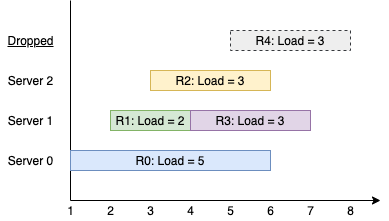
You are given an array nums of positive integers. In one operation, you can choose any number from nums and reduce it to exactly half the number. (Note that you may choose this reduced number in future operations.)
Return the minimum number of operations to reduce the sum of nums by at least half.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,19,8,1] Output: 3 Explanation: The initial sum of nums is equal to 5 + 19 + 8 + 1 = 33. The following is one of the ways to reduce the sum by at least half: Pick the number 19 and reduce it to 9.5. Pick the number 9.5 and reduce it to 4.75. Pick the number 8 and reduce it to 4. The final array is [5, 4.75, 4, 1] with a total sum of 5 + 4.75 + 4 + 1 = 14.75. The sum of nums has been reduced by 33 - 14.75 = 18.25, which is at least half of the initial sum, 18.25 >= 33/2 = 16.5. Overall, 3 operations were used so we return 3. It can be shown that we cannot reduce the sum by at least half in less than 3 operations.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,8,20] Output: 3 Explanation: The initial sum of nums is equal to 3 + 8 + 20 = 31. The following is one of the ways to reduce the sum by at least half: Pick the number 20 and reduce it to 10. Pick the number 10 and reduce it to 5. Pick the number 3 and reduce it to 1.5. The final array is [1.5, 8, 5] with a total sum of 1.5 + 8 + 5 = 14.5. The sum of nums has been reduced by 31 - 14.5 = 16.5, which is at least half of the initial sum, 16.5 >= 31/2 = 16.5. Overall, 3 operations were used so we return 3. It can be shown that we cannot reduce the sum by at least half in less than 3 operations.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 107
Solution: Greedy + PriorityQueue/Max Heap
Always half the largest number, put all the numbers onto a max heap (priority queue), extract the largest one, and put reduced number back.
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int halveArray(vector<int>& nums) { double sum = accumulate(begin(nums), end(nums), 0.0); priority_queue<double> q; for (int num : nums) q.push(num); int ans = 0; for (double cur = sum; cur > sum / 2; ++ans) { double num = q.top(); q.pop(); cur -= num / 2; q.push(num / 2); } return ans; } }; |