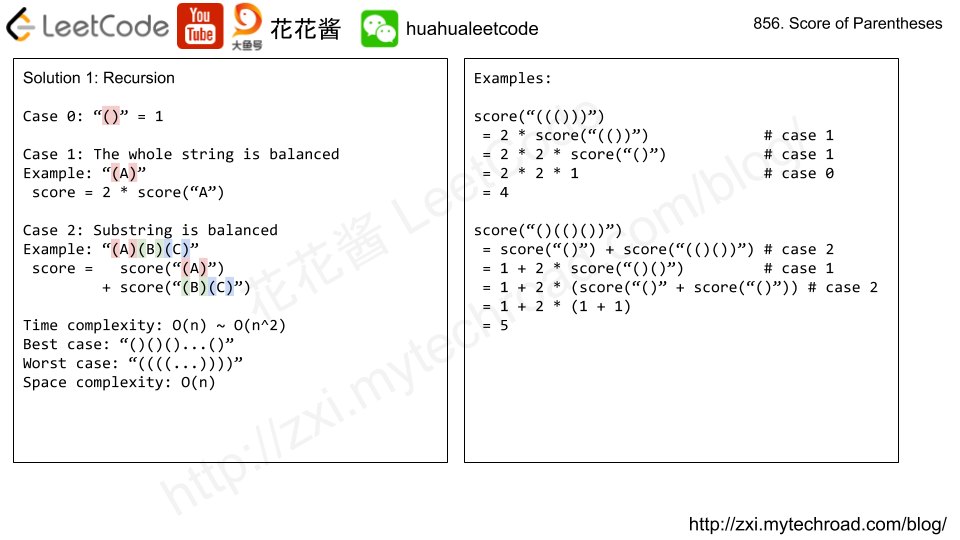
Solution1: Recursion
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 4ms class Solution { public: int scoreOfParentheses(string S) { return score(S, 0, S.length() - 1); } private: int score(const string& S, int l, int r) { if (r - l == 1) return 1; // "()" int b = 0; for (int i = l; i < r; ++i) { if (S[i] == '(') ++b; if (S[i] == ')') --b; if (b == 0) // balanced // score("(A)(B)") = score("(A)") + score("(B)") return score(S, l, i) + score(S, i + 1, r); } // score("(A)") = 2 * score("A") return 2 * score(S, l + 1, r - 1); } }; |
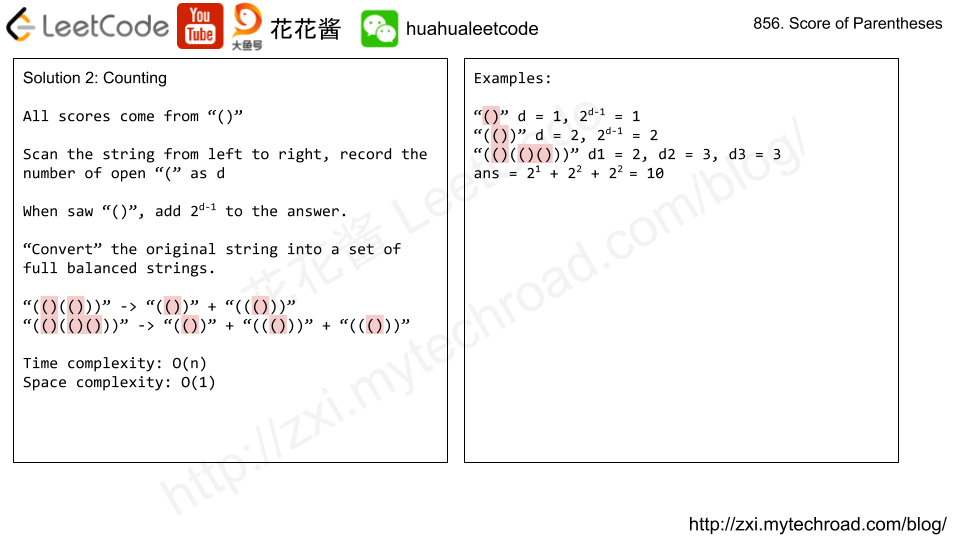
Solution2: Counting
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 4 ms class Solution { public: int scoreOfParentheses(string S) { int ans = 0; int d = -1; for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); ++i) { d += S[i] == '(' ? 1 : -1; if (S[i] == '(' && S[i + 1] == ')') ans += 1 << d; } return ans; } }; |