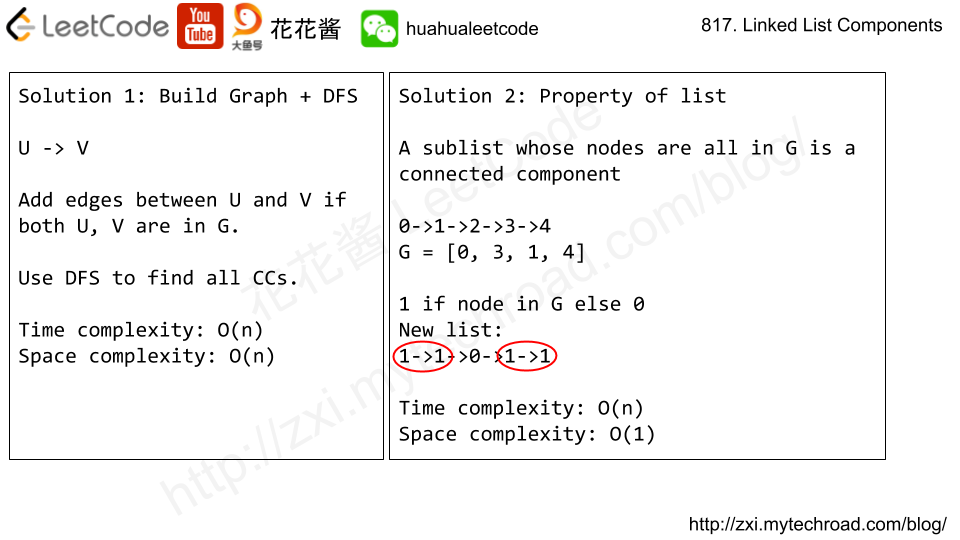
Problem
题目大意:给你一棵二叉树(根结点root)和一个target节点。返回所有到target的距离为K的节点。
We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
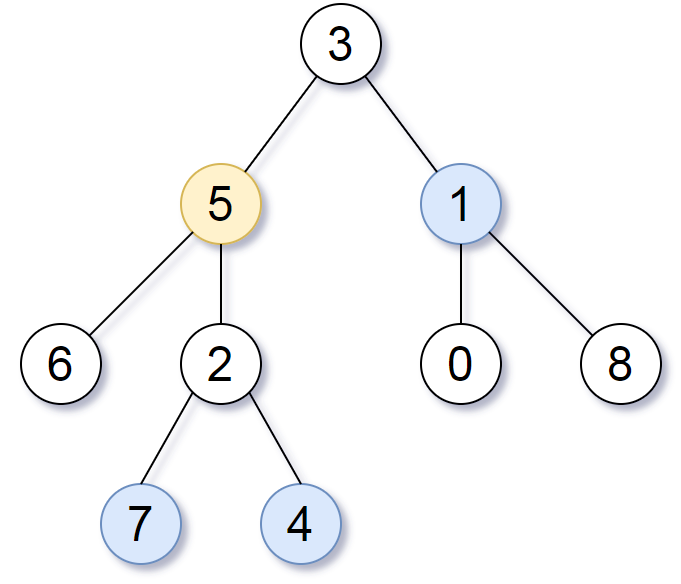
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2 Output: [7,4,1] Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes. The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note:
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values
0 <= node.val <= 500. - The
targetnode is a node in the tree. 0 <= K <= 1000.
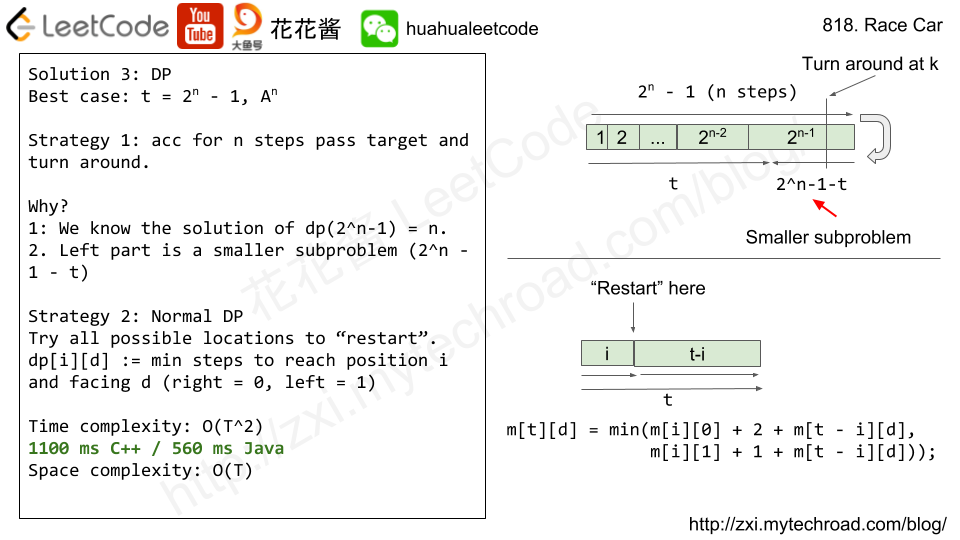
Solution1: DFS + BFS
Use DFS to build the graph, and use BFS to find all the nodes that are exact K steps from target.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 6 ms class Solution { public: vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) { buildGraph(nullptr, root); vector<int> ans; unordered_set<TreeNode*> seen; queue<TreeNode*> q; seen.insert(target); q.push(target); int k = 0; while (!q.empty() && k <= K) { int s = q.size(); while (s--) { TreeNode* node = q.front(); q.pop(); if (k == K) ans.push_back(node->val); for (TreeNode* child : g[node]) { if (seen.count(child)) continue; q.push(child); seen.insert(child); } } ++k; } return ans; } private: unordered_map<TreeNode*, vector<TreeNode*>> g; void buildGraph(TreeNode* parent, TreeNode* child) { if (parent) { g[parent].push_back(child); g[child].push_back(parent); } if (child->left) buildGraph(child, child->left); if (child->right) buildGraph(child, child->right); } }; |
Array version
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 6 ms class Solution { public: vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) { constexpr int kMaxN = 500 + 1; g = vector<vector<int>>(kMaxN); buildGraph(nullptr, root); vector<int> ans; vector<int> seen(kMaxN); queue<int> q; seen[target->val] = 1; q.push(target->val); int k = 0; while (!q.empty() && k <= K) { int s = q.size(); while (s--) { int node = q.front(); q.pop(); if (k == K) ans.push_back(node); for (int child : g[node]) { if (seen[child]) continue; q.push(child); seen[child] = 1; } } ++k; } return ans; } private: vector<vector<int>> g; void buildGraph(TreeNode* parent, TreeNode* child) { if (parent) { g[parent->val].push_back(child->val); g[child->val].push_back(parent->val); } if (child->left) buildGraph(child, child->left); if (child->right) buildGraph(child, child->right); } }; |
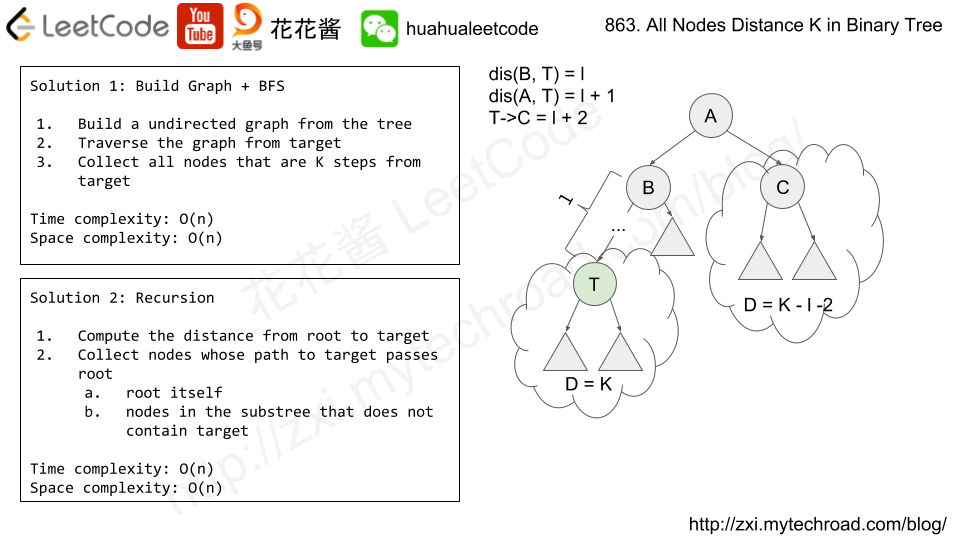
Solution 2: Recursion
Recursively compute the distance from root to target, and collect nodes accordingly.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 5 ms class Solution { public: vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) { ans.clear(); dis(root, target, K); return ans; } private: vector<int> ans; // Returns the distance from root to target. // Returns -1 if target does not in the tree. int dis(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) { if (root == nullptr) return -1; if (root == target) { collect(target, K); return 0; } int l = dis(root->left, target, K); int r = dis(root->right, target, K); // Target in the left subtree if (l >= 0) { if (l == K - 1) ans.push_back(root->val); // Collect nodes in right subtree with depth K - l - 2 collect(root->right, K - l - 2); return l + 1; } // Target in the right subtree if (r >= 0) { if (r == K - 1) ans.push_back(root->val); // Collect nodes in left subtree with depth K - r - 2 collect(root->left, K - r - 2); return r + 1; } return -1; } // Collect nodes that are d steps from root. void collect(TreeNode* root, int d) { if (root == nullptr || d < 0) return; if (d == 0) ans.push_back(root->val); collect(root->left, d - 1); collect(root->right, d - 1); } }; |
 Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.